The jet 3,000 light years long that causes nearby stars to explode
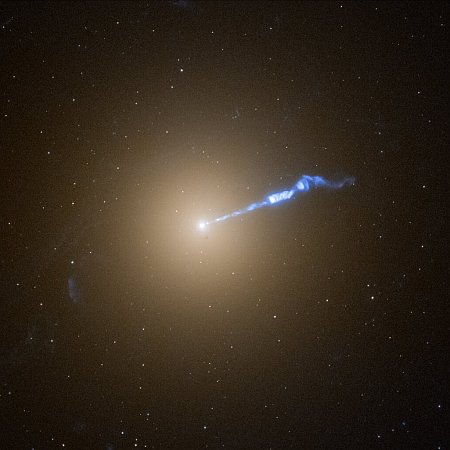
Cool image time! The picture to the left, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the giant eliptical galaxy M87, known for more than a century by astronomers for the jet of gas that points outward from its center. Astronomers now know that this jet is produced by a supermassive black hole in the center of M87, weighing 6.5 billion times the mass of our Sun.
The blowtorch-like jet seems to cause stars to erupt along its trajectory. These novae are not caught inside the jet, but are apparently in a dangerous neighbourhood nearby. During a recent 9-month survey, astronomers using Hubble found twice as many of these novae going off near the jet as elsewhere in the galaxy. The galaxy is the home of several trillion stars and thousands of star-like globular star clusters.
M87 is considered an old galaxy, but its entire formation process remains uncertain.
Cool image time! The picture to the left, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope of the giant eliptical galaxy M87, known for more than a century by astronomers for the jet of gas that points outward from its center. Astronomers now know that this jet is produced by a supermassive black hole in the center of M87, weighing 6.5 billion times the mass of our Sun.
The blowtorch-like jet seems to cause stars to erupt along its trajectory. These novae are not caught inside the jet, but are apparently in a dangerous neighbourhood nearby. During a recent 9-month survey, astronomers using Hubble found twice as many of these novae going off near the jet as elsewhere in the galaxy. The galaxy is the home of several trillion stars and thousands of star-like globular star clusters.
M87 is considered an old galaxy, but its entire formation process remains uncertain.