Author: Robert Zimmerman
January 23, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
826aska – James Bond theme
An evening pause: Who needs an orchestra when you have a modern synthesizer, properly programmed?
Hat tip Cotour.
January 23, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Axiom touts its lunar spacesuit
The video at the link compares this suit with footage of the Apollo astronauts on the Moon.
- On this day in 2003, Pioneer 10 sent back its last signal, sent from 7.6 billion miles away
That last signal was very weak and took 11 hours to reach Earth.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Axiom touts its lunar spacesuit
The video at the link compares this suit with footage of the Apollo astronauts on the Moon.
- On this day in 2003, Pioneer 10 sent back its last signal, sent from 7.6 billion miles away
That last signal was very weak and took 11 hours to reach Earth.
Blue Origin to reuse first stage on next New Glenn flight
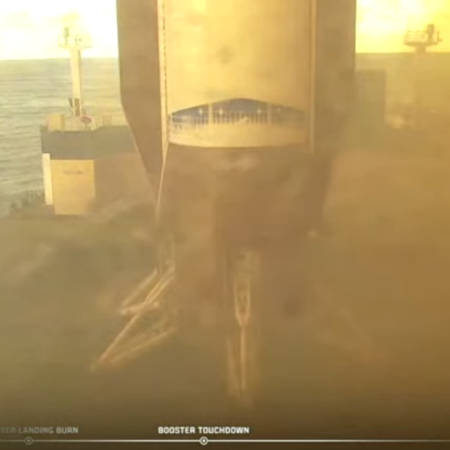

The New Glenn first stage after landing
in November.
In a sign that Blue Origin’s CEO David Limp is beginning to reshape the previously slow culture of the company, it announced yesterday that its next New Glenn launch, set for no earlier than late Feburary, will reuse the first stage that the company successfully landed on the last New Glenn flight in November 2025.
If this launch takes place as scheduled, it will mean Blue Origin was also able to inspect, refurbish as necessary, and prepare that used first stage in a little over three months. While not as fast as SpaceX is now doing with its Falcon 9 first stages, it is still remarkably fast, considering it is the first booster Blue Origin has recovered. SpaceX didn’t attempt its first reuse of a recovered first stage for a little more than a year after its first successful landing.
Of course, SpaceX was breaking new ground, so more caution and engineering work was needed. Blue Origin has the advantage of almost a decade of experience to draw upon. Nonetheless, Blue Origin’s decision to reuse so quickly is still impressive. It suggests its engineering behind New Glenn is very robust.
Limp still has work to do, however, to get Blue Origin operating with the speed matching SpaceX. This third launch of New Glenn will place an AST SpaceMobile Bluebird satellite into orbit, because the original payload, Blue Origin’s unmanned Blue Moon MK1 lunar lander, wasn’t ready as planned, and is still undergoing final ground check-ups.

The New Glenn first stage after landing
in November.
In a sign that Blue Origin’s CEO David Limp is beginning to reshape the previously slow culture of the company, it announced yesterday that its next New Glenn launch, set for no earlier than late Feburary, will reuse the first stage that the company successfully landed on the last New Glenn flight in November 2025.
If this launch takes place as scheduled, it will mean Blue Origin was also able to inspect, refurbish as necessary, and prepare that used first stage in a little over three months. While not as fast as SpaceX is now doing with its Falcon 9 first stages, it is still remarkably fast, considering it is the first booster Blue Origin has recovered. SpaceX didn’t attempt its first reuse of a recovered first stage for a little more than a year after its first successful landing.
Of course, SpaceX was breaking new ground, so more caution and engineering work was needed. Blue Origin has the advantage of almost a decade of experience to draw upon. Nonetheless, Blue Origin’s decision to reuse so quickly is still impressive. It suggests its engineering behind New Glenn is very robust.
Limp still has work to do, however, to get Blue Origin operating with the speed matching SpaceX. This third launch of New Glenn will place an AST SpaceMobile Bluebird satellite into orbit, because the original payload, Blue Origin’s unmanned Blue Moon MK1 lunar lander, wasn’t ready as planned, and is still undergoing final ground check-ups.
Paul McCartney – Let It Be
An evening pause: Performed live 2009.
I must ask: It seems almost no one in pop music writes gentle ballads like this any longer. Everything must pound, with beautiful melody no longer a major consideration.
Fake scientist Michael Mann slapped down hard by DC superior court

Fake leftist scientist Michael Mann
In the never-ending legal battle between fake climate scientist Michael Mann and his critics, Rand Simberg and Mark Steyn, Mann has once again lost badly in an appeal to a higher court, with the Superior Court in DC not only ruling that Mann must immediately pay Simberg and Steyn a total of more than $27K in court costs and fees, but blasting Mann for his lies to the court during the proceedings.
The fact remains that Dr. Mann throughout this litigation complained that he suffered lost grant funding directly stemming from the defamatory statements of Messrs. Simberg and Steyn, while providing very little in the way of specifics about the dollar amounts of his losses directly attributable to the statements (such as corroborating testimony from percipient witnesses), all while promising to illuminate the Court at trial. At trial, Dr. Mann elected through his attorneys to present to the jury a blown-up demonstrative, without redaction or explanation, a demonstrative intentionally prepared for its use at trial, which included a budget (loss) amount of $9,713,924.00, when the correct amount, previously corrected during a third round of discovery, was $112,000.
…the Court simply cannot condone such bad faith litigation tactics, particularly in a case that had been zealously litigated across several years and a case involving complicated facts. Thus, the Court’s ruling must stand. It is the Court’s duty to punish and deter bad faith litigation tactics.
In other words, Mann didn’t simply falsify his scientific results, using false data in his infamous hockey stick graph to create the illusion of human-caused global warming, when Simberg and Steyn called him out on this fake science, he tried to sue them using more fake data that was quickly revealed in discovery to be outright lies.
The court has thankfully decided it cannot tolerate such behavior.
What must be understood about Mann is that he is a very typical leftist radical, who thinks that because his cause is just and good, he is somehow immune from any consequences for bad behavior. Such leftists increasingly believe they are allowed to lie, cheat, defame, and even sometimes commit violence, because anyone who disagrees with them is evil. Mann did not do the last item (though many other leftists now are), but he did all the others, and truly believed he could get away with it. He is now finding out otherwise.

