Author: Robert Zimmerman
Virgin Orbit shuts down
Unable to secure new funding, the managers of Virgin Orbit have shuttered the company, possibly forever.
Virgin Orbit is ceasing operations “for the foreseeable future” after failing to secure a funding lifeline, CEO Dan Hart told employees during an all-hands meeting Thursday afternoon. The company will lay off nearly all of its workforce. “Unfortunately, we’ve not been able to secure the funding to provide a clear path for this company,” Hart said, according to audio of the 5 p.m. ET meeting obtained by CNBC.
The layoffs include all but 100 positions, about 85% of its workforce.
The company was killed because the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) took an extra six months approving a launch license, during which the company could launch nothing and thus make no money. Lacking revenue, it ran out of cash. If the company goes into bankruptcy, this detail is most intriguing:
Branson has first priority over Virgin Orbit’s assets, as the company raised $60 million in debt from the investment arm of Virgin Group.
In other words, Branson will be able to walk off with everything, and even resurrect the company as his own, for pennies on the dollar. If he does, I guarantee our bankrupt mainstream press will shower him with praise, calling him a hero.
Unable to secure new funding, the managers of Virgin Orbit have shuttered the company, possibly forever.
Virgin Orbit is ceasing operations “for the foreseeable future” after failing to secure a funding lifeline, CEO Dan Hart told employees during an all-hands meeting Thursday afternoon. The company will lay off nearly all of its workforce. “Unfortunately, we’ve not been able to secure the funding to provide a clear path for this company,” Hart said, according to audio of the 5 p.m. ET meeting obtained by CNBC.
The layoffs include all but 100 positions, about 85% of its workforce.
The company was killed because the UK’s Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) took an extra six months approving a launch license, during which the company could launch nothing and thus make no money. Lacking revenue, it ran out of cash. If the company goes into bankruptcy, this detail is most intriguing:
Branson has first priority over Virgin Orbit’s assets, as the company raised $60 million in debt from the investment arm of Virgin Group.
In other words, Branson will be able to walk off with everything, and even resurrect the company as his own, for pennies on the dollar. If he does, I guarantee our bankrupt mainstream press will shower him with praise, calling him a hero.
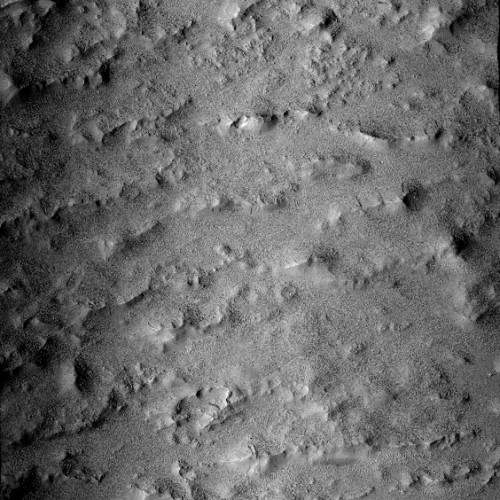
A bubbly cauldron on the surface of Mars
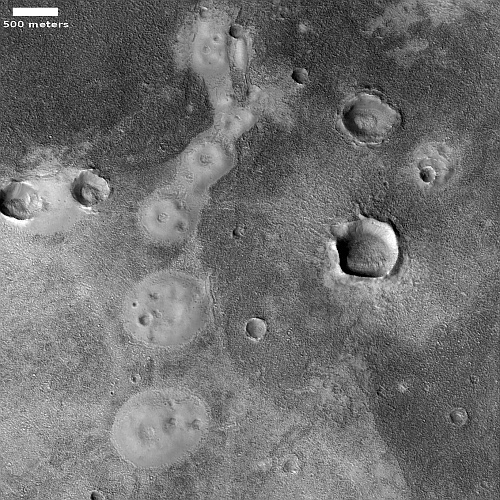
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on December 20, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a strange terrain of craters and mounds, with all the mounds having pits within them like volcanic calderas. In between the surface has a two-toned stippled look, as if two different materials are in the process of mixing.
My immediate impression was that of the bubbly surface of a vat of tomato sauce simmering. Or maybe the vile mixture created by the witches in Shakespeare’s Macbeth, which as they mix they chant:
First witch:
Round about the cauldron go;
In the poison’d entrails throw.
Toad, that under cold stone
Days and nights has thirty-one
Swelter’d venom sleeping got,
Boil thou first i’ the charmed pot.
ALL:
Double, double toil and trouble;
Fire burn, and cauldron bubble.
Of course, this is not a vat of witch’s brew or tomato sauce. It is the surface of the planet Mars, but an alien surface nonetheless.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on December 20, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a strange terrain of craters and mounds, with all the mounds having pits within them like volcanic calderas. In between the surface has a two-toned stippled look, as if two different materials are in the process of mixing.
My immediate impression was that of the bubbly surface of a vat of tomato sauce simmering. Or maybe the vile mixture created by the witches in Shakespeare’s Macbeth, which as they mix they chant:
First witch:
Round about the cauldron go;
In the poison’d entrails throw.
Toad, that under cold stone
Days and nights has thirty-one
Swelter’d venom sleeping got,
Boil thou first i’ the charmed pot.ALL:
Double, double toil and trouble;
Fire burn, and cauldron bubble.
Of course, this is not a vat of witch’s brew or tomato sauce. It is the surface of the planet Mars, but an alien surface nonetheless.
» Read more
Frank Rubio’s flight to ISS will exceed a year, setting a new American record

Frank Rubio
Initially, Frank Rubio’s first flight in space was intended to be a standard six month mission on ISS. Launched on September 21, 2022 on a Soyuz-2 rocket inside a Soyuz capsule, the plan was for him and his two crewmates to return in March, 2023.
Then their Soyuz capsule developed a leak in its coolant system in December 2022. Not knowing if it was safe to use this capsule with humans inside, a replacement unmanned Soyuz capsule was launched by the Russians to ISS in February 2023, with the leaking Soyuz capsule brought back unmanned earlier this week.
The Russians however decided that this new capsule, designed for a six month mission, would stay in orbit for six months, so that it would be used to its planned capability. This decision also hinged on the lack of a new crew arriving on this new capsule. If it brought Rubio and his crew home earlier, ISS would be short three crew members for at least several months.
The planned return date, September 27, 2023, now means that Rubio’s mission will be at least 371 days long, making him the first American to fly a full year in space. Previously NASA falsely touted Scott Kelly’s 340-day mission as a year-long mission, when it never was. Later, Mark Vande Hei’s mission, also launched on a Soyuz, was extended to 355 days, still just short of a year, because the Russians wanted to send a film crew to ISS and return them on the capsule which Vande Hei was intended to come home on.
Whether Rubio truly does spend a year in space however remains uncertain. Two different Russian spacecraft — the Soyuz and a Progress freighter — have developed this coolant leak in the past three months. If this problem is a systemic manufacturing error, which Russia is now investigating, the decision might be to return the new capsule sooner than planned, out of fear it will develop its own leak. We shall likely find out sometime in the next three months.
If Rubio does end up in space for a full year, however, it will likely be a dream come true, having become an astronaut in 2017 but waiting six years for his first flight.

Frank Rubio
Initially, Frank Rubio’s first flight in space was intended to be a standard six month mission on ISS. Launched on September 21, 2022 on a Soyuz-2 rocket inside a Soyuz capsule, the plan was for him and his two crewmates to return in March, 2023.
Then their Soyuz capsule developed a leak in its coolant system in December 2022. Not knowing if it was safe to use this capsule with humans inside, a replacement unmanned Soyuz capsule was launched by the Russians to ISS in February 2023, with the leaking Soyuz capsule brought back unmanned earlier this week.
