Axiom unveils its spacesuit design
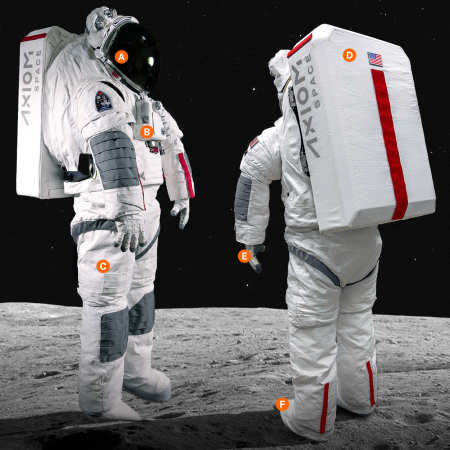
Axiom today unveiled its proposed spacesuit for NASA’s Moon missions, designed in partnership with the fashion company Prada.
The graphic to the left, cropped and reduced to post here, shows the suit. The letters refer to detailed descriptions contained in the full image.
The suit accommodates a wide range of crewmembers, including males and females from the first to 99th percentile (anthropomorphic sizing). It will withstand extreme temperatures at the lunar south pole and endure the coldest temperatures in the permanently shadowed regions for at least two hours. Astronauts will be able to perform spacewalks for at least eight hours.
The AxEMU incorporates multiple redundant systems and an onboard diagnostic system to ensure safety for crewmembers. The suit also uses a regenerable carbon dioxide scrubbing system and a robust cooling technology to remove heat from the system. It includes advanced coatings on the helmet and visor to enhance the astronauts’ view of their surroundings, as well as custom gloves made in-house featuring several advancements over the gloves used today. The spacesuit architecture includes life support systems, pressure garments, avionics and other innovative systems to meet exploration needs and expand scientific opportunities.
It appears the suit follows the design concept of the Russian Orlan suit, with access in and out using the backpack as the access hatch.
Axiom had won the $228 million contract to build this suit in 2022. In two years it is now testing the suit as it nears what it calls “the final development stage.” Compare that with NASA’s failed effort over fourteen years and a billion dollars to create its own suit, never getting much past powerpoint presentations.
Axiom today unveiled its proposed spacesuit for NASA’s Moon missions, designed in partnership with the fashion company Prada.
The graphic to the left, cropped and reduced to post here, shows the suit. The letters refer to detailed descriptions contained in the full image.
The suit accommodates a wide range of crewmembers, including males and females from the first to 99th percentile (anthropomorphic sizing). It will withstand extreme temperatures at the lunar south pole and endure the coldest temperatures in the permanently shadowed regions for at least two hours. Astronauts will be able to perform spacewalks for at least eight hours.
The AxEMU incorporates multiple redundant systems and an onboard diagnostic system to ensure safety for crewmembers. The suit also uses a regenerable carbon dioxide scrubbing system and a robust cooling technology to remove heat from the system. It includes advanced coatings on the helmet and visor to enhance the astronauts’ view of their surroundings, as well as custom gloves made in-house featuring several advancements over the gloves used today. The spacesuit architecture includes life support systems, pressure garments, avionics and other innovative systems to meet exploration needs and expand scientific opportunities.
It appears the suit follows the design concept of the Russian Orlan suit, with access in and out using the backpack as the access hatch.
Axiom had won the $228 million contract to build this suit in 2022. In two years it is now testing the suit as it nears what it calls “the final development stage.” Compare that with NASA’s failed effort over fourteen years and a billion dollars to create its own suit, never getting much past powerpoint presentations.