Swirls and layers in Martian depression


Click for full resolution image.
Cool image time! The southern highlands of Mars is littered with numerous craters, making it look from a distance not unlike the Moon. A closer inspection of each crater and feature, however has consistently revealed a much more complex history than seen on the Moon, with the origins of many features often difficult to explain.
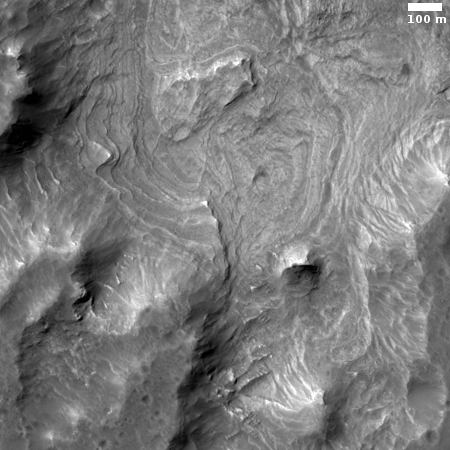
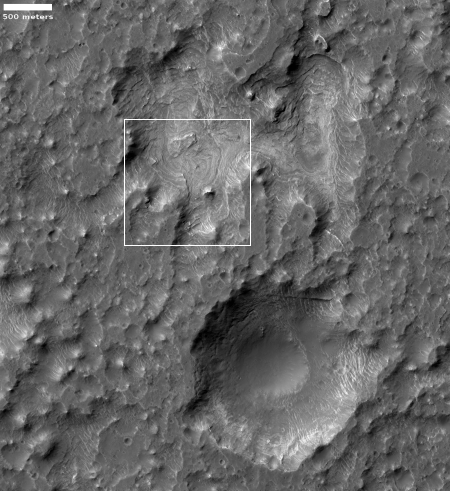
The two images on the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, shows one such feature in the floor of one southern highlands crater, dubbed Columbus Crater. The top image is a close-up of the area shown by the box in the bottom image.
The uncaptioned full photograph was taken on May 20, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and was simply titled “Depression in Columbus Crater.” Since the photo included two large depressions, as shown in the wider view in the bottom image, I’m not sure which depression this title refers. In both cases the features do not appear to be impact craters. The top depression is far too irregular, while both do not have the upraised rims that are found on most impact craters.
I have zoomed into the top depression because of its many swirls and layers. On Earth such terrain is usually caused by either water or wind erosion, slowly carving a smooth path across multiple geological layers. Here, there is no obvious evidence of any flows in any direction. Something ate out the material in this depression, exposing the many layers, but what is not clear.
The lower depression reminds me of sinkholes on Earth, where the ground is subsiding into a void below ground The same process could have also formed the top depression.
The surrounding terrain is equally baffling, resembling the eroded surface of an ice block that has been sprayed with warm water. In fact, the entire floor of Columbus Crater appears to have intrigued planetary scientists, as they have requested a lot of images of it from MRO. So far they do not have enough of these images to produce a full map. Since the terrain appears to change drastically over short distances, it is therefore hard to fit the geology of each image together. The overall context is missing.
When I first saw this image I tried to reach the scientist who requested it in the hope he might provide me a more nuanced explanation of what we see here, but despite repeated requests he never responded. Therefore let me propose one theory, based on my limited knowledge of Martian geology.
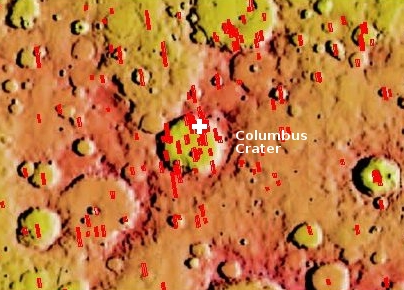
Columbus crater is located at 29 degrees south latitude, just outside the southern of the planet’s two 30 to 60 degree latitude bands where scientists have found many buried glaciers. Based on present theories about the long term evolution of the Martian climate, the glaciers in those glacial bands are presently decaying, the ice sublimating away to return to the planet’s poles.
What if in the past those glacial bands had been wider and had extended closer to the equator? If so, than Columbus Crater would have once had ice on its crater floor, and what we are looking at now is the eroded material left behind when those glaciers disappeared. These depressions even suggest that some of that ice might have seeped downward into an underground frozen aquifer.
That’s my best guess. I suspect the answer is far more complicated, and almost certainly requires a better and more complete data set, including some actual exploration on the surface.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News


Click for full resolution image.
Cool image time! The southern highlands of Mars is littered with numerous craters, making it look from a distance not unlike the Moon. A closer inspection of each crater and feature, however has consistently revealed a much more complex history than seen on the Moon, with the origins of many features often difficult to explain.
The two images on the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, shows one such feature in the floor of one southern highlands crater, dubbed Columbus Crater. The top image is a close-up of the area shown by the box in the bottom image.
The uncaptioned full photograph was taken on May 20, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and was simply titled “Depression in Columbus Crater.” Since the photo included two large depressions, as shown in the wider view in the bottom image, I’m not sure which depression this title refers. In both cases the features do not appear to be impact craters. The top depression is far too irregular, while both do not have the upraised rims that are found on most impact craters.
I have zoomed into the top depression because of its many swirls and layers. On Earth such terrain is usually caused by either water or wind erosion, slowly carving a smooth path across multiple geological layers. Here, there is no obvious evidence of any flows in any direction. Something ate out the material in this depression, exposing the many layers, but what is not clear.
The lower depression reminds me of sinkholes on Earth, where the ground is subsiding into a void below ground The same process could have also formed the top depression.
The surrounding terrain is equally baffling, resembling the eroded surface of an ice block that has been sprayed with warm water. In fact, the entire floor of Columbus Crater appears to have intrigued planetary scientists, as they have requested a lot of images of it from MRO. So far they do not have enough of these images to produce a full map. Since the terrain appears to change drastically over short distances, it is therefore hard to fit the geology of each image together. The overall context is missing.
When I first saw this image I tried to reach the scientist who requested it in the hope he might provide me a more nuanced explanation of what we see here, but despite repeated requests he never responded. Therefore let me propose one theory, based on my limited knowledge of Martian geology.

Columbus crater is located at 29 degrees south latitude, just outside the southern of the planet’s two 30 to 60 degree latitude bands where scientists have found many buried glaciers. Based on present theories about the long term evolution of the Martian climate, the glaciers in those glacial bands are presently decaying, the ice sublimating away to return to the planet’s poles.
What if in the past those glacial bands had been wider and had extended closer to the equator? If so, than Columbus Crater would have once had ice on its crater floor, and what we are looking at now is the eroded material left behind when those glaciers disappeared. These depressions even suggest that some of that ice might have seeped downward into an underground frozen aquifer.
That’s my best guess. I suspect the answer is far more complicated, and almost certainly requires a better and more complete data set, including some actual exploration on the surface.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News


It is intriguing that the depressions seem to be connected by relatively shallow channels… The whole picture reminds me of when hard ice starts melting, then freezes again ( at the end of the Swedish winter…), Random depressions are connected by channels in a similar way.
It seems to me the glacier theory is sound, but perhaps sublimation combined with warm periods and liquid water?