The Russians however decided that this new capsule, designed for a six month mission, would stay in orbit for six months, so that it would be used to its planned capability. This decision also hinged on the lack of a new crew arriving on this new capsule. If it brought Rubio and his crew home earlier, ISS would be short three crew members for at least several months.
The planned return date, September 27, 2023, now means that Rubio’s mission will be at least 371 days long, making him the first American to fly a full year in space. Previously NASA falsely touted Scott Kelly’s 340-day mission as a year-long mission, when it never was. Later, Mark Vande Hei’s mission, also launched on a Soyuz, was extended to 355 days, still just short of a year, because the Russians wanted to send a film crew to ISS and return them on the capsule which Vande Hei was intended to come home on.
Whether Rubio truly does spend a year in space however remains uncertain. Two different Russian spacecraft — the Soyuz and a Progress freighter — have developed this coolant leak in the past three months. If this problem is a systemic manufacturing error, which Russia is now investigating, the decision might be to return the new capsule sooner than planned, out of fear it will develop its own leak. We shall likely find out sometime in the next three months.
If Rubio does end up in space for a full year, however, it will likely be a dream come true, having become an astronaut in 2017 but waiting six years for his first flight.
New startup unveils 3D printer for making rocket tanks and fairings
Rosotics, a new startup focusing on providing manufacturing components for rocket companies, has now unveiled a prototype of its proposed 3D printer, dubbed Mantis, for making rocket tanks and fairings.
Mesa, Arizona-based Rosotics plans to begin delivering the Mantis in the third quarter of 2023 to customers who place $95,000 deposits and sign hardware-as-a-service contracts. After delivery, Rosotics “will install, maintain and upgrade your hardware over time without any cost to you,” LaRosa said.
While the Mantis can be configured for various tasks, the starting point is a one printhead to additively manufacture aluminum or steel structures ranging in size from 1.5 to 8 meters in diameter.
The idea is sell this manufacturing capability to rocket companies as well as other manufacturers who need large structures built. Rather than machining these large structures themselves, or have outside machining companies do it for them, the companies would buy Mantis to do it in-house instead.
Whether this model will work depends on price and operations. Is it cheaper and quicker to use this 3D printer to make large rocket parts, or traditional methods? Obviously, Rosotics thinks it is. We will find out if others think so if Rosotics survives.
Rosotics, a new startup focusing on providing manufacturing components for rocket companies, has now unveiled a prototype of its proposed 3D printer, dubbed Mantis, for making rocket tanks and fairings.
Mesa, Arizona-based Rosotics plans to begin delivering the Mantis in the third quarter of 2023 to customers who place $95,000 deposits and sign hardware-as-a-service contracts. After delivery, Rosotics “will install, maintain and upgrade your hardware over time without any cost to you,” LaRosa said.
While the Mantis can be configured for various tasks, the starting point is a one printhead to additively manufacture aluminum or steel structures ranging in size from 1.5 to 8 meters in diameter.
The idea is sell this manufacturing capability to rocket companies as well as other manufacturers who need large structures built. Rather than machining these large structures themselves, or have outside machining companies do it for them, the companies would buy Mantis to do it in-house instead.
Whether this model will work depends on price and operations. Is it cheaper and quicker to use this 3D printer to make large rocket parts, or traditional methods? Obviously, Rosotics thinks it is. We will find out if others think so if Rosotics survives.
H3 failure delays Japan’s entire space program
According to one official of Japan’s space agency JAXA, the failure of the first launch of its new H3 rocket in early March now threatens the schedule of much of Japan’s entire space program, even those missions being launched on the older H2A rocket.
The investigation into the launch failure, when the upper stage of the H3 rocket failed to ignite, remains unfinished with no word when it will be completed.
The H3 upper stage uses an engine designated LE-5B-3 developed by MHI [Mitsubishi Heavy Industries] and similar to the LE-5B engine used on the existing H-2A rocket. That is putting launches of the H-2A on hold while the investigation continues.
That may delay the upcoming launch of two science missions sharing an H-2A. The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM), an X-ray astronomy spacecraft, and the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM), a lunar lander, were scheduled to launch together as soon as May on an H-2A.
The article notes that XRISM replaces a 2016 Japanese X-ray telescope that failed immediately after launch. That failure then was bad, but just as bad is the seven years it has taken JAXA to have a replacement ready.
The H3 failure also threatens a JAXA Mars mission scheduled for launch in 2024, during the next launch window to Mars.
Japan’s space program more and more resembles Russia’s. It is controlled entirely by the government, which it appears does not allow competition within Japan, as all major rocket work is apparently confined to Mitsubishi. There have been unending quality control problems, within many probes as well as in the development of both the H3 and the Epsilon rockets. And the pace of operations is slow, much slower than other nations or companies.
It seems a major reform is needed, and it should start with Japanese government officials reading Capitalism in Space. They need to open up competition and release their space program from the control of JAXA, especially because JAXA is not doing a very good job. Like NASA, it would be better if JAXA stopped being a designer and builder, and become merely a customer obtaining products from many different competing private companies.
According to one official of Japan’s space agency JAXA, the failure of the first launch of its new H3 rocket in early March now threatens the schedule of much of Japan’s entire space program, even those missions being launched on the older H2A rocket.
The investigation into the launch failure, when the upper stage of the H3 rocket failed to ignite, remains unfinished with no word when it will be completed.
The H3 upper stage uses an engine designated LE-5B-3 developed by MHI [Mitsubishi Heavy Industries] and similar to the LE-5B engine used on the existing H-2A rocket. That is putting launches of the H-2A on hold while the investigation continues.
That may delay the upcoming launch of two science missions sharing an H-2A. The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM), an X-ray astronomy spacecraft, and the Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM), a lunar lander, were scheduled to launch together as soon as May on an H-2A.
The article notes that XRISM replaces a 2016 Japanese X-ray telescope that failed immediately after launch. That failure then was bad, but just as bad is the seven years it has taken JAXA to have a replacement ready.
The H3 failure also threatens a JAXA Mars mission scheduled for launch in 2024, during the next launch window to Mars.
Japan’s space program more and more resembles Russia’s. It is controlled entirely by the government, which it appears does not allow competition within Japan, as all major rocket work is apparently confined to Mitsubishi. There have been unending quality control problems, within many probes as well as in the development of both the H3 and the Epsilon rockets. And the pace of operations is slow, much slower than other nations or companies.
It seems a major reform is needed, and it should start with Japanese government officials reading Capitalism in Space. They need to open up competition and release their space program from the control of JAXA, especially because JAXA is not doing a very good job. Like NASA, it would be better if JAXA stopped being a designer and builder, and become merely a customer obtaining products from many different competing private companies.
Russia’s Soyuz-2 rocket launches classified military satellite
Russia today successfully launched a classified military satellite, using its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from Plesetsk spaceport in northern Russia.
The rocket traveled north over the Arctic Ocean, so its first stage fell harmlessly into the ocean.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
21 SpaceX
11 China
6 Russia
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise still leads China 24 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 24 to 21. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 21 to 24.
Russia today successfully launched a classified military satellite, using its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from Plesetsk spaceport in northern Russia.
The rocket traveled north over the Arctic Ocean, so its first stage fell harmlessly into the ocean.
The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
21 SpaceX
11 China
6 Russia
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise still leads China 24 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 24 to 21. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 21 to 24.
March 29, 2023 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Joan Blondell & Etta Moten – Remember My Forgotten Man
An evening pause: From the movie Gold Diggers of 1933. At least then there was an effort to remember the forgotten man. Today, it is considered racist to mention it.
