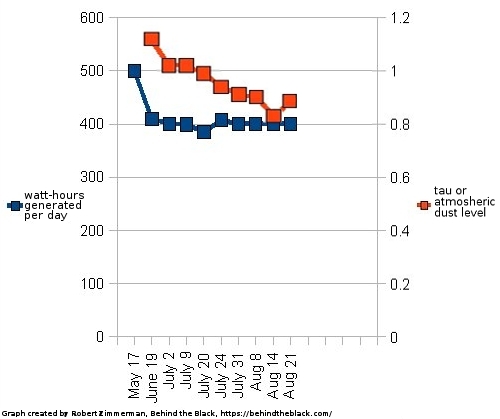
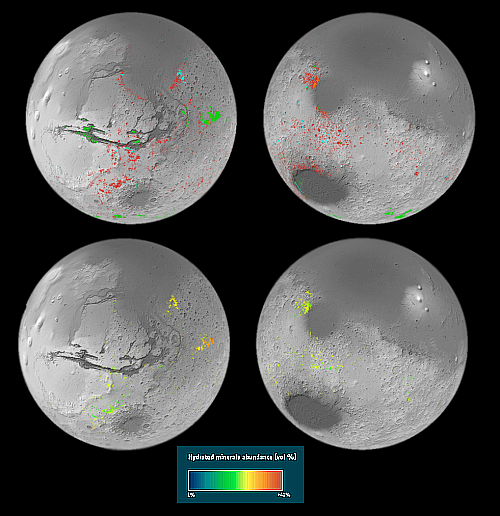
Webb detects carbon dioxide in atmosphere of exoplanet
Scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope have detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a hot gas giant exoplanet about 700 light years away.
WASP-39 b is a hot gas-giant with a mass roughly one-quarter that of Jupiter (about the same as Saturn) and a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter. Its extreme puffiness is partly related to its high temperature (about 900° Celsius or 1170 Kelvin). Unlike the cooler, more compact gas giants in our solar system, WASP-39 b orbits very close to its star – only about one-eighth the distance between the Sun and Mercury – completing one circuit in just over four Earth-days. The planet’s discovery, reported in 2011, was made based on ground-based detections of the subtle, periodic dimming of light from its host star as the planet transits or passes in front of the star.
Previous observations from other telescopes, including the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, revealed the presence of water vapour, sodium, and potassium in the planet’s atmosphere. Webb’s unmatched infrared sensitivity has now confirmed the presence of carbon dioxide on this planet as well.
This is only the beginning. Astronomers have told me repeatedly that the most important area of research in astronomy in the next few decades will be the study of known exoplanets and their make-up. Webb is now a new tool in that effort. Combined with other telescopes looking at other wavelengths scientists will be able to identify a whole range of molecules in the atmospheres of these transiting exoplanets. We will begin to get our first glimpse into what other solar systems are like.
Scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope have detected carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of a hot gas giant exoplanet about 700 light years away.
WASP-39 b is a hot gas-giant with a mass roughly one-quarter that of Jupiter (about the same as Saturn) and a diameter 1.3 times greater than Jupiter. Its extreme puffiness is partly related to its high temperature (about 900° Celsius or 1170 Kelvin). Unlike the cooler, more compact gas giants in our solar system, WASP-39 b orbits very close to its star – only about one-eighth the distance between the Sun and Mercury – completing one circuit in just over four Earth-days. The planet’s discovery, reported in 2011, was made based on ground-based detections of the subtle, periodic dimming of light from its host star as the planet transits or passes in front of the star.
Previous observations from other telescopes, including the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, revealed the presence of water vapour, sodium, and potassium in the planet’s atmosphere. Webb’s unmatched infrared sensitivity has now confirmed the presence of carbon dioxide on this planet as well.
This is only the beginning. Astronomers have told me repeatedly that the most important area of research in astronomy in the next few decades will be the study of known exoplanets and their make-up. Webb is now a new tool in that effort. Combined with other telescopes looking at other wavelengths scientists will be able to identify a whole range of molecules in the atmospheres of these transiting exoplanets. We will begin to get our first glimpse into what other solar systems are like.