Fake leftist scientist Michael Mann
In the never-ending legal battle between fake climate scientist Michael Mann and his critics, Rand Simberg and Mark Steyn, Mann has once again lost badly in an appeal to a higher court, with the Superior Court in DC not only ruling that Mann must immediately pay Simberg and Steyn a total of more than $27K in court costs and fees, but blasting Mann for his lies to the court during the proceedings.
The fact remains that Dr. Mann throughout this litigation complained that he suffered lost grant funding directly stemming from the defamatory statements of Messrs. Simberg and Steyn, while providing very little in the way of specifics about the dollar amounts of his losses directly attributable to the statements (such as corroborating testimony from percipient witnesses), all while promising to illuminate the Court at trial. At trial, Dr. Mann elected through his attorneys to present to the jury a blown-up demonstrative, without redaction or explanation, a demonstrative intentionally prepared for its use at trial, which included a budget (loss) amount of $9,713,924.00, when the correct amount, previously corrected during a third round of discovery, was $112,000.
…the Court simply cannot condone such bad faith litigation tactics, particularly in a case that had been zealously litigated across several years and a case involving complicated facts. Thus, the Court’s ruling must stand. It is the Court’s duty to punish and deter bad faith litigation tactics.
In other words, Mann didn’t simply falsify his scientific results, using false data in his infamous hockey stick graph to create the illusion of human-caused global warming, when Simberg and Steyn called him out on this fake science, he tried to sue them using more fake data that was quickly revealed in discovery to be outright lies.
The court has thankfully decided it cannot tolerate such behavior.
What must be understood about Mann is that he is a very typical leftist radical, who thinks that because his cause is just and good, he is somehow immune from any consequences for bad behavior. Such leftists increasingly believe they are allowed to lie, cheat, defame, and even sometimes commit violence, because anyone who disagrees with them is evil. Mann did not do the last item (though many other leftists now are), but he did all the others, and truly believed he could get away with it. He is now finding out otherwise.
Blue Origin’s proposed TeraWave constellation: Is it really competition with SpaceX?

Blue Origin announced yesterday that it going to build a major satellite constellation — dubbed TeraWave and comprising more than 5,000 satellites — to provide internet service to the globe while also providing data center capability for those companies that wish to establish space-based cloud computing facilities.
It plans to begin launching satellites in 2027.
As I noted in today’s quick links below, such a story would normally merit a full post, “but considering Blue Origin’s inability to get almost anything off the ground, this proposal doesn’t deserve that much coverage at this point.” I just can’t get excited about any Blue Origin proposal, until they actually start launching it. For almost a decade this company has been making these kind of grand announcements, and has only so far managed to achieve one, its New Glenn rocket. And that has come years late and at a pace that is glacial.
Not surprisingly, the mainstream propaganda press immediately went bonkers over this proposal, immediately declaring most absurdly that TeraWave is already a major challenger to SpaceX’s Starlink constellation. Here are just a few very typical examples:
- BBC: Bezos’ Blue Origin announces satellite rival to Musk’s Starlink
- CNBC: Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin launches satellite internet service to rival SpaceX, Amazon
- Business Insider: Jeff Bezos’s grand plan for a satellite constellation to rival SpaceX is coming together
- The Verge: Blue Origin’s Starlink rival TeraWave promises 6-terabit satellite internet
This adulation by the mainstream press of Bezos is far from unusual. For reasons that baffle me, the propaganda press has consistently considered any project proposal coming from a Jeff Bezos’ company to instantly be God’s gift to humanity. For more than a decade now it has been touting Blue Origin as the company that SpaceX needs to beat, flipping reality on its head. Now it ranks Blue Origin’s TeraWave constellation a major Starlink rival, when it is at least two years from even launching its first satellite.
There is one aspect of this story however that does deserve to be highlighted because it appears no one else is noticing it, which is why I after some thought I decided to write this full post. » Read more
January 22, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin announces a new satellite communications network named TeraWave
It would comprise 5,408 optically interconnected satellites, and appears designed to catch the data center market that has appeared out of nowhere in the past year. I would have made this story a full post, but considering Blue Origin’s inability to get almost anything off the ground, this proposal doesn’t deserve that much coverage at this point.
- On this day in 1976 the supersonic airplane Concorde entered commercial service
Jointly built by Air France and British Airways, two flights took off at the same time, one operated by the former and the other by the latter.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Blue Origin announces a new satellite communications network named TeraWave
It would comprise 5,408 optically interconnected satellites, and appears designed to catch the data center market that has appeared out of nowhere in the past year. I would have made this story a full post, but considering Blue Origin’s inability to get almost anything off the ground, this proposal doesn’t deserve that much coverage at this point.
- On this day in 1976 the supersonic airplane Concorde entered commercial service
Jointly built by Air France and British Airways, two flights took off at the same time, one operated by the former and the other by the latter.
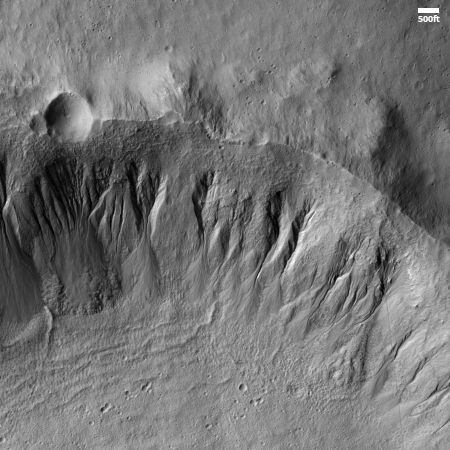
New gullies on Mars?
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on November 6, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this image “Fresh-Looking Gullies.” It was clearly taken to study the gullies flowing down the north interior crater wall of this 4.4 mile-wide unnamed crater, about 1,500 feet deep.
What causes these gullies remains an open question. They are found in many places in the Martian mid-latitudes. When first discovered scientists thought they might be related to the sublimation of underground ice. More recent research suggests they are formed by the seasonal dry ice frost cycle that in the high latitudes has carbon dioxide condense to fall as snow in autumn and then sublimate away in the spring.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on November 6, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this image “Fresh-Looking Gullies.” It was clearly taken to study the gullies flowing down the north interior crater wall of this 4.4 mile-wide unnamed crater, about 1,500 feet deep.
What causes these gullies remains an open question. They are found in many places in the Martian mid-latitudes. When first discovered scientists thought they might be related to the sublimation of underground ice. More recent research suggests they are formed by the seasonal dry ice frost cycle that in the high latitudes has carbon dioxide condense to fall as snow in autumn and then sublimate away in the spring.
» Read more
Rocket Lab completes its first launch in 2026
Early this morning Rocket Lab successfully placed into orbit two satellites for the satellite company Open Cosmos, its Electron rocket lifting off from one of the company’s two launchpads in New Zealand.
The satellites appear to be test satellites designed to demonstrate Open Cosmos’s capabilities.
The 2026 launch race:
9 SpaceX
5 China
1 Rocket Lab
Early this morning Rocket Lab successfully placed into orbit two satellites for the satellite company Open Cosmos, its Electron rocket lifting off from one of the company’s two launchpads in New Zealand.
The satellites appear to be test satellites designed to demonstrate Open Cosmos’s capabilities.
The 2026 launch race:
9 SpaceX
5 China
1 Rocket Lab
Isar postpones 2nd Spectrum rocket launch attempt, no new date set

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace yesterday canceled its second attempt to launch its Spectrum rocket from Norway’s Andoya spaceport, citing an issue with a “pressurization valve”.
We are standing down from today’s launch attempt to address an issue with a pressurization valve. The teams are currently assessing the next possible launch opportunities and a new target date will be announced shortly.
The update also stated the company is moving to a “new launch window” without noting the dates of that window. This statement however suggests that no new launch attempt will occur for at least a month. And considering it is winter at Andoya in the high north, it is quite possible the launch will be delayed until March.
Meanwhile, Andoya continues to lead the race to become the first spaceport in Europe to achieve an orbital launch. Sweden’s Estrange spaceport is limited because of its interior location. The two sea platforms proposed for the North Sea are not yet ready.
And the United Kingdom has effectively eliminated itself from the competition. Its bureaucracy and Byzantine regulations have now put two rocket companies out of business, and that same red tape (combined with location opposition) has essentially shut down the Sutherland spaceport. I doubt there are any rocket companies willing to deal with the UK at this point.