Hat tip Wayne DeVette.
In U.S. sales of dumb phones are up
It appears that American users of mobile phones are shifting every so slightly away from smart phones, with sales of simple flip-phones lacking a screen rising in the past year.
In the U.S., feature flip phone sales were up in 2022 for HMD Global, with tens of thousands sold each month. At the same time, HMD’s global feature phone sales were down, according to the company.
In 2022, almost 80% of feature phone sales in 2022 came from the Middle East, Africa and India, according to Counterpoint Research. But some see that number shifting, as a contingency of young people in the U.S. revert back to dumb or minimalist phones. “In North America, the market for dumb phones is pretty much flatlined,” said Moorhead. “But I could see it getting up to 5% increase in the next five years if nothing else, based on the public health concerns that are out there.”
Companies like Punkt and Light are catering to the trend, selling devices geared toward those with a desire to spend less time on their phones and social media. On YouTube, you will find a slew of influencers touting these phones.
It is not clear if this is a real trend, or merely a bit of press release salesmanship by HMD and others. If it is however I think it is a good trend. Smart phones do very little to make people smarter. Instead, they foster a shallow thinking process focused on emotion. The more people who get away from them the better.
It appears that American users of mobile phones are shifting every so slightly away from smart phones, with sales of simple flip-phones lacking a screen rising in the past year.
In the U.S., feature flip phone sales were up in 2022 for HMD Global, with tens of thousands sold each month. At the same time, HMD’s global feature phone sales were down, according to the company.
In 2022, almost 80% of feature phone sales in 2022 came from the Middle East, Africa and India, according to Counterpoint Research. But some see that number shifting, as a contingency of young people in the U.S. revert back to dumb or minimalist phones. “In North America, the market for dumb phones is pretty much flatlined,” said Moorhead. “But I could see it getting up to 5% increase in the next five years if nothing else, based on the public health concerns that are out there.”
Companies like Punkt and Light are catering to the trend, selling devices geared toward those with a desire to spend less time on their phones and social media. On YouTube, you will find a slew of influencers touting these phones.
It is not clear if this is a real trend, or merely a bit of press release salesmanship by HMD and others. If it is however I think it is a good trend. Smart phones do very little to make people smarter. Instead, they foster a shallow thinking process focused on emotion. The more people who get away from them the better.
Psyche asteroid mission now scheduled for October 2023 launch
After a year delay because certain flight software was not ready on time for its first launch window in the fall of 2022, the science team for the Psyche asteroid mission are now aiming for an October 2023 launch.
The launch period will open Oct. 5 and close Oct. 25. The asteroid, which lies in the outer portion of the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, may be the remains of a core of a planetesimal, a building block of a rocky planet.
Due to the new launch date, Psyche has a new mission plan, which includes a flyby of Mars for a gravity assist and arrival at the asteroid in August 2029. The mission then will enter its 26-month science phase, collecting observations and data as the spacecraft orbits the asteroid at different altitudes.
Meanwhile, the two Janus probes that were to launch with Psyche last year remain in limbo, as this new Psyche launch date is useless to that mission’s plan to fly past a different asteroid.
After a year delay because certain flight software was not ready on time for its first launch window in the fall of 2022, the science team for the Psyche asteroid mission are now aiming for an October 2023 launch.
The launch period will open Oct. 5 and close Oct. 25. The asteroid, which lies in the outer portion of the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, may be the remains of a core of a planetesimal, a building block of a rocky planet.
Due to the new launch date, Psyche has a new mission plan, which includes a flyby of Mars for a gravity assist and arrival at the asteroid in August 2029. The mission then will enter its 26-month science phase, collecting observations and data as the spacecraft orbits the asteroid at different altitudes.
Meanwhile, the two Janus probes that were to launch with Psyche last year remain in limbo, as this new Psyche launch date is useless to that mission’s plan to fly past a different asteroid.
Boeing & NASA; 1st Starliner manned mission to now launch on July 21
In a update posted by NASA today, agency and Boeing officials announced that they are now aiming to launch Boeing’s Starliner capsule on July 21, 2023 on its first manned mission to ISS.
The new target date provides NASA and Boeing the necessary time to complete subsystem verification testing and close out test flight certification products and aligns with the space station manifest and range launch opportunities.
The specifics behind this somewhat meaningless press release jargon can be found at this twitter thread. Apparently Boeing & NASA want to do more ground tests of the capsule’s parachute system as well as its flight software. There also appears to be some issue relating to the capsule’s batteries.
Boeing is also mulling a redesign of Starliner’s batteries for after this delayed crewed flight test. It also expects to redesign Starliner’s smart initiator system, which separates the crew from service module. NASA’s paying $24 million for that redesign amid added requirements
Though Boeing has a fixed price contract with NASA, if NASA demands redesigns or changes it has to pay for them. That Boeing and NASA are finding these issues at this late date, four years after Starliner was first supposed to launch, does not speak well of Boeing’s workmanship and quality control systems.
In a update posted by NASA today, agency and Boeing officials announced that they are now aiming to launch Boeing’s Starliner capsule on July 21, 2023 on its first manned mission to ISS.
The new target date provides NASA and Boeing the necessary time to complete subsystem verification testing and close out test flight certification products and aligns with the space station manifest and range launch opportunities.
The specifics behind this somewhat meaningless press release jargon can be found at this twitter thread. Apparently Boeing & NASA want to do more ground tests of the capsule’s parachute system as well as its flight software. There also appears to be some issue relating to the capsule’s batteries.
Boeing is also mulling a redesign of Starliner’s batteries for after this delayed crewed flight test. It also expects to redesign Starliner’s smart initiator system, which separates the crew from service module. NASA’s paying $24 million for that redesign amid added requirements
Though Boeing has a fixed price contract with NASA, if NASA demands redesigns or changes it has to pay for them. That Boeing and NASA are finding these issues at this late date, four years after Starliner was first supposed to launch, does not speak well of Boeing’s workmanship and quality control systems.
The chaos between galaxies following their head-on collision
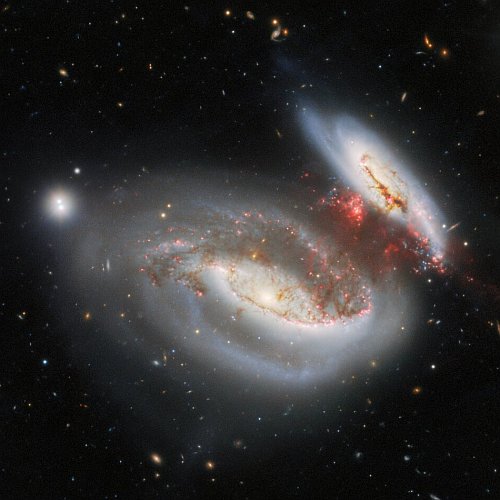
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken using the Gemini North ground-based 8-meter telescope in Hawaii. It shows two spiral galaxies about 180 million light years away following a head-on collision about 25 million years ago, in which the smaller spiral moved through the larger from the bottom to the top.
Upon exiting, the smaller spiral trailed behind it the reddish stream of material, while its outside arms on the right were bent downward. That trailing material is why astronomers have dubbed these the “Taffy Galaxies.” Imagine pulling two clumps of taffy apart. The stretched material linking the two clumps is the bridge of trailing material between these two galaxies. From the caption:
When the Taffy Galaxies’ collided, their galactic disks and gaseous components smashed right into each other. This resulted in a massive injection of energy into the gas, causing it to become highly turbulent. As the pair emerged from their collision, high-velocity gas was pulled from each galaxy, creating a massive gas bridge between them. The turbulence of the stellar material throughout the bridge is now prohibiting the collection and compression of gas that are required to form new stars.
