Unknown objects in space
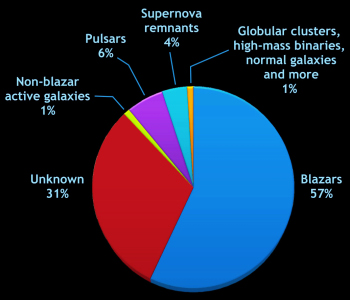
NASA’s Fermi Gamma-Ray Telescope today released an updated catalog of the last two years of its survey of the sky at high energy emissions. All told, there are 1873 objects in the catalog, more than half of which are supermassive black holes at the center of distant galaxies. You can see this all-sky map below the fold.
Many of the objects are quite familiar, such as the Crab Nebula, the remnant of a supernova that exploded a little less than a thousand years ago.
For decades, most astronomers regarded the Crab Nebula as the steadiest beacon at X-ray energies. But data from several orbiting instruments — including Fermi’s Gamma-ray Burst Monitor — now show unexpected variations. Astronomers have shown that since 2008, the nebula has faded by 7 percent at high energies, a reduction likely tied to the environment around its central neutron star.
Since 2007, Fermi and the Italian Space Agency’s AGILE satellite have detected several short-lived gamma-ray flares at energies hundreds of times higher than the nebula’s observed X-ray variations. In April, the satellites detected two of the most powerful yet recorded. To account for these “superflares,” scientists say that electrons near the pulsar must be accelerated to energies a thousand trillion times greater than that of visible light — and far beyond what can be achieved by the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, now the most powerful particle accelerator on Earth.
What I, and many astronomers, find even most interesting about this catalog, however, is the large number of completely mysterious objects scattered across the sky, objects that emit powerful gamma rays but are not visible in any other wavelengths. All told, these unidentified objects comprise almost one third of the entire catalog.
» Read more
