A really really big landslide on Mars
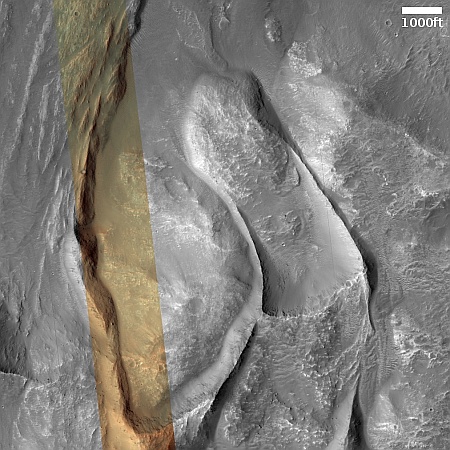
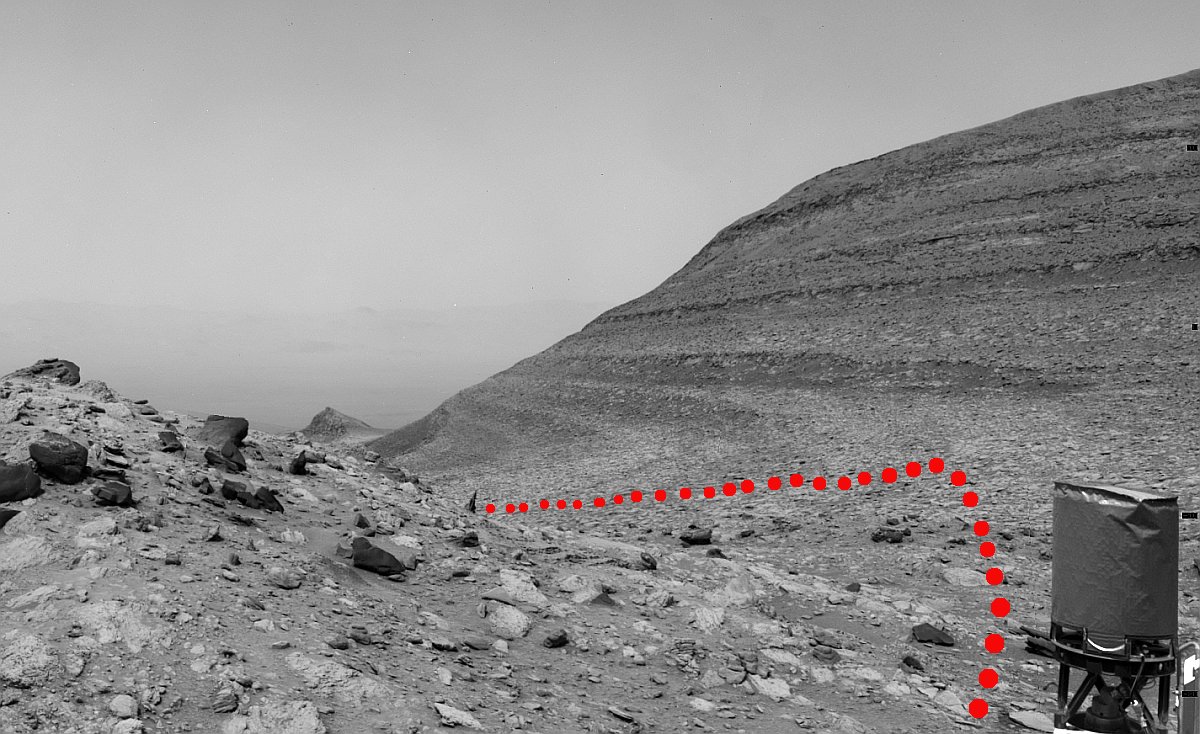
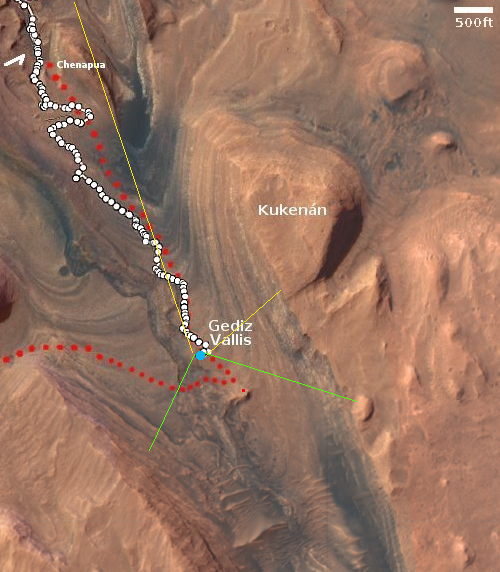
Sometimes the cool geological features I find in the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) image archive are so large they are difficult to present on this webpage. Today is an example. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on March 13, 2024 by the high resolution camera on MRO. It shows the distinct run-out of debris from a landslide that flowed downhill to the north as a single unit of material. Along the way it carved its track in the ground, almost like a ramp.