The evolution of galaxies is incredibly slow, from the perspective of human existence. For example, this first collision 25 million years ago seems like it took a long time, but it will likely be followed by many more over the next billion years, eventually resulting in a single spherical elliptical galaxy. On the time scale of the universe, collisions every 100 million years or so means galaxies like this can mix and collide many times, and do so well within the existence of the theorized lifespan of the universe itself.
To us short-lived humans, however, this process just seems so slow it can’t possibly happen as described. But it does.
Sidebar: It appears this image was released to herald the repair of Gemini North’s primary mirror, which was damaged in two places on its edge during a recoating operation on October 20, 2022. Since then the telescope has been shut down as repair operations were undertaken. That repair is now complete, and it is expected the telescope will resume science observations in a few weeks.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken using the Gemini North ground-based 8-meter telescope in Hawaii. It shows two spiral galaxies about 180 million light years away following a head-on collision about 25 million years ago, in which the smaller spiral moved through the larger from the bottom to the top.
Upon exiting, the smaller spiral trailed behind it the reddish stream of material, while its outside arms on the right were bent downward. That trailing material is why astronomers have dubbed these the “Taffy Galaxies.” Imagine pulling two clumps of taffy apart. The stretched material linking the two clumps is the bridge of trailing material between these two galaxies. From the caption:
When the Taffy Galaxies’ collided, their galactic disks and gaseous components smashed right into each other. This resulted in a massive injection of energy into the gas, causing it to become highly turbulent. As the pair emerged from their collision, high-velocity gas was pulled from each galaxy, creating a massive gas bridge between them. The turbulence of the stellar material throughout the bridge is now prohibiting the collection and compression of gas that are required to form new stars.
The evolution of galaxies is incredibly slow, from the perspective of human existence. For example, this first collision 25 million years ago seems like it took a long time, but it will likely be followed by many more over the next billion years, eventually resulting in a single spherical elliptical galaxy. On the time scale of the universe, collisions every 100 million years or so means galaxies like this can mix and collide many times, and do so well within the existence of the theorized lifespan of the universe itself.
To us short-lived humans, however, this process just seems so slow it can’t possibly happen as described. But it does.
Sidebar: It appears this image was released to herald the repair of Gemini North’s primary mirror, which was damaged in two places on its edge during a recoating operation on October 20, 2022. Since then the telescope has been shut down as repair operations were undertaken. That repair is now complete, and it is expected the telescope will resume science observations in a few weeks.
SpaceX launches another 56 Starlink satellites
SpaceX today successfully launched another 56 Starlink satellites, using its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The first stage successfully completed its fourth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Russia was also launching at almost the exact same time a classified military satellite, using its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from Plesetsk spaceport in northern Russia, but at the moment there is no word on whether that launch was a success.
For the moment then the leaders in the 2023 launch race are as follows:
21 SpaceX
11 China
5 Russia (with a planned launch today)
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads China 24 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 24 to 20. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 21 to 23.
SpaceX today successfully launched another 56 Starlink satellites, using its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The first stage successfully completed its fourth flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Russia was also launching at almost the exact same time a classified military satellite, using its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from Plesetsk spaceport in northern Russia, but at the moment there is no word on whether that launch was a success.
For the moment then the leaders in the 2023 launch race are as follows:
21 SpaceX
11 China
5 Russia (with a planned launch today)
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise now leads China 24 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 24 to 20. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 21 to 23.
Zhurong: Small polygons on light curved dunes indicate regular atmospheric water interaction
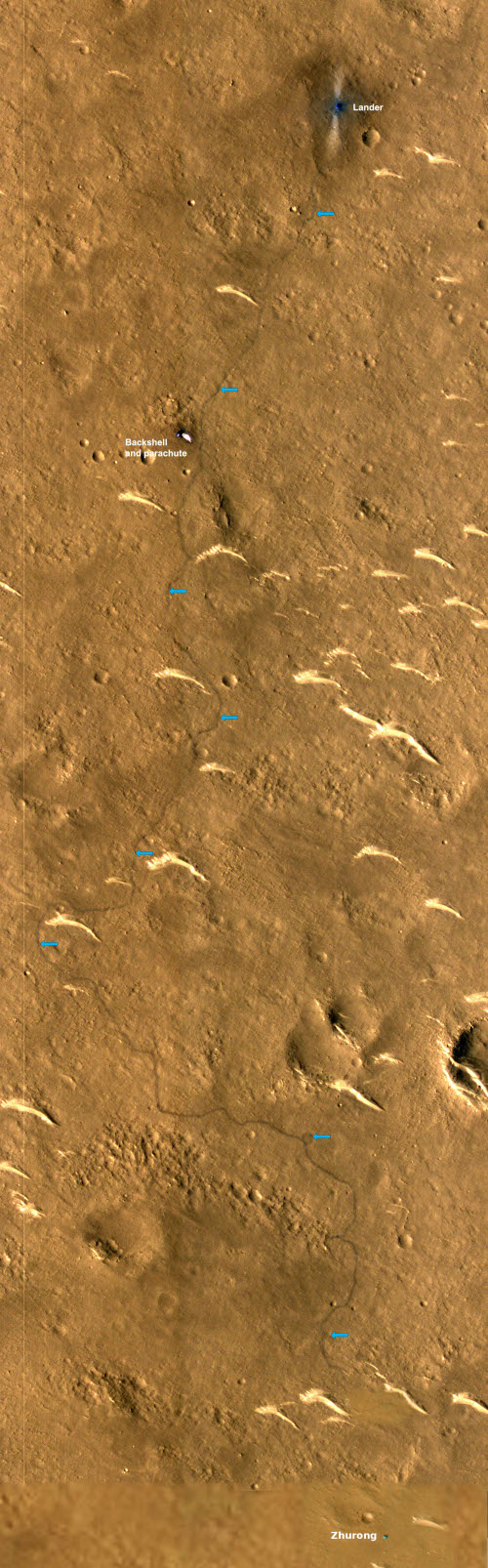
A paper published this week in Geophysical Research Letters by the science team for China Zhurong Martian rover has revealed the discovery of small polygon cracks on the surface of the many curved light-colored small dunes found in the region where Zhurong landed, suggesting the possibility of relatively recent water activity between the atmosphere and the dune surfaces.
Those dunes, dubbed transverse aeolian ridges (TARs) by the science team, are the many light curves visible in the labeled Mars Reconnaissance mosaic to the right. The blue arrows indicate Zhurong’s path south from its landing spot at the top and ending near the bottom of the picture after traveling about 1,400 feet.
According to the paper, the TARs were formed by the prevailing winds over many eons, coming first from the north and then from the northwest. The edges of the ridges, being smaller, are pushed ahead quicker, thus creating the curved shape. The polygons were small, never larger than 4 inches in size, with five to six sides. The scientists theorize that they were formed when atmospheric water interacted with the dune crust, causing fractures “due to temperature/moisture changes or deliquescence/dehydration cycling of salts”. This process could be slow or fast, and could actually be occurring in relatively recent times, as the scientists say it requires only a little water in the atmosphere.
More likely however we are seeing evidence of water from the past, from tens of thousands to several million years ago.
Zhurong meanwhile remains in hibernation, and might never come out of that condition. Orbital images indicate that its solar panels are dust-covered, the result of the heavy winter dust storm season. The project team however is hopeful that with time and the arrival of Martian summer the dust will be blown off and they can reactivate the rover. This hope however entirely depends on the arrival of a dust devil acoss the top of Zhurong, a random event that cannot be predicted. With both the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, such events happened regularly, allowing those missions to last years instead of only 90 days. With InSight it never happened, and the lander died after two-plus years on Mars.