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace yesterday canceled its second attempt to launch its Spectrum rocket from Norway’s Andoya spaceport, citing an issue with a “pressurization valve”.
We are standing down from today’s launch attempt to address an issue with a pressurization valve. The teams are currently assessing the next possible launch opportunities and a new target date will be announced shortly.
The update also stated the company is moving to a “new launch window” without noting the dates of that window. This statement however suggests that no new launch attempt will occur for at least a month. And considering it is winter at Andoya in the high north, it is quite possible the launch will be delayed until March.
Meanwhile, Andoya continues to lead the race to become the first spaceport in Europe to achieve an orbital launch. Sweden’s Estrange spaceport is limited because of its interior location. The two sea platforms proposed for the North Sea are not yet ready.
And the United Kingdom has effectively eliminated itself from the competition. Its bureaucracy and Byzantine regulations have now put two rocket companies out of business, and that same red tape (combined with location opposition) has essentially shut down the Sutherland spaceport. I doubt there are any rocket companies willing to deal with the UK at this point.
French smallsat rocket startup Latitude targeting a first launch in early ’27
In a long interview released yesterday, the CEO of the French smallsat rocket startup Latitude revealed that they expect to do the first launch its Zephyr rocket no later than early ’27, and that launch will not take place in French Guiana, where it is presently developing facilities for launches.
The spaceport at French Guiana is developing a single launchpad designed to serve multiple rocket companies, and so it can’t handle Latitude’s planned launch rate. Thus the company is presently negotiating with other spaceports for its first launch, to give it more flexibility.
Zephyr will also not be reusable, as the company has determined that it isn’t profitable for small rockets.
Latitude has deliberately chosen not to pursue first-stage reusability for Zephyr, a decision Maximin defended with detailed economic analysis. “Our calculations show that with that size, it is not economically viable,” he stated, noting that even with parachute recovery, the maintenance costs and performance penalties outweigh manufacturing savings for a rocket of Zephyr’s class. He pointed to Rocket Lab’s paused reusability efforts as validation: “They have stopped it, despite having done everything. I think it’s not that profitable, if not at all.”
If the company upgrades to a larger rocket in the future it plans to revisit this issue.
Video of the interview is available here.
In a long interview released yesterday, the CEO of the French smallsat rocket startup Latitude revealed that they expect to do the first launch its Zephyr rocket no later than early ’27, and that launch will not take place in French Guiana, where it is presently developing facilities for launches.
The spaceport at French Guiana is developing a single launchpad designed to serve multiple rocket companies, and so it can’t handle Latitude’s planned launch rate. Thus the company is presently negotiating with other spaceports for its first launch, to give it more flexibility.
Zephyr will also not be reusable, as the company has determined that it isn’t profitable for small rockets.
Latitude has deliberately chosen not to pursue first-stage reusability for Zephyr, a decision Maximin defended with detailed economic analysis. “Our calculations show that with that size, it is not economically viable,” he stated, noting that even with parachute recovery, the maintenance costs and performance penalties outweigh manufacturing savings for a rocket of Zephyr’s class. He pointed to Rocket Lab’s paused reusability efforts as validation: “They have stopped it, despite having done everything. I think it’s not that profitable, if not at all.”
If the company upgrades to a larger rocket in the future it plans to revisit this issue.
Video of the interview is available here.
German startup Spark Microgravity to build first space-based commercial cancer lab
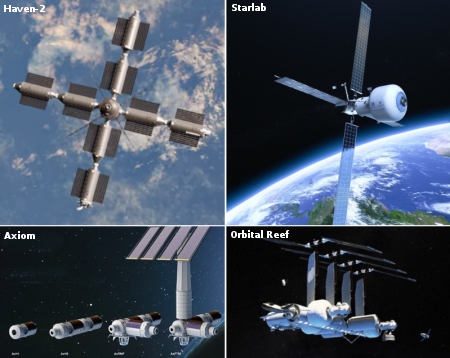
The American space stations under development
The German startup Spark Microgravity announced yesterday it is negotiating with two commercial space stations, one re-entry capsule company, and one French rocket startup to launch the first commercial cancer lab in space.
SPARK Microgravity is collaborating with Axiom Space and Voyager Technologies on commercial low Earth orbit (LEO) opportunities, with ATMOS Space Cargo supporting future return missions. A first flight demonstration with Swedish Space Corporation is scheduled in May. The cancer research will be launched in partnership with HyPrSpace, which developed Baguette-One, the first rocket to be launched from France.
Axiom hopes to launch its first modules in ’28, while Voyager’s Starlab station can’t launch until Starship is operational, possibly about the same time. ATMOS is a German startup developing a returnable capsule that can fly in orbit for several months. It has a deal with Hyperspace to fly a demo capsule on Baguette-1, which is a suborbital rocket.
Similar research has been done on ISS, but NASA’s rules forbid that research to produce a product for sale. Those rules won’t apply on the private stations, and Spark’s existence is a reflection of this new profit-oriented reality. Spark is going to attract investment capital from the pharmaceutical and academic communities, and thus is another profit center for the commercial space stations, outside of government funding.
The market for these new space stations is growing, making any NASA construction contracts less critical in the long run.