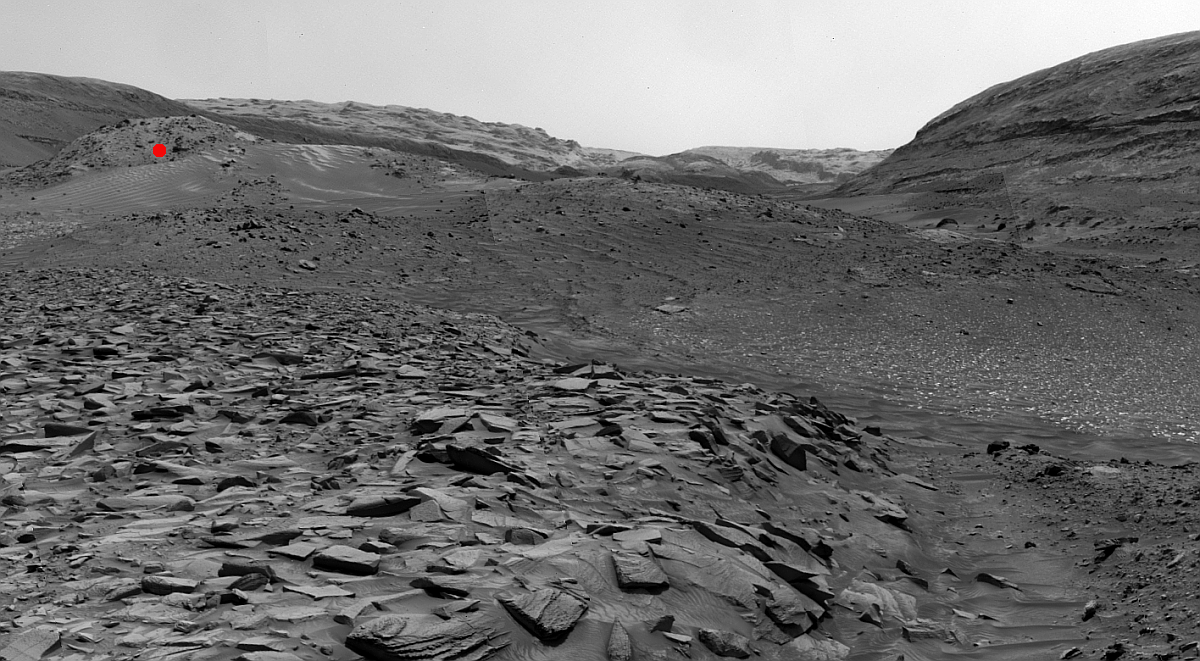
The full picture however suggested something much more spectacular. In that full image this landslide is merely a small side avalanche to a landslide many times larger. And that high resolution picture only shows what appears to be a small section of that giant slide. Obviously, this required a look at the global mosaic produced by MRO’s context camera to find out how far that avalanche actually extended.
» Read more
Sometimes the cool geological features I find in the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) image archive are so large they are difficult to present on this webpage. Today is an example. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on March 13, 2024 by the high resolution camera on MRO. It shows the distinct run-out of debris from a landslide that flowed downhill to the north as a single unit of material. Along the way it carved its track in the ground, almost like a ramp.
The full picture however suggested something much more spectacular. In that full image this landslide is merely a small side avalanche to a landslide many times larger. And that high resolution picture only shows what appears to be a small section of that giant slide. Obviously, this required a look at the global mosaic produced by MRO’s context camera to find out how far that avalanche actually extended.
» Read more