Rocket startup Orbex raises another $16.7 million in private investment capital
The British rocket startup Orbex has raised another $16.7 million in private investment capital, bringing the total it has raised now to over $100 million.
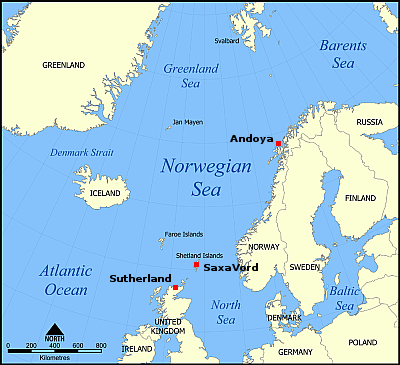
It remains unclear when the company’s Prime rocket will complete its first launch. It now says it will have its rocket and launch facility at the Sutherland spaceport ready by the end of this year, but it had previously hoped to launch the rocket in 2023. It appears that goal failed because the spaceport could not get either the spaceport license or its own launch license approved by the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA). Those licenses have still not been issued, even though the applications had been submitted in Feburary 2022, more than two years ago.
Those delays by the CAA probably explains why the company has had four different CEO’s in the past year. Though the fault of the delays lies with the government, others have had to take the blame. Meanwhile, company officials now state that it is now exploring using other launch sites, including its own near the equator.
The British rocket startup Orbex has raised another $16.7 million in private investment capital, bringing the total it has raised now to over $100 million.
It remains unclear when the company’s Prime rocket will complete its first launch. It now says it will have its rocket and launch facility at the Sutherland spaceport ready by the end of this year, but it had previously hoped to launch the rocket in 2023. It appears that goal failed because the spaceport could not get either the spaceport license or its own launch license approved by the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA). Those licenses have still not been issued, even though the applications had been submitted in Feburary 2022, more than two years ago.
Those delays by the CAA probably explains why the company has had four different CEO’s in the past year. Though the fault of the delays lies with the government, others have had to take the blame. Meanwhile, company officials now state that it is now exploring using other launch sites, including its own near the equator.