The American space stations under development
The German startup Spark Microgravity announced yesterday it is negotiating with two commercial space stations, one re-entry capsule company, and one French rocket startup to launch the first commercial cancer lab in space.
SPARK Microgravity is collaborating with Axiom Space and Voyager Technologies on commercial low Earth orbit (LEO) opportunities, with ATMOS Space Cargo supporting future return missions. A first flight demonstration with Swedish Space Corporation is scheduled in May. The cancer research will be launched in partnership with HyPrSpace, which developed Baguette-One, the first rocket to be launched from France.
Axiom hopes to launch its first modules in ’28, while Voyager’s Starlab station can’t launch until Starship is operational, possibly about the same time. ATMOS is a German startup developing a returnable capsule that can fly in orbit for several months. It has a deal with Hyperspace to fly a demo capsule on Baguette-1, which is a suborbital rocket.
Similar research has been done on ISS, but NASA’s rules forbid that research to produce a product for sale. Those rules won’t apply on the private stations, and Spark’s existence is a reflection of this new profit-oriented reality. Spark is going to attract investment capital from the pharmaceutical and academic communities, and thus is another profit center for the commercial space stations, outside of government funding.
The market for these new space stations is growing, making any NASA construction contracts less critical in the long run.
Rocket Lab experiences a tank failure during Neutron pressure test

Artist’s rendering of Neutron’s first stage fairings opening
to deploy the payload with the second stage engine.
According to an update posted yesterday, during a pressure test of a first stage tank for Rocket Lab’s new Neutron rocket, the tank ruptured.
As the company pushes Neutron to the limits and beyond to qualify its systems and structures for launch, qualification testing of the Stage 1 tank overnight resulted in a rupture during a hydrostatic pressure trial. Testing failures are not uncommon during qualification testing. We intentionally test structures to their limits to validate structural integrity and safety margins to ensure the robust requirements for a successful launch can be comfortably met.
There was no significant damage to the test structure or facilities, the next Stage 1 tank is already in production, and Neutron’s development campaign continues while the team assesses today’s test outcome.
The team is reviewing the Stage 1 test data, which will determine the extent of the impact to Neutron’s launch schedule.
The company was aiming to do Neutron’s first launch in the first quarter of this year. Though the press release is vague on this point, its language suggests the rupture did not occur at the expected maximum pressure, but took place sooner, at a lower pressure level. If the tank failed at maximum pressure, then there would be no need to reconsider the launch schedule. A failure at lower pressures would require changes in tank design, and thus a launch delay.
The company says it will provide an update in February, which further suggests a launch in the first quarter is now unlikely.

Artist’s rendering of Neutron’s first stage fairings opening
to deploy the payload with the second stage engine.
According to an update posted yesterday, during a pressure test of a first stage tank for Rocket Lab’s new Neutron rocket, the tank ruptured.
As the company pushes Neutron to the limits and beyond to qualify its systems and structures for launch, qualification testing of the Stage 1 tank overnight resulted in a rupture during a hydrostatic pressure trial. Testing failures are not uncommon during qualification testing. We intentionally test structures to their limits to validate structural integrity and safety margins to ensure the robust requirements for a successful launch can be comfortably met.
There was no significant damage to the test structure or facilities, the next Stage 1 tank is already in production, and Neutron’s development campaign continues while the team assesses today’s test outcome.
The team is reviewing the Stage 1 test data, which will determine the extent of the impact to Neutron’s launch schedule.
The company was aiming to do Neutron’s first launch in the first quarter of this year. Though the press release is vague on this point, its language suggests the rupture did not occur at the expected maximum pressure, but took place sooner, at a lower pressure level. If the tank failed at maximum pressure, then there would be no need to reconsider the launch schedule. A failure at lower pressures would require changes in tank design, and thus a launch delay.
The company says it will provide an update in February, which further suggests a launch in the first quarter is now unlikely.
Orbex’s Danish subsidiary to file for bankruptcy
In what appears to confirm the story yesterday that the rocket startup Orbex was about to be bought out by the French startup The Exploration Company — thus likely ending operations in Great Britain — there was a second follow-up story later in the day that claimed Orbex’s Danish subsidiary is about to file for bankruptcy.
On 20 January, more than 15 Orbital Express Launch ApS employees announced at around the same time on LinkedIn that they were looking for work. Since then, European Spaceflight has received confirmation from three independent sources, who wished to remain anonymous, that the subsidiary has dismissed its entire workforce, with the company expected to officially file for bankruptcy on 22 January.
The article notes that this subsidiary had been losing millions in the past two years, and was entirely reliant on cash from its parent company. Unfortunately, Orbex has had no incoming revenue itself, because red tape in the United Kingdom had prevented it from launching for the past four years.
If true, this story confirms that Orbex’s negotiations with The Exploration Company is likely an attempt to make as much money from its remaining assets as possible before closing down.
Congratulations to the United Kingdom, the land where rocket companies go to die!
In what appears to confirm the story yesterday that the rocket startup Orbex was about to be bought out by the French startup The Exploration Company — thus likely ending operations in Great Britain — there was a second follow-up story later in the day that claimed Orbex’s Danish subsidiary is about to file for bankruptcy.
On 20 January, more than 15 Orbital Express Launch ApS employees announced at around the same time on LinkedIn that they were looking for work. Since then, European Spaceflight has received confirmation from three independent sources, who wished to remain anonymous, that the subsidiary has dismissed its entire workforce, with the company expected to officially file for bankruptcy on 22 January.
The article notes that this subsidiary had been losing millions in the past two years, and was entirely reliant on cash from its parent company. Unfortunately, Orbex has had no incoming revenue itself, because red tape in the United Kingdom had prevented it from launching for the past four years.
If true, this story confirms that Orbex’s negotiations with The Exploration Company is likely an attempt to make as much money from its remaining assets as possible before closing down.
Congratulations to the United Kingdom, the land where rocket companies go to die!
Orbital tug startup Starfish Space wins $52.5 million Space Force contract to de-orbit its defunct satellites

Images taken by Starfish’s camera during rendezvous
maneuvers.
The orbital tug startup Starfish Space yesterday announced it has been awarded a $52.5 million contract from the Space Force’s Space Development Agency (SDA) to use its Otter tug to de-orbit satellites when they have reached their end-of-life.
Under the contract, Starfish Space will build, launch, and operate an Otter spacecraft in low Earth orbit (LEO) to safely and efficiently dispose of SDA satellites at the end of their operational lives. The mission begins with an initial deorbit, with options for multiple additional deorbits, enabled by Otter’s significant capacity and ability to service several satellites in a single mission. The mission is targeting launch in 2027.
While a number of contracts have been issued in the U.S., Europe, and Japan to demonstrate de-orbit technology, this is the first operational contract ever issued. Moreover, I don’t think any of those other demo missions have actually achieved a de-orbit as of yet. Starfish itself has only successfully demonstrated rendezvous and proximity capabilities on two missions, with a third a failure. In the most recent late last year (as shown by the image on the right), Impulse’s Mira tug used Starfish software and camera to move within 1.2 kilometers of another Mira tug.
As for docking, its Otter Pup tug has flown two missions. The first failed in 2023 when both spacecraft began spinning unexpected. The second was supposed to achieve a docking, but after completing rendezvous maneuvers the company has provided no new updates. As far as we know, the docking never occurred or was a failure.
Nonetheless, it appears Starfish’s overall recent performance convinced the Space Force it could handle this new de-orbit contract.

