Mob of Democrats threatens violence against conservative students at the University of Memphis

Democrats in Georgia in 1915, lynching Leo Frank
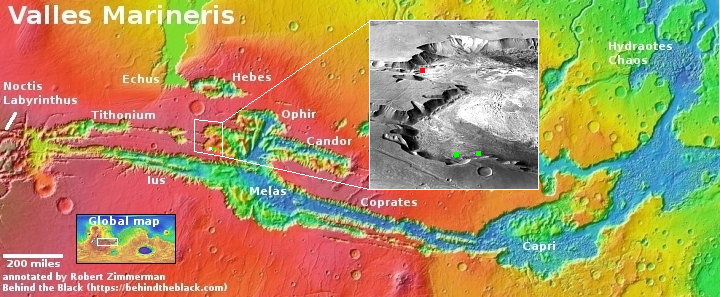
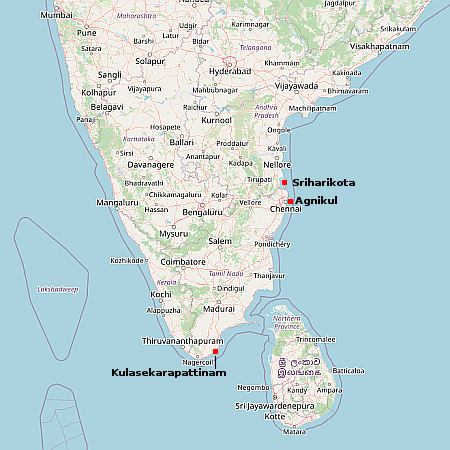
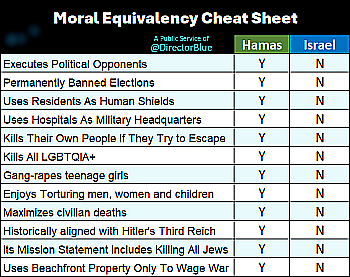
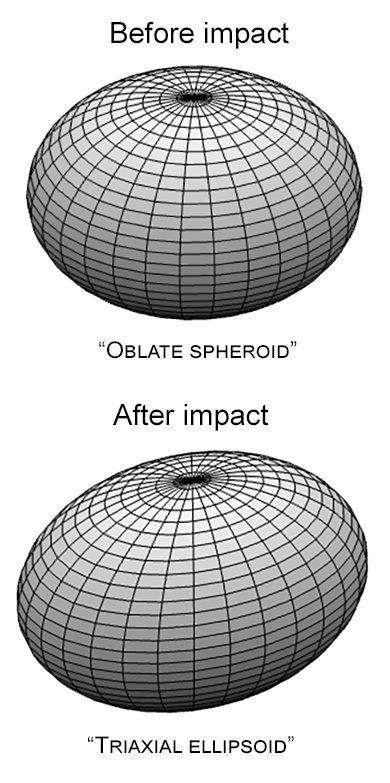
In a now typical display of the modern leftist protest movement, a mob of Democrats threatened to kill attendees at a Turning Point USA event at the University of Memphis on March 20, 2024 where Kyle Rittenhouse was scheduled to appear.
A savage mob terrorized conservative students attending a Turning Point USA event featuring Kyle Rittenhouse at the University of Memphis. The mob literally chased conservative students shouting obscenities and violent threats. Several students who had been attending a campus Bible study were also caught up in the melee. Eyewitnesses say the mob made direct threats against TPUSA leadership. Radical black activists cheered the chaos. There are no reports of arrests. The TPUSA group later found refuge in a nearby safe house
When Rittenhouse attempted to give his speech, he was shouted down and forced to go directly to Q&As. Though it seemed from at least one clip that this Q&A proceeded with some civility (though interspersed with many angry catcalls from the crowd), it ended abruptly after thirty minutes, which according to Rittenhouse was because they had a hard cut off time.
At the first link are numerous videos showing that mob in all its glory, one of which is embedded below. It shows several attendees of the event being escorted into the building by police, as the mob surrounds and chases them, shouting curses and threats.
» Read more

Democrats in Georgia in 1915, lynching Leo Frank
In a now typical display of the modern leftist protest movement, a mob of Democrats threatened to kill attendees at a Turning Point USA event at the University of Memphis on March 20, 2024 where Kyle Rittenhouse was scheduled to appear.
A savage mob terrorized conservative students attending a Turning Point USA event featuring Kyle Rittenhouse at the University of Memphis. The mob literally chased conservative students shouting obscenities and violent threats. Several students who had been attending a campus Bible study were also caught up in the melee. Eyewitnesses say the mob made direct threats against TPUSA leadership. Radical black activists cheered the chaos. There are no reports of arrests. The TPUSA group later found refuge in a nearby safe house
When Rittenhouse attempted to give his speech, he was shouted down and forced to go directly to Q&As. Though it seemed from at least one clip that this Q&A proceeded with some civility (though interspersed with many angry catcalls from the crowd), it ended abruptly after thirty minutes, which according to Rittenhouse was because they had a hard cut off time.
At the first link are numerous videos showing that mob in all its glory, one of which is embedded below. It shows several attendees of the event being escorted into the building by police, as the mob surrounds and chases them, shouting curses and threats.
» Read more