Zhurong’s future fate thus remains unknown, but not promising at this moment.

A paper published this week in Geophysical Research Letters by the science team for China Zhurong Martian rover has revealed the discovery of small polygon cracks on the surface of the many curved light-colored small dunes found in the region where Zhurong landed, suggesting the possibility of relatively recent water activity between the atmosphere and the dune surfaces.
Those dunes, dubbed transverse aeolian ridges (TARs) by the science team, are the many light curves visible in the labeled Mars Reconnaissance mosaic to the right. The blue arrows indicate Zhurong’s path south from its landing spot at the top and ending near the bottom of the picture after traveling about 1,400 feet.
According to the paper, the TARs were formed by the prevailing winds over many eons, coming first from the north and then from the northwest. The edges of the ridges, being smaller, are pushed ahead quicker, thus creating the curved shape. The polygons were small, never larger than 4 inches in size, with five to six sides. The scientists theorize that they were formed when atmospheric water interacted with the dune crust, causing fractures “due to temperature/moisture changes or deliquescence/dehydration cycling of salts”. This process could be slow or fast, and could actually be occurring in relatively recent times, as the scientists say it requires only a little water in the atmosphere.
More likely however we are seeing evidence of water from the past, from tens of thousands to several million years ago.
Zhurong meanwhile remains in hibernation, and might never come out of that condition. Orbital images indicate that its solar panels are dust-covered, the result of the heavy winter dust storm season. The project team however is hopeful that with time and the arrival of Martian summer the dust will be blown off and they can reactivate the rover. This hope however entirely depends on the arrival of a dust devil acoss the top of Zhurong, a random event that cannot be predicted. With both the Spirit and Opportunity rovers, such events happened regularly, allowing those missions to last years instead of only 90 days. With InSight it never happened, and the lander died after two-plus years on Mars.
Zhurong’s future fate thus remains unknown, but not promising at this moment.
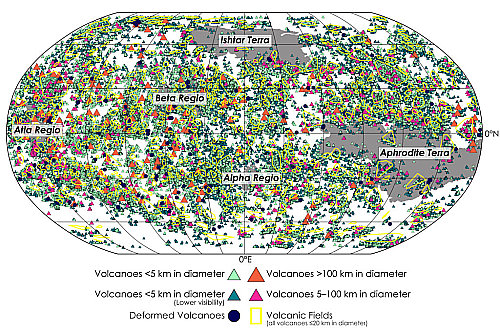
New map of the volcanoes of Venus
Using the archival radar data from the Magellan orbiter that circled Venus in the early 1990s, scientists have produced a new map of the volcanoes of Venus.
That map is to the right, and is publicly available for download.
Byrne and Hahn’s new study includes detailed analyses of where volcanoes are, where and how they’re clustered, and how their spatial distributions compare with geophysical properties of the planet such as crustal thickness. Taken together, this work provides the most comprehensive understanding of Venus’ volcanic properties — and perhaps of any world’s volcanism so far … because, although we know a great deal about the volcanoes on Earth that are on land, there are still likely a great many yet to be discovered under the oceans. Lacking oceans of its own, Venus’ entire surface can be viewed with Magellan radar imagery.
Although there are volcanoes across almost the entire surface of Venus, the scientists found relatively fewer volcanoes in the 20-100 km diameter range, which may be a function of magma availability and eruption rate, they surmise.
This new map catalogs about 85,000 volcanoes, but is also considered incomplete because the resolution of the Magellan data makes identifying volcanoes smaller than 1 kilometer impossible. It will require new orbiters to spot these volcanoes.
Using the archival radar data from the Magellan orbiter that circled Venus in the early 1990s, scientists have produced a new map of the volcanoes of Venus.
That map is to the right, and is publicly available for download.
Byrne and Hahn’s new study includes detailed analyses of where volcanoes are, where and how they’re clustered, and how their spatial distributions compare with geophysical properties of the planet such as crustal thickness. Taken together, this work provides the most comprehensive understanding of Venus’ volcanic properties — and perhaps of any world’s volcanism so far … because, although we know a great deal about the volcanoes on Earth that are on land, there are still likely a great many yet to be discovered under the oceans. Lacking oceans of its own, Venus’ entire surface can be viewed with Magellan radar imagery.
Although there are volcanoes across almost the entire surface of Venus, the scientists found relatively fewer volcanoes in the 20-100 km diameter range, which may be a function of magma availability and eruption rate, they surmise.
This new map catalogs about 85,000 volcanoes, but is also considered incomplete because the resolution of the Magellan data makes identifying volcanoes smaller than 1 kilometer impossible. It will require new orbiters to spot these volcanoes.
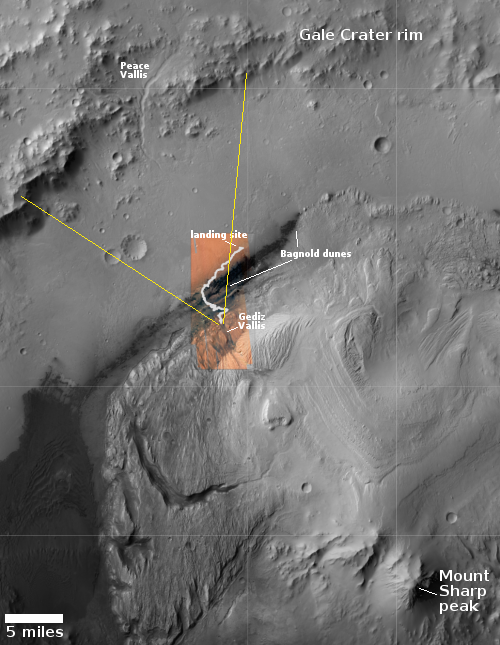
Looking back from the foothills of Mount Sharp
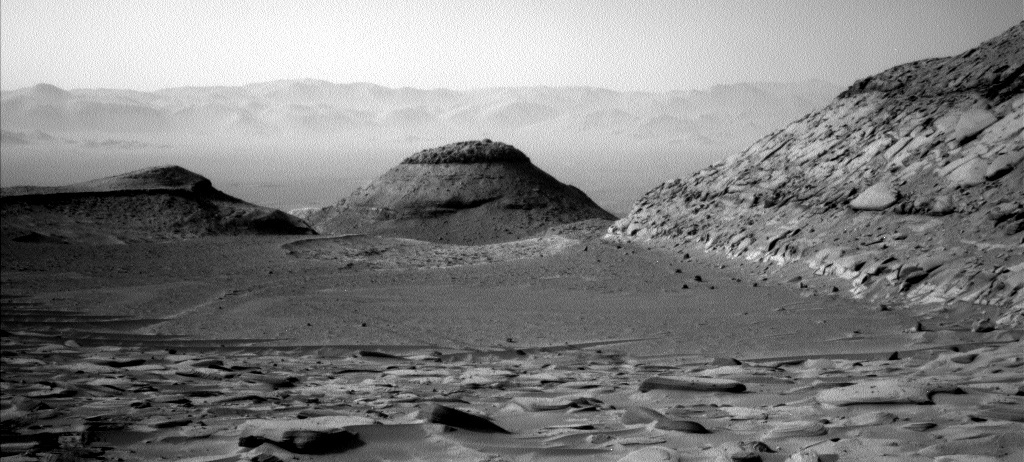
The panorama above, cropped to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks back at the rover’s previous travels, though only the terrain traveled in the past few months is visible, the rover having reached this point through the notch to the left of the distinctly dark mesa in the center of the picture. The lower flanks of Mount Sharp the rover traversed to get here are now blocked from view.