Images taken by Starfish’s camera during rendezvous
maneuvers.
The orbital tug startup Starfish Space yesterday announced it has been awarded a $52.5 million contract from the Space Force’s Space Development Agency (SDA) to use its Otter tug to de-orbit satellites when they have reached their end-of-life.
Under the contract, Starfish Space will build, launch, and operate an Otter spacecraft in low Earth orbit (LEO) to safely and efficiently dispose of SDA satellites at the end of their operational lives. The mission begins with an initial deorbit, with options for multiple additional deorbits, enabled by Otter’s significant capacity and ability to service several satellites in a single mission. The mission is targeting launch in 2027.
While a number of contracts have been issued in the U.S., Europe, and Japan to demonstrate de-orbit technology, this is the first operational contract ever issued. Moreover, I don’t think any of those other demo missions have actually achieved a de-orbit as of yet. Starfish itself has only successfully demonstrated rendezvous and proximity capabilities on two missions, with a third a failure. In the most recent late last year (as shown by the image on the right), Impulse’s Mira tug used Starfish software and camera to move within 1.2 kilometers of another Mira tug.
As for docking, its Otter Pup tug has flown two missions. The first failed in 2023 when both spacecraft began spinning unexpected. The second was supposed to achieve a docking, but after completing rendezvous maneuvers the company has provided no new updates. As far as we know, the docking never occurred or was a failure.
Nonetheless, it appears Starfish’s overall recent performance convinced the Space Force it could handle this new de-orbit contract.
SpaceX launches 25 more Starlink satellites
SpaceX tonight successfully launched another 25 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage completed its 10th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
The 2026 launch race:
9 SpaceX
5 China
SpaceX tonight successfully launched another 25 Starlink satellites, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage completed its 10th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
The 2026 launch race:
9 SpaceX
5 China
January 20, 2026 Zimmerman/Space Show appearance
David Livingston has now uploaded my appearance on the Space Show from yesterday, January 20, 2026.
You can download the audio of the program here.
To watch the Zoom broadcast go here, here, or here.
Twas I think one of the best shows, especially because of the excellent questions and comments from the other participants. If you don’t know why NASA’s entire Artemis program is a mess, you need to watch or listen to this show.
David Livingston has now uploaded my appearance on the Space Show from yesterday, January 20, 2026.
You can download the audio of the program here.
To watch the Zoom broadcast go here, here, or here.
Twas I think one of the best shows, especially because of the excellent questions and comments from the other participants. If you don’t know why NASA’s entire Artemis program is a mess, you need to watch or listen to this show.
January 21, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Dionne Warwick, Hal David, Burt Bacharach – I Say A Little Prayer studio rehearsal
Communications resume with Mars
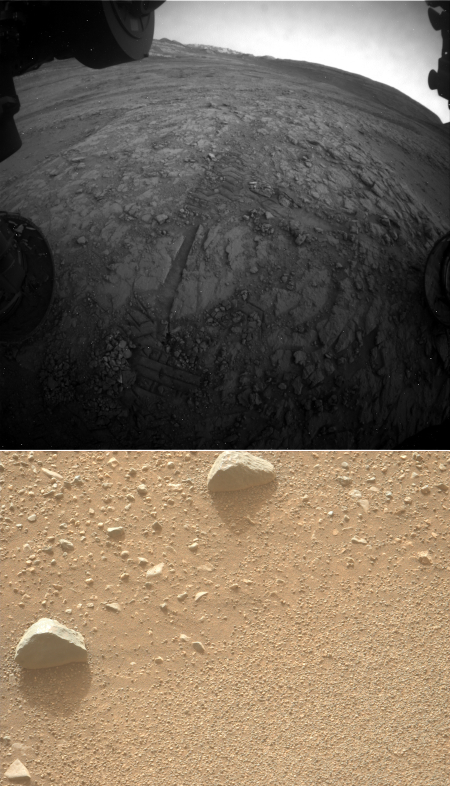
Go here and here for the original images.
It appears the solar conjunction that has blocked all communications with the rovers and orbiters for the past three weeks around Mars has now fully ended, with the first new images appearing today from both Curiosity and Perseverance.
The two images to the right were downloaded today. The top image was taken on January 20, 2026 by Curiosity’s front hazard avoidance camera. It appears to be looking uphill in the direction the rover is soon to travel, climbing Mount Sharp. If you look closely you can see the mountain’s higher ranges on the horizon, just to the right of the rover itself.
The bottom picture was actually taken on January 15, 2026 by Perseverance, but was only downloaded today. Both science teams had programmed their rovers to take images throughout the conjunction, scheduled for download when communications resumed.
The picture was taken by Perseverance’s left high resolution camera located on top of the rover’s mast. It looks down at the ground near the rover at the pebbles and rocks that strewn the relatively smooth surface of the terrain west of Jezero crater.
Neither image is particularly ground-breaking. What is important however is that both images prove the rovers are functioning as expected. Expect a lot more data to arrive in the next few days, all gathered during three weeks of blackout.

Go here and here for the original images.
It appears the solar conjunction that has blocked all communications with the rovers and orbiters for the past three weeks around Mars has now fully ended, with the first new images appearing today from both Curiosity and Perseverance.
The two images to the right were downloaded today. The top image was taken on January 20, 2026 by Curiosity’s front hazard avoidance camera. It appears to be looking uphill in the direction the rover is soon to travel, climbing Mount Sharp. If you look closely you can see the mountain’s higher ranges on the horizon, just to the right of the rover itself.
The bottom picture was actually taken on January 15, 2026 by Perseverance, but was only downloaded today. Both science teams had programmed their rovers to take images throughout the conjunction, scheduled for download when communications resumed.
The picture was taken by Perseverance’s left high resolution camera located on top of the rover’s mast. It looks down at the ground near the rover at the pebbles and rocks that strewn the relatively smooth surface of the terrain west of Jezero crater.
Neither image is particularly ground-breaking. What is important however is that both images prove the rovers are functioning as expected. Expect a lot more data to arrive in the next few days, all gathered during three weeks of blackout.
Haven-1 launch delayed until 2027
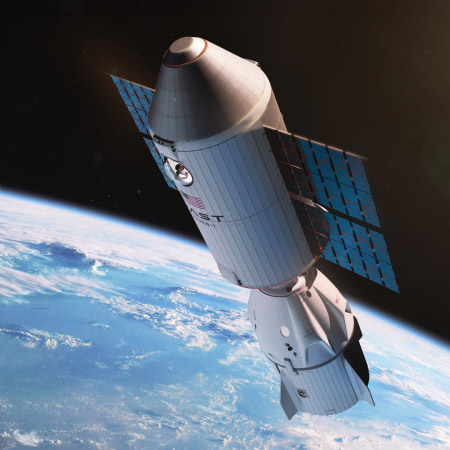

