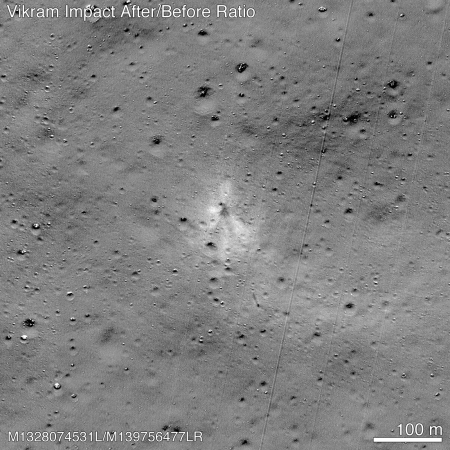
ISRO officially requests funds for new lunar lander/rover
The new colonial movement: India’s space agency ISRO has now officially requested funding to build a new lunar lander/rover, dubbed Chandrayaan-3, to launch as early as November 2020.
The TOI [Times of India], which was the first to report that Isro is looking to launch another Moon landing mission as early as next November, has now been able to get a confirmation from the department of economic affairs that the space agency has, in fact, sought Rs 75 crore [approximately $14 million] for Chandrayaan-3.
As per initial plans, Chandrayaan-3 will have a lander, a rover and a detachable propulsion module to carry fuel.
The money has been sought under the provisions of a supplementary budget for the present financial year. Of this, Rs 60 crore will be for “meeting expenditure towards machinery, equipment and other capital expenditure,” while the remaining Rs 15 crore is sought under revenue expenditure head.
The article also notes that ISRO “has already set up multiple committees to work on Chandrayaan-3.”
The new colonial movement: India’s space agency ISRO has now officially requested funding to build a new lunar lander/rover, dubbed Chandrayaan-3, to launch as early as November 2020.
The TOI [Times of India], which was the first to report that Isro is looking to launch another Moon landing mission as early as next November, has now been able to get a confirmation from the department of economic affairs that the space agency has, in fact, sought Rs 75 crore [approximately $14 million] for Chandrayaan-3.
As per initial plans, Chandrayaan-3 will have a lander, a rover and a detachable propulsion module to carry fuel.
The money has been sought under the provisions of a supplementary budget for the present financial year. Of this, Rs 60 crore will be for “meeting expenditure towards machinery, equipment and other capital expenditure,” while the remaining Rs 15 crore is sought under revenue expenditure head.
The article also notes that ISRO “has already set up multiple committees to work on Chandrayaan-3.”