Instead, the image provides a spectacular example of the views north from Curiosity’s present position. The overview map to the right provides us the full context of the entire ten-plus year journey since Curiosity landed safely on Mars on August 5, 2012. The white squiggly line indicates the rover’s route. The yellow lines mark the approximate area covered by the panorama. The rim of Gale Crater is about 20-25 miles away.
As you can see, as spectacular as this view is, the journey up Mount Sharp has barely begun. Mount Sharp’s peak is about 18,000 feet high. The rover at this point has only climbed about 4,600 feet from the floor of Gale Crater.
The panorama above, cropped to post here, was taken today by the left navigation camera on the Mars rover Curiosity. It looks back at the rover’s previous travels, though only the terrain traveled in the past few months is visible, the rover having reached this point through the notch to the left of the distinctly dark mesa in the center of the picture. The lower flanks of Mount Sharp the rover traversed to get here are now blocked from view.
Instead, the image provides a spectacular example of the views north from Curiosity’s present position. The overview map to the right provides us the full context of the entire ten-plus year journey since Curiosity landed safely on Mars on August 5, 2012. The white squiggly line indicates the rover’s route. The yellow lines mark the approximate area covered by the panorama. The rim of Gale Crater is about 20-25 miles away.
As you can see, as spectacular as this view is, the journey up Mount Sharp has barely begun. Mount Sharp’s peak is about 18,000 feet high. The rover at this point has only climbed about 4,600 feet from the floor of Gale Crater.
Hakuto-R1 snaps first picture of Moon from lunar orbit
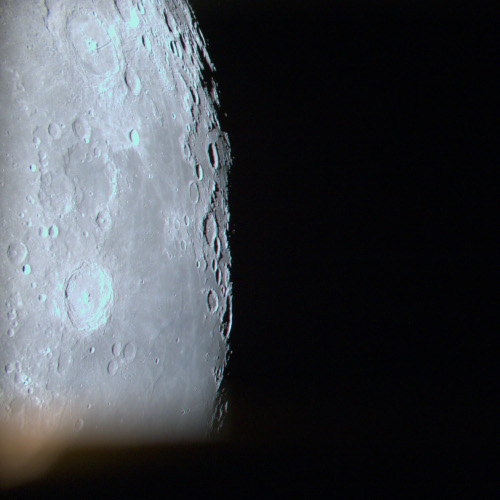
The science team for Ispace’s Hakuto-R1 privately-built lunar orbiter/lander earlier this week released the spacecraft’s first picture of the Moon since entering lunar orbit on March 20, 2023.
That image is to the right, cropped and reduced to post here. The photo resolution is quite good. It also demonstrates that the spacecraft’s attitude control systems for pointing the camera are working correctly.
Launched on December 11, 2022 by a Falcon 9 rocket, Hakuto-R1 will land in Atlas Crater on the northeast quadrant of the Moon’s visible hemisphere sometime in April, making it the first successful private commercial planetary lander to reach another world. If successful, it will then release the United Arab Emirates Rashid rover, that nation’s first planetary lander but its second planetary mission, following the Mars orbiter, Al-Amal, now circling Mars.
The science team for Ispace’s Hakuto-R1 privately-built lunar orbiter/lander earlier this week released the spacecraft’s first picture of the Moon since entering lunar orbit on March 20, 2023.
That image is to the right, cropped and reduced to post here. The photo resolution is quite good. It also demonstrates that the spacecraft’s attitude control systems for pointing the camera are working correctly.
Launched on December 11, 2022 by a Falcon 9 rocket, Hakuto-R1 will land in Atlas Crater on the northeast quadrant of the Moon’s visible hemisphere sometime in April, making it the first successful private commercial planetary lander to reach another world. If successful, it will then release the United Arab Emirates Rashid rover, that nation’s first planetary lander but its second planetary mission, following the Mars orbiter, Al-Amal, now circling Mars.
Israel launches spy satellite
Israel yesterday successfully launched a radar reconnaissance satellite using its Shavit-2 solid-fueled three-stage rocket.
This was Israel’s first launch since 2020. It took place from Israel’s coastal launchpad, and traveled west over the Mediterranean so that its stages would not fall on habitable areas. This retrograde orbit, opposite of the Earth’s rotation, is costly in terms of fuel and the size of payload put in orbit, which is why the satellite weighed only 661 pounds.
The leader board for the 2023 launch race remains the same:
20 SpaceX (with a planned launch later today)
11 China
5 Russia (with a planned launch later today)
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise still leads China 23 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 23 to 20. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 20 to 23.
Israel yesterday successfully launched a radar reconnaissance satellite using its Shavit-2 solid-fueled three-stage rocket.
This was Israel’s first launch since 2020. It took place from Israel’s coastal launchpad, and traveled west over the Mediterranean so that its stages would not fall on habitable areas. This retrograde orbit, opposite of the Earth’s rotation, is costly in terms of fuel and the size of payload put in orbit, which is why the satellite weighed only 661 pounds.
The leader board for the 2023 launch race remains the same:
20 SpaceX (with a planned launch later today)
11 China
5 Russia (with a planned launch later today)
3 Rocket Lab
American private enterprise still leads China 23 to 11 in the national rankings, and the entire world combined 23 to 20. SpaceX now trails the rest of the world, including other American companies, 20 to 23.
Midnight repost: Genocide is coming to America

Will the murder and mutilation of innocent children
finally wake Americans up?
Considering the recent horrible murders of three young school children as well as three adults at Covenant School, a Christian elementary school in Nashville, merely because some sexually confused woman (not a “trans-person” as the insane insist we call her) decided it was her right to murder people, I thought it might be worthwhile to post my essay below from July 2020. In it I predicted that mass murder by the left was only around the corner, if the good people of America did not finally wake up and take seriously the madness that is taking over that part of the political spectrum.
I am still unsure whether ordinary decent Americans have finally awakened, but it appears the recent school violence might finally be providing the spark. We shall see.
————————-
Genocide is coming to America
In my last visit to Israel in 2018, my brother and sister-in-law took me sight-seeing to the northern parts of Israel near the Sea of Galilee. On our first night, we stayed at the home of one of their older friends, a man in his seventies.
That night we sat around their kitchen table so that they could catch up on family matters. At one point in the conversation our host reminisced about an older woman, now gone, who he had known in his childhood in the 1950s who had lived in Germany before and during World War II and had survived a concentration camp.
To paraphrase the story he told us, what this woman always remembered most starkly about that time, especially in the 1930s, was how difficult it was to get German friends who were not Jewish to believe the horrors she and other Jews were going through. To her, their calm nonchalant dismissal of the Nazi bigotry and oppression of Jews — too unbelievable to take seriously — was what had horrified her the most. Even twenty years later, it was this dismissal that appalled her the most, despite her time in a concentration camp and the death she had seen around her.
As he told us this story, what struck me was how similar my own experience has been. Time after time for the past four decades my liberal friends and relatives have refused to believe anything I say to them — always based on actual events — about politics and the growing corruption and bigotry within the Democratic Party. Like those decent Germans in the 1930s, these decent Americans find reasons to quickly dismiss what I say, without making any effort to find out if there is any merit to it.
In fact, less than two days after this very conversation it happened again. » Read more
Zladko “Zlad” Vladcik – Elektronik Supersonik
An evening pause: Actually, this was created by filmmaker Santo Cilauro, who plays Vladcik in the video. I think it showed up on Youtube in the 2000s, but this isn’t confirmed. It is meant to be as silly as Spike Jones.