Artist rendering of Haven-1 with docked
Dragon capsule
According to Vast’s CEO, Max Haot, the launch of its single module Haven-1 space station has now been pushed back to the first quarter of ’27.
Last Saturday (January 10) we reached the key milestone of fully completing the primary structure, and some of the secondary structure; all of the acceptance testing occurred in November as well. Now we are starting clean room integration, which starts with TCS (thermal control system), propulsion, interior shells, and then moving on to avionics. And then final close out, which we expect will be done by the fall, and then we have on the books with NASA a full test campaign at the end of the year at Plum Brook. Then the launch in Q1 next year.
Until recently the company had been targeting a launch in the first half of 2026. This is a delay of almost a full year, and suggests the previous launch date has not been a serious target for quite some time.
Haot at the article at the link provides some new details about the manned missions to the station. It will launch unmanned, and after check-out in orbit that could last two weeks or longer, a professional SpaceX Dragon crew will fly a two-week mission there to do further check-outs.
After this up to three more two-week missions are planned, with Vast already having a deposit for the first. It also is willing to do more during Haven-1’s three year lifespan.
More and more it appears to me that in my rankings below of the five commercial space stations presently under development, the top three space stations are practically tied. And of the five stations, three are hoping to begin launching modules in the ’27-’28 time frame.
» Read more

Artist rendering of Haven-1 with docked
Dragon capsule
According to Vast’s CEO, Max Haot, the launch of its single module Haven-1 space station has now been pushed back to the first quarter of ’27.
Last Saturday (January 10) we reached the key milestone of fully completing the primary structure, and some of the secondary structure; all of the acceptance testing occurred in November as well. Now we are starting clean room integration, which starts with TCS (thermal control system), propulsion, interior shells, and then moving on to avionics. And then final close out, which we expect will be done by the fall, and then we have on the books with NASA a full test campaign at the end of the year at Plum Brook. Then the launch in Q1 next year.
Until recently the company had been targeting a launch in the first half of 2026. This is a delay of almost a full year, and suggests the previous launch date has not been a serious target for quite some time.
Haot at the article at the link provides some new details about the manned missions to the station. It will launch unmanned, and after check-out in orbit that could last two weeks or longer, a professional SpaceX Dragon crew will fly a two-week mission there to do further check-outs.
After this up to three more two-week missions are planned, with Vast already having a deposit for the first. It also is willing to do more during Haven-1’s three year lifespan.
More and more it appears to me that in my rankings below of the five commercial space stations presently under development, the top three space stations are practically tied. And of the five stations, three are hoping to begin launching modules in the ’27-’28 time frame.
» Read more
January 21, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
I am posting this early because I am busy this morning dealing with a scheduled family medical procedure. Nothing critical, but I will be out of the office for a good portion of the day. I plan to catch up in the afternoon.
- NASA astronaut Suni Williams retires
She spent 27 years at NASA, logging 608 days in space.
- Stratolaunch raises “significant capital” from two new investment partners
The press release says nothing about the amount of money raised. Nor does it indicate how this deal changes the company’s management.
- Airbus’s plan to consolidate its satellite divisions opposed by unions
It is unclear from the article how that opposition might impact Airbus’s plans.
- Chinese pseudo-company Galactic Energy claims its new CQ-90 engine is more powerful than SpaceX’s Merlin engine
This engine has not flown yet. It is to be used on a planned reusable first stage.
- In November 2026 Voyager-1 will be one light-day away from Earth (16 billion miles)
In other words, any signals will take a full 24 hours to reach the spacecraft. It will also take that long for data to come back.
- On this day in 1965 an Apollo test command module was launched atop a Little Joe II rocket
The suborbital flight successfully tested the capsule’s launch abort escape system.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
I am posting this early because I am busy this morning dealing with a scheduled family medical procedure. Nothing critical, but I will be out of the office for a good portion of the day. I plan to catch up in the afternoon.
- NASA astronaut Suni Williams retires
She spent 27 years at NASA, logging 608 days in space.
- Stratolaunch raises “significant capital” from two new investment partners
The press release says nothing about the amount of money raised. Nor does it indicate how this deal changes the company’s management.
- Airbus’s plan to consolidate its satellite divisions opposed by unions
It is unclear from the article how that opposition might impact Airbus’s plans.
- Chinese pseudo-company Galactic Energy claims its new CQ-90 engine is more powerful than SpaceX’s Merlin engine
This engine has not flown yet. It is to be used on a planned reusable first stage.
- In November 2026 Voyager-1 will be one light-day away from Earth (16 billion miles)
In other words, any signals will take a full 24 hours to reach the spacecraft. It will also take that long for data to come back.
- On this day in 1965 an Apollo test command module was launched atop a Little Joe II rocket
The suborbital flight successfully tested the capsule’s launch abort escape system.
French startup The Exploration Company negotiating purchase of UK rocket startup Orbex

The prototype of Orbex’s never-launched Prime rocket,
on the launchpad in 2022
In what appears to be a direct consequence of British red tape blocking Orbex from launching in the past four years, it is now in negotiations to sell its assets to the French startup The Exploration Company.
On 21 January, Orbex published a brief press release stating that a letter of intent had been signed and that negotiations had begun. The company added that all details about the transaction remain confidential at this stage. A statement from Orbex CEO Phil Chambers suggests that the company’s financial position factored into its decision to pursue a buyer. “Our Series D fundraising could have led us in many directions,” said Chambers. “We believe this opportunity plays to the strengths of both businesses, and we look forward to sharing more when the time is right.”
Let me translate: In 2022 Orbex had set up a factory close to the proposed Sutherland spaceport on the north coast of Scotland, had signed a 50 year lease with that facility to launch its Prime rocket there, had built a launch platform and tested a prototype of the rocket, and was poised to do its first launch. All it needed was license approvals from the United Kingdom’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
And then it waited, and waited, and waited, and waited. By 2024 it gave up on Sutherland, because the authorities (local and national) kept rejecting its spaceport license for environmental and political reasons. It switched its launch site to the SaxaVord spaceport on the Shetland Islands, pushing back that first launch to 2026. Along the way the UK gave it a $25 million grant, likely to keep the company above water because the UK was blocking its ability to launch.
All for naught. It is very clear Orbex has run out of cash waiting, and is now looking to salvage its work by selling everything to the French company, which so far has focused on building a cargo capsule to supply the upcoming commercial space stations.
If the sale goes through, do not be surprised if Orbex’s assets exit the UK entirely. And at that point, the CAA’s red tape can be given credit for destroying a second rocket company, following Virgin Orbit.

