New radar technology now available for radio astronomy
Astronomers have now demonstrated a spectacular new radar technology using radio telescopes and capable of producing high resolution images of all solar system bodies, as far away as Neptune.
[S]cientists built a miniature transmitter, powered at less than a kilowatt and about the size of a refrigerator, Beasley said, and in November hauled it up for a brief stint at the prime focus of Green Bank Telescope, suspended over the large dish.
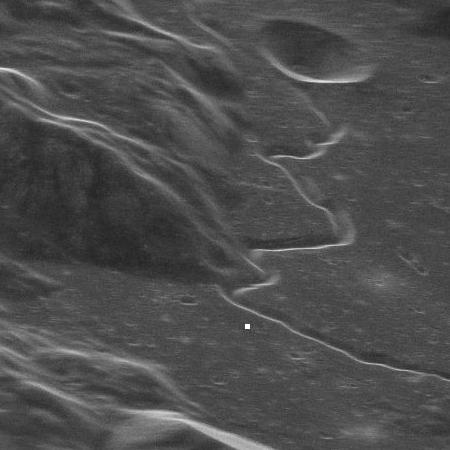
Then, the team took advantage of the telescope’s superlative: It’s the largest fully steerable radio telescope in the world, able to study objects across 85% of the sky. So the team pointed the telescope and fired the radar system at the moon — more specifically, at the Apollo 15 mission’s landing site in the Hadley-Apennine region [the white dot in the image to the right]. The team used antennas of the NRAO’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) to catch the signal that bounced back.
The image, with its sloping hills, stark crater and slinking rille, offers a hint of what could come. But the moon is our old companion. Scientists would much rather use a shiny new planetary radar system to study more mysterious objects, like the asteroids zipping through our neighborhood of the solar system, most of which are blurs and blobs, or the strange moons of the outer planets that have received few spacecraft visitors.
Without question this technology would be a major breakthrough for the observation of asteroids, especially those that are considered a threat of impacting the Earth for which we have little concrete information.
The article however notes that the technology had been developed with the assumption that the Arecibo radio telescope would be available. That telescope however is now dead, having been destroyed when its instrument platform fell in early December. With a limited number of radio telescopes available, all of which are oversubscribed for other work, it will be difficult to find time for the use of this technology on any of them.
But don’t worry. The Chinese will definitely want to steal it and put it on their giant FAST radio telescope, and I am sure the Biden administration will be agreeable to letting them.

Astronomers have now demonstrated a spectacular new radar technology using radio telescopes and capable of producing high resolution images of all solar system bodies, as far away as Neptune.
[S]cientists built a miniature transmitter, powered at less than a kilowatt and about the size of a refrigerator, Beasley said, and in November hauled it up for a brief stint at the prime focus of Green Bank Telescope, suspended over the large dish.
Then, the team took advantage of the telescope’s superlative: It’s the largest fully steerable radio telescope in the world, able to study objects across 85% of the sky. So the team pointed the telescope and fired the radar system at the moon — more specifically, at the Apollo 15 mission’s landing site in the Hadley-Apennine region [the white dot in the image to the right]. The team used antennas of the NRAO’s Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) to catch the signal that bounced back.
The image, with its sloping hills, stark crater and slinking rille, offers a hint of what could come. But the moon is our old companion. Scientists would much rather use a shiny new planetary radar system to study more mysterious objects, like the asteroids zipping through our neighborhood of the solar system, most of which are blurs and blobs, or the strange moons of the outer planets that have received few spacecraft visitors.
Without question this technology would be a major breakthrough for the observation of asteroids, especially those that are considered a threat of impacting the Earth for which we have little concrete information.
The article however notes that the technology had been developed with the assumption that the Arecibo radio telescope would be available. That telescope however is now dead, having been destroyed when its instrument platform fell in early December. With a limited number of radio telescopes available, all of which are oversubscribed for other work, it will be difficult to find time for the use of this technology on any of them.
But don’t worry. The Chinese will definitely want to steal it and put it on their giant FAST radio telescope, and I am sure the Biden administration will be agreeable to letting them.
