Potential Artemis-3 landing site on the Moon


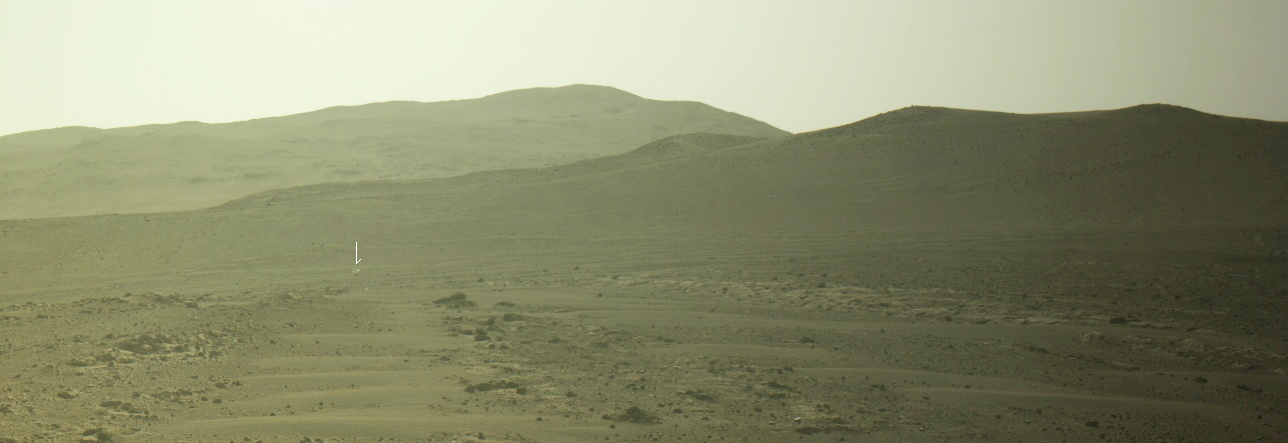
The panorama above was released today by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) science team, and shows one of the candidate landing sites (arrow) where Starship could land as part of the Artemis-3 mission to the Moon.
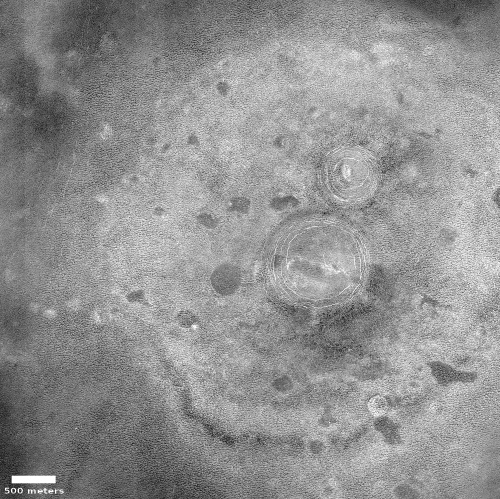
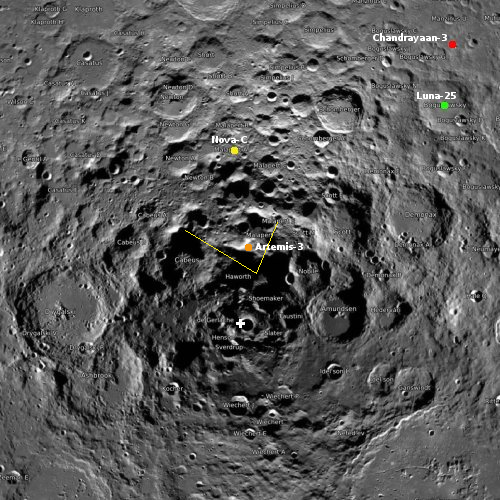
The map of the south pole to the right, created from LRO images and annotated by me, gives the context. The yellow lines indicate the approximate area covered by the panorama. The terrain here is rugged, to put it mildly. As the science team notes,
Imagine the view from the summit; it rises more than 5000 meters (16,400 feet) above its base. Off in the distance, you could see a 3500 meter (11,480 feet) tall cliff. One could argue that the sheer grandeur of this region makes it a prime candidate. But then again, a landing here might be too exciting?
That 11,480-foot-high cliff is the crater wall to the right of the arrow. Make sure you go to the link to view the original image. This will be a spectacular place to visit. Whether the astronauts however will be able to find out anything about ice in the shadowed crater floor thousands of feet below them remains questionable.
Artemis-3 is presently scheduled for 2025 but no one should be surprised if it is delayed.


The panorama above was released today by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) science team, and shows one of the candidate landing sites (arrow) where Starship could land as part of the Artemis-3 mission to the Moon.
The map of the south pole to the right, created from LRO images and annotated by me, gives the context. The yellow lines indicate the approximate area covered by the panorama. The terrain here is rugged, to put it mildly. As the science team notes,
Imagine the view from the summit; it rises more than 5000 meters (16,400 feet) above its base. Off in the distance, you could see a 3500 meter (11,480 feet) tall cliff. One could argue that the sheer grandeur of this region makes it a prime candidate. But then again, a landing here might be too exciting?
That 11,480-foot-high cliff is the crater wall to the right of the arrow. Make sure you go to the link to view the original image. This will be a spectacular place to visit. Whether the astronauts however will be able to find out anything about ice in the shadowed crater floor thousands of feet below them remains questionable.
Artemis-3 is presently scheduled for 2025 but no one should be surprised if it is delayed.