The prototype of Orbex’s never-launched Prime rocket,
on the launchpad in 2022
In what appears to be a direct consequence of British red tape blocking Orbex from launching in the past four years, it is now in negotiations to sell its assets to the French startup The Exploration Company.
On 21 January, Orbex published a brief press release stating that a letter of intent had been signed and that negotiations had begun. The company added that all details about the transaction remain confidential at this stage. A statement from Orbex CEO Phil Chambers suggests that the company’s financial position factored into its decision to pursue a buyer. “Our Series D fundraising could have led us in many directions,” said Chambers. “We believe this opportunity plays to the strengths of both businesses, and we look forward to sharing more when the time is right.”
Let me translate: In 2022 Orbex had set up a factory close to the proposed Sutherland spaceport on the north coast of Scotland, had signed a 50 year lease with that facility to launch its Prime rocket there, had built a launch platform and tested a prototype of the rocket, and was poised to do its first launch. All it needed was license approvals from the United Kingdom’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA).
And then it waited, and waited, and waited, and waited. By 2024 it gave up on Sutherland, because the authorities (local and national) kept rejecting its spaceport license for environmental and political reasons. It switched its launch site to the SaxaVord spaceport on the Shetland Islands, pushing back that first launch to 2026. Along the way the UK gave it a $25 million grant, likely to keep the company above water because the UK was blocking its ability to launch.
All for naught. It is very clear Orbex has run out of cash waiting, and is now looking to salvage its work by selling everything to the French company, which so far has focused on building a cargo capsule to supply the upcoming commercial space stations.
If the sale goes through, do not be surprised if Orbex’s assets exit the UK entirely. And at that point, the CAA’s red tape can be given credit for destroying a second rocket company, following Virgin Orbit.
JAXA releases preliminary results of investigation into December 2025 H3 rocket launch failure

JAXA yesterday released the preliminary results of its investigation into upper stage failure during the December 2025 launch of its H3 rocket.
Previously the agency had indicated it believed the cause was linked to the separation of the rocket’s payload fairings. This new report changes that conclusion:
After liftoff, the No. 8 H3 rocket sustained damage to the section where the Michibiki No. 5 positioning satellite was mounted, when the satellite cover, called fairing, was separated.
In addition, the fuel tubing of the rocket’s second-stage engine was damaged, presumably causing combustion to stop earlier than planned, JAXA said in a progress report on its investigation into the failure at a meeting of a subgroup of a science ministry panel.
As the section was damaged, the satellite was no longer attached to the second stage of the rocket. The satellite fell off when the first stage separated.
In other words, as the fairings released, the satellite apparently deployed, damaging the fuel feed to the upper stage engine. It is as yet unclear whether the deployment system worked as intended, but did so prematurely, or if it failed entirely, allowing the satellite to fall away once the fairings separated.
At the moment Japan has no launch capability. Both of JAXA’s rockets, the H3 and the Epsilon-S are grounded due to launch failures. Meanwhile, the country has only recently begun to develop private launch companies, none of which are ready to launch.

JAXA yesterday released the preliminary results of its investigation into upper stage failure during the December 2025 launch of its H3 rocket.
Previously the agency had indicated it believed the cause was linked to the separation of the rocket’s payload fairings. This new report changes that conclusion:
After liftoff, the No. 8 H3 rocket sustained damage to the section where the Michibiki No. 5 positioning satellite was mounted, when the satellite cover, called fairing, was separated.
In addition, the fuel tubing of the rocket’s second-stage engine was damaged, presumably causing combustion to stop earlier than planned, JAXA said in a progress report on its investigation into the failure at a meeting of a subgroup of a science ministry panel.
As the section was damaged, the satellite was no longer attached to the second stage of the rocket. The satellite fell off when the first stage separated.
In other words, as the fairings released, the satellite apparently deployed, damaging the fuel feed to the upper stage engine. It is as yet unclear whether the deployment system worked as intended, but did so prematurely, or if it failed entirely, allowing the satellite to fall away once the fairings separated.
At the moment Japan has no launch capability. Both of JAXA’s rockets, the H3 and the Epsilon-S are grounded due to launch failures. Meanwhile, the country has only recently begun to develop private launch companies, none of which are ready to launch.
Foreigner – Urgent
An evening pause: Performed live 1982, with a truly great sax solo by Mark Rivera.
Hat tip Ferris Akel.
January 20, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- PLD tests the throttle capabilities of the first stage engines it will use on its Mirura-5 orbital rocket
This capability is essential for the vertical landing of that planned reusable stage.
- NOAA predicts a major geomagnetic storm to reach Earth January 20, 2026
While much of the press will scream like Chicken Little, the NOAA prediction notes that the heaviest impact will be above 60 degrees latitude, and that it will have a “minor impact” on satellites and cause “weak fluctuations” in the power grid. In other words, we are not gonna die, though we might see some cool auroras.
- On this day in 2005 New Horizons was launched on a decade-long journey to Pluto
When it flew past Pluto in 2015 proved that even in the utter cold of the outer solar system, planets can be geologically active.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- PLD tests the throttle capabilities of the first stage engines it will use on its Mirura-5 orbital rocket
This capability is essential for the vertical landing of that planned reusable stage.
- NOAA predicts a major geomagnetic storm to reach Earth January 20, 2026
While much of the press will scream like Chicken Little, the NOAA prediction notes that the heaviest impact will be above 60 degrees latitude, and that it will have a “minor impact” on satellites and cause “weak fluctuations” in the power grid. In other words, we are not gonna die, though we might see some cool auroras.
- On this day in 2005 New Horizons was launched on a decade-long journey to Pluto
When it flew past Pluto in 2015 proved that even in the utter cold of the outer solar system, planets can be geologically active.
I will be on the Space Show with David Livingston tonight
I will be appearing with David Livingston on the Space Show tonight at 7 pm (Pacific). This will be a Zoom presentation, so if you wish to participate or ask questions, this is the announcement David sent out today:
You can listen and participate with us in our program tonight with Bob Zimmerman by using one of the following two Zoom phone numbers. Bob will be talking about his recent Op-Ed on Artemis and safety plus numerous other timely and important space topics.
One tap mobile
+1-253-200468,,81561774534# US
+1-253-21-8782,,81561774534# US (Tacoma)
I will be appearing with David Livingston on the Space Show tonight at 7 pm (Pacific). This will be a Zoom presentation, so if you wish to participate or ask questions, this is the announcement David sent out today:
You can listen and participate with us in our program tonight with Bob Zimmerman by using one of the following two Zoom phone numbers. Bob will be talking about his recent Op-Ed on Artemis and safety plus numerous other timely and important space topics.
One tap mobile
+1-253-200468,,81561774534# US
+1-253-21-8782,,81561774534# US (Tacoma)
Computer simulations suggest Jupiter and Saturn have fundamentally different interiors
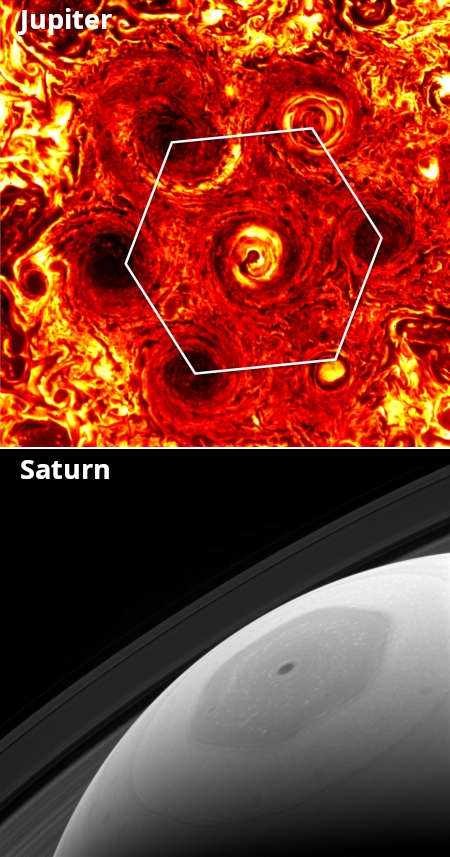
The uncertainty of science: In attempting to explain why the polar vortexes of Jupiter and Saturn are so different, scientists running large computer simulations have found that the difference could be because Jupiter’s interior is “softer” than Saturn’s.
The two images to the right illustrate the different polar vortexes of both planets. Jupiter’s (top) is made up of multiple chaotic small storms that form a hexagon-like ring around the pole. Saturn’s (bottom) is a single very coherent hexagon-shaped storm.
Over multiple different simulations, they observed that some scenarios evolved to form a single large polar vortex, like Saturn, whereas others formed multiple smaller vortices, like Jupiter. After analyzing the combinations of parameters and variables in each scenario and how they related to the final outcome, they landed on a single mechanism to explain whether a single or multiple vortices evolve: As random fluid motions start to coalesce into individual vortices, the size to which a vortex can grow is limited by how soft the bottom of the vortex is. The softer, or lighter the gas is that is rotating at the bottom of a vortex, the smaller the vortex is in the end, allowing for multiple smaller-scale vortices to coexist at a planet’s pole, similar to those on Jupiter.
Conversely, the harder or denser a vortex bottom is, the larger the system can grow, to a size where eventually it can follow the planet’s curvature as a single, planetary-scale vortex, like the one on Saturn.
If this mechanism is indeed what is at play on both gas giants, it would suggest that Jupiter could be made of softer, lighter material, while Saturn may harbor heavier stuff in its interior.
This conclusion however runs completely counter to what we should expect. Jupiter has a much great mass, and one would assume from this that its interior would therefore be denser and thus harder.