Hat tip sippin_bourbon.
Mars’ largest mountain region
The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on September 21, 2015 by the context camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). I originally was going to post a high resolution image of some of these mountains, taken on January 1, 2023 that showed some slope streaks, but quickly realized that a wider view of this mountain region was a much more interesting story.
This picture covers an area about 50 by 50 miles. As you can see, it is endless series of random hills ridges and peaks, with only a vague hint of a northeast to southwest alignment. Ground travel through this region would be slow and twisty, immediately reminding me of my many trips to West Virginia, where the hills and valleys are almost as random and never ending.
The overview map below however suggests the scale of this region exceeds West Virginia many times over.
» Read more
The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on September 21, 2015 by the context camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). I originally was going to post a high resolution image of some of these mountains, taken on January 1, 2023 that showed some slope streaks, but quickly realized that a wider view of this mountain region was a much more interesting story.
This picture covers an area about 50 by 50 miles. As you can see, it is endless series of random hills ridges and peaks, with only a vague hint of a northeast to southwest alignment. Ground travel through this region would be slow and twisty, immediately reminding me of my many trips to West Virginia, where the hills and valleys are almost as random and never ending.
The overview map below however suggests the scale of this region exceeds West Virginia many times over.
» Read more
NASA goes woke!
NASA yesterday announced that it has named two individuals, based on their race and gender, to lead the agency’s effort to promote the Marxist and racist Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) movement.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announced Monday he is taking additional steps forward to advance diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility (DEIA) at the agency. Nelson named Steve Shih to serve in a new position as the agency’s first Diversity Ambassador and selected Elaine Ho as the next associate administrator for the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity at NASA Headquarters in Washington, effective immediately.
…As diversity ambassador, Shih will further NASA’s DEIA initiatives by building key strategic alliances with external partners, enabling NASA to continue being a model agency and leader for DEIA. In this role, Shih will engage NASA’s partners – including across the government, private sector, academia, and non-governmental organizations – to learn and promote best practices for NASA to recruit, hire, engage, and retain the most talented individuals from all backgrounds and life experiences. With his experience leading the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity since 2017, Shih will build on his three decades of federal expertise and help NASA continue to enable everyone to contribute inclusively to NASA and to the United States.
As Shih transitions to the role of diversity ambassador, Ho will bring extensive DEIA expertise to the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity. She most recently has served as the deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, leading a wide-ranging portfolio of projects benefiting students, universities, and educational institutions across the country to inspire, engage, and educate the Artemis Generation.
To further prove NASA’s commitment to favor some races over others, the agency also announced yesterday that it is committing $3 million to support “seven Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) and one Predominantly Black Institution (PBI).”
Note the focus on race, not achievement. While it is nice to help the disadvantaged, these programs are not really aimed at that goal. Instead, this entire DEI movement is designed to give power to specific races, to the detriment of others. Or to put it more bluntly, it is a race-based apartheid system that encourages race hatred and resentment.
It is also probably illegal, based on the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Of course, the law is now irrelevant when it comes to the new racism. Supporters of DEI are allowed to break it whenever they want, because clearly they are superior to all others and have that right.
Finally, this stuff has absolutely nothing to do with NASA’s fundamental purpose, which is to help American industry more successfully explore space. It is instead a return to the Obama administration’s policy of making NASA’s most important priority that of helping minorities. Then it was Muslims, now it is the alphabet soup of LBGQTBIPOCZXYZ (and so on).
NASA yesterday announced that it has named two individuals, based on their race and gender, to lead the agency’s effort to promote the Marxist and racist Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) movement.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announced Monday he is taking additional steps forward to advance diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility (DEIA) at the agency. Nelson named Steve Shih to serve in a new position as the agency’s first Diversity Ambassador and selected Elaine Ho as the next associate administrator for the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity at NASA Headquarters in Washington, effective immediately.
…As diversity ambassador, Shih will further NASA’s DEIA initiatives by building key strategic alliances with external partners, enabling NASA to continue being a model agency and leader for DEIA. In this role, Shih will engage NASA’s partners – including across the government, private sector, academia, and non-governmental organizations – to learn and promote best practices for NASA to recruit, hire, engage, and retain the most talented individuals from all backgrounds and life experiences. With his experience leading the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity since 2017, Shih will build on his three decades of federal expertise and help NASA continue to enable everyone to contribute inclusively to NASA and to the United States.
As Shih transitions to the role of diversity ambassador, Ho will bring extensive DEIA expertise to the Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity. She most recently has served as the deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, leading a wide-ranging portfolio of projects benefiting students, universities, and educational institutions across the country to inspire, engage, and educate the Artemis Generation.
To further prove NASA’s commitment to favor some races over others, the agency also announced yesterday that it is committing $3 million to support “seven Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs) and one Predominantly Black Institution (PBI).”
Note the focus on race, not achievement. While it is nice to help the disadvantaged, these programs are not really aimed at that goal. Instead, this entire DEI movement is designed to give power to specific races, to the detriment of others. Or to put it more bluntly, it is a race-based apartheid system that encourages race hatred and resentment.
It is also probably illegal, based on the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Of course, the law is now irrelevant when it comes to the new racism. Supporters of DEI are allowed to break it whenever they want, because clearly they are superior to all others and have that right.
Finally, this stuff has absolutely nothing to do with NASA’s fundamental purpose, which is to help American industry more successfully explore space. It is instead a return to the Obama administration’s policy of making NASA’s most important priority that of helping minorities. Then it was Muslims, now it is the alphabet soup of LBGQTBIPOCZXYZ (and so on).
Webb finds Earth-sized exoplanet likely too hot to have atmosphere
The uncertainty of science: Using the infrared Webb Space Telescope, scientists have measured the temperature of the Earth-sized exoplanet, dubbed Trappist-1b, and found its temperature is probably too hot to have atmosphere.
The red dwarf star Trappist-1is about 40 light years from Earth, and in 2017 was found to have a solar system of seven exoplanets, all rocky terrestrial planets like the inner planets of our solar system. Trappist-1b is the innermost exoplanet. To measure its temperature, Webb observed the star while the planet was eclipsed by the star as well as when it was not, and measured the tiny difference in infrared light.
The team analyzed data from five separate secondary eclipse observations. “We compared the results to computer models showing what the temperature should be in different scenarios,” explained Ducrot. “The results are almost perfectly consistent with a blackbody made of bare rock and no atmosphere to circulate the heat. We also didn’t see any signs of light being absorbed by carbon dioxide, which would be apparent in these measurements.”
As this was the innermost of the star’s solar system, it is also the one most likely to lack an atmosphere. Webb’s observations of the system continue, so there is a chance that data about the other exoplanets will eventually tell us more about them.
The uncertainty of science: Using the infrared Webb Space Telescope, scientists have measured the temperature of the Earth-sized exoplanet, dubbed Trappist-1b, and found its temperature is probably too hot to have atmosphere.
The red dwarf star Trappist-1is about 40 light years from Earth, and in 2017 was found to have a solar system of seven exoplanets, all rocky terrestrial planets like the inner planets of our solar system. Trappist-1b is the innermost exoplanet. To measure its temperature, Webb observed the star while the planet was eclipsed by the star as well as when it was not, and measured the tiny difference in infrared light.
The team analyzed data from five separate secondary eclipse observations. “We compared the results to computer models showing what the temperature should be in different scenarios,” explained Ducrot. “The results are almost perfectly consistent with a blackbody made of bare rock and no atmosphere to circulate the heat. We also didn’t see any signs of light being absorbed by carbon dioxide, which would be apparent in these measurements.”