The uncertainty of science: In attempting to explain why the polar vortexes of Jupiter and Saturn are so different, scientists running large computer simulations have found that the difference could be because Jupiter’s interior is “softer” than Saturn’s.
The two images to the right illustrate the different polar vortexes of both planets. Jupiter’s (top) is made up of multiple chaotic small storms that form a hexagon-like ring around the pole. Saturn’s (bottom) is a single very coherent hexagon-shaped storm.
Over multiple different simulations, they observed that some scenarios evolved to form a single large polar vortex, like Saturn, whereas others formed multiple smaller vortices, like Jupiter. After analyzing the combinations of parameters and variables in each scenario and how they related to the final outcome, they landed on a single mechanism to explain whether a single or multiple vortices evolve: As random fluid motions start to coalesce into individual vortices, the size to which a vortex can grow is limited by how soft the bottom of the vortex is. The softer, or lighter the gas is that is rotating at the bottom of a vortex, the smaller the vortex is in the end, allowing for multiple smaller-scale vortices to coexist at a planet’s pole, similar to those on Jupiter.
Conversely, the harder or denser a vortex bottom is, the larger the system can grow, to a size where eventually it can follow the planet’s curvature as a single, planetary-scale vortex, like the one on Saturn.
If this mechanism is indeed what is at play on both gas giants, it would suggest that Jupiter could be made of softer, lighter material, while Saturn may harbor heavier stuff in its interior.
This conclusion however runs completely counter to what we should expect. Jupiter has a much great mass, and one would assume from this that its interior would therefore be denser and thus harder.
Australian rocket startup Gilmour Space raises $145 million in investment capital
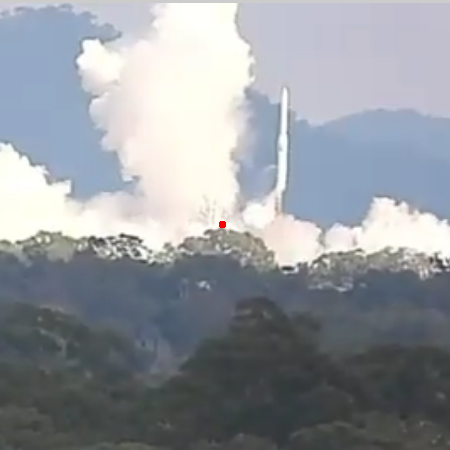

Gilmour’s Eris rocket falling sideways from launchpad
(indicated by red dot) in July 2025. Click for much better
video.
The Australian rocket startup Gilmour Space, whose one orbital test launch in 2025 failed, has now raised an additional A$217 million ($145 million American) in investment capital, in addition to the A$142 million it had previously raised.
The Series E round was jointly led by the National Reconstruction Fund Corporation (NRFC) and Hostplus, with participation from Future Fund, Blackbird, Funds SA, HESTA, NGS Super, Main Sequence, QIC, and Brighter Super.
…Proceeds from the raise will be used to support continued development and qualification of its Eris orbital launch vehicle, scale rocket and satellite manufacturing, expand test and launch infrastructure, and grow the company’s workforce to meet global demand for space launch services.
The National Reconstruction Fund Corporation is a government agency with a A$15 billion budget tasked to help finance new industries. It contributed A$75 million in this fund raising round.
The other major contributor was Hostplus, which matched that contribution.
Though the company has said it will attempt a second orbital test launch in 2026, no dates have been announced.

Gilmour’s Eris rocket falling sideways from launchpad
(indicated by red dot) in July 2025. Click for much better
video.
The Australian rocket startup Gilmour Space, whose one orbital test launch in 2025 failed, has now raised an additional A$217 million ($145 million American) in investment capital, in addition to the A$142 million it had previously raised.
The Series E round was jointly led by the National Reconstruction Fund Corporation (NRFC) and Hostplus, with participation from Future Fund, Blackbird, Funds SA, HESTA, NGS Super, Main Sequence, QIC, and Brighter Super.
…Proceeds from the raise will be used to support continued development and qualification of its Eris orbital launch vehicle, scale rocket and satellite manufacturing, expand test and launch infrastructure, and grow the company’s workforce to meet global demand for space launch services.
The National Reconstruction Fund Corporation is a government agency with a A$15 billion budget tasked to help finance new industries. It contributed A$75 million in this fund raising round.
The other major contributor was Hostplus, which matched that contribution.
Though the company has said it will attempt a second orbital test launch in 2026, no dates have been announced.