As this was the innermost of the star’s solar system, it is also the one most likely to lack an atmosphere. Webb’s observations of the system continue, so there is a chance that data about the other exoplanets will eventually tell us more about them.
Virgin Orbit extends pause in operations, having failed to get new financing
Virgin Orbit has extended its worker furlough and pause in operations now that a $200 million deal with a Texas investor has fallen through.
Reuters reported last week that Texas-based Matthew Brown had been in talks to invest $200 million in the company. Those talks have collapsed, said two people familiar with the discussions who asked not to be identified. Brown declined to comment on Monday.
Virgin Orbit, teetering on bankruptcy after a January rocket failure and struggles to raise funds, furloughed nearly all its 750 employees on March 15 while it sought a financial lifeline that would allow it to focus on upgrading its launch business.
This is very bad news for the company, because it indicates that there might not be a financial savior for it.
Virgin Orbit has extended its worker furlough and pause in operations now that a $200 million deal with a Texas investor has fallen through.
Reuters reported last week that Texas-based Matthew Brown had been in talks to invest $200 million in the company. Those talks have collapsed, said two people familiar with the discussions who asked not to be identified. Brown declined to comment on Monday.
Virgin Orbit, teetering on bankruptcy after a January rocket failure and struggles to raise funds, furloughed nearly all its 750 employees on March 15 while it sought a financial lifeline that would allow it to focus on upgrading its launch business.
This is very bad news for the company, because it indicates that there might not be a financial savior for it.
Leaking Soyuz capsule returns unmanned to Earth
The Soyuz capsule with a leaking coolant system successfully landed in Kazakhstan today, returning to Earth unmanned because of that leak.
Russian engineers will now analyze whether a crew would have been able to come home safely in that spacecraft, despite its damaged coolant system, which will provide information for future such problems. They will not be able to study the leak itself, however, as it was part of the capsule’s service module, which separates upon return and burns up in the atmosphere.
The Soyuz capsule with a leaking coolant system successfully landed in Kazakhstan today, returning to Earth unmanned because of that leak.
Russian engineers will now analyze whether a crew would have been able to come home safely in that spacecraft, despite its damaged coolant system, which will provide information for future such problems. They will not be able to study the leak itself, however, as it was part of the capsule’s service module, which separates upon return and burns up in the atmosphere.
German rocket startup raises $168 million in private investment capital
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace has raised $168 million in new private investment capital, bringing the total it has raised to $310 million.
At present the company is targeting the second half of this year for the first launch of its Spectrum rocket, lifting off from a new spaceport in Norway.
Isar is one of three German rocket startups, with the other two Rocket Factory Augsburg and HyImpulse Technologies. Both Isar and Rocket Factory are getting close to launch.
The German rocket startup Isar Aerospace has raised $168 million in new private investment capital, bringing the total it has raised to $310 million.
At present the company is targeting the second half of this year for the first launch of its Spectrum rocket, lifting off from a new spaceport in Norway.
Isar is one of three German rocket startups, with the other two Rocket Factory Augsburg and HyImpulse Technologies. Both Isar and Rocket Factory are getting close to launch.
Scientists detect water inside lunar samples returned to Earth by Chang’e-5
Chinese scientists have found water molecules trapped within glass beads found within the lunar samples returned to Earth by the lunar lander Chang’e-5.
The team polished and analysed 117 glass beads which were scooped up by China’s Chang’e-5 spacecraft in December 2020 and brought back to Earth. The beads are formed by tiny meteorites that bombard the surface of the Moon, which lacks the protection of an atmosphere. The heat of the impact melts the surface material, which cools into round glass beads around the width of a strand of hair.
…The glass beads may make up around three to five percent of lunar soil, according to the study. A “back of the envelope” calculation suggested that there could be around a third of a trillion tonnes of water inside all the Moon’s glass beads, he added. And it only takes mild heat of around 100 degrees Celsius (210 Fahrenheit) to liberate the water from the beads, Anand said.
According to the paper, the water’s origin might be tied to the solar wind, and might have been implanted in the beads after their impact formation.
If this analysis is correct, it might explain the hydrogen signature found in large parts of the lunar surface, where it is believed water simply couldn’t exist. It also might explain why the first images inside permanently shadowed lunar craters show no obvious ice, only what appear to be ponds of dark dust. The dust might contain these beads, and thus explain the hydrogen signature detected there as well.
Chinese scientists have found water molecules trapped within glass beads found within the lunar samples returned to Earth by the lunar lander Chang’e-5.
The team polished and analysed 117 glass beads which were scooped up by China’s Chang’e-5 spacecraft in December 2020 and brought back to Earth. The beads are formed by tiny meteorites that bombard the surface of the Moon, which lacks the protection of an atmosphere. The heat of the impact melts the surface material, which cools into round glass beads around the width of a strand of hair.
…The glass beads may make up around three to five percent of lunar soil, according to the study. A “back of the envelope” calculation suggested that there could be around a third of a trillion tonnes of water inside all the Moon’s glass beads, he added. And it only takes mild heat of around 100 degrees Celsius (210 Fahrenheit) to liberate the water from the beads, Anand said.
According to the paper, the water’s origin might be tied to the solar wind, and might have been implanted in the beads after their impact formation.
If this analysis is correct, it might explain the hydrogen signature found in large parts of the lunar surface, where it is believed water simply couldn’t exist. It also might explain why the first images inside permanently shadowed lunar craters show no obvious ice, only what appear to be ponds of dark dust. The dust might contain these beads, and thus explain the hydrogen signature detected there as well.
Rick Wakeman – Summertime
A Martian crater with a surface pattern that resembles hanging draperies
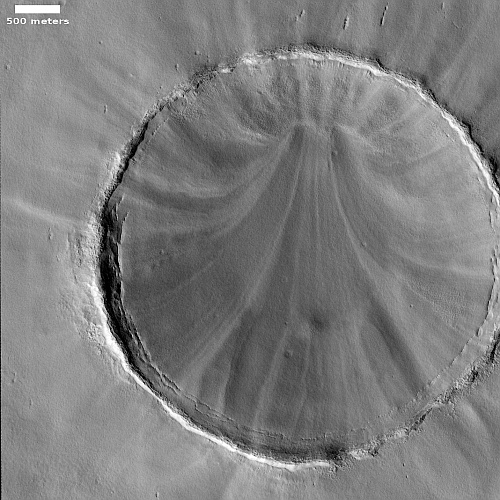

Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on January 27, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows what the scientists label a “streak-spoke pattern” inside the crater. To my eye, the pattern more resembles hanging draperies, neatly tied near the top and then pulled apart as they descend to the ground.
This photo was a follow-up to a previous picture by MRO on February 4, 2008, more than seven Martian years ago, to see if there had been any identifiable changes in that time. Both images were taken in springtime, and despite the passage of time, the 2023 image shows no obvious changes from the 2008 photo.
What caused this distinct pattern? The first guess would be the wind, except if so shouldn’t there have been some change over seven Martian years?
» Read more

Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on January 27, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows what the scientists label a “streak-spoke pattern” inside the crater. To my eye, the pattern more resembles hanging draperies, neatly tied near the top and then pulled apart as they descend to the ground.
This photo was a follow-up to a previous picture by MRO on February 4, 2008, more than seven Martian years ago, to see if there had been any identifiable changes in that time. Both images were taken in springtime, and despite the passage of time, the 2023 image shows no obvious changes from the 2008 photo.
What caused this distinct pattern? The first guess would be the wind, except if so shouldn’t there have been some change over seven Martian years?
» Read more