Pointy rocks on Mars
We have two cool images today from both of America’s rovers on Mars, each of which illustrates the alien nature of the red planet.
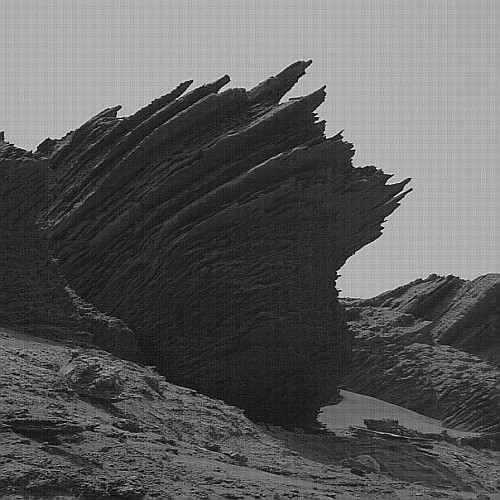
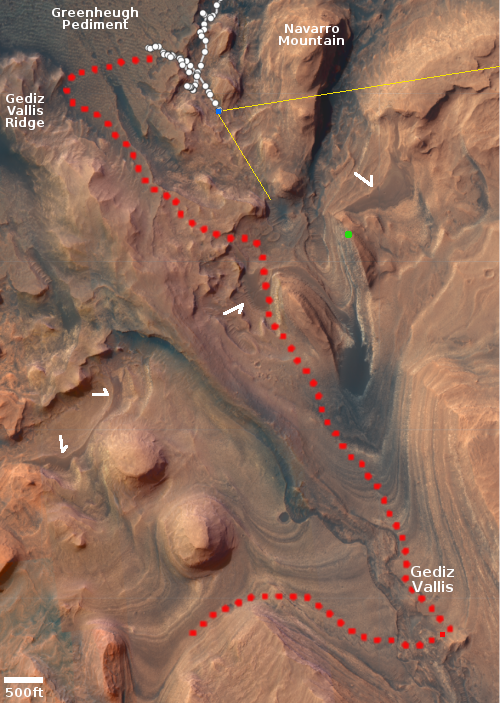
First on the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, is a close-up taken by Curiosity’s high resolution camera on May 14, 2022 of the rightmost jagged boulder in yesterday’s navigation panorama. The number of layers is astonishing, though hardly a unique phenomenon as seen by Curiosity in its travels. Each likely marks one of many climate and geological cycles, each laying down another unique stratum for a relatively short period of geological time. Some might be volcanic ash or lava layers. Some might be layers caused by climatic changes.
The ability of these thin layers to extend outward so much, almost like they were floating, illustrates the weak Martian gravity, as well as the thinness of its atmosphere. On Earth, if the wind and weather didn’t cause these flakes to break, the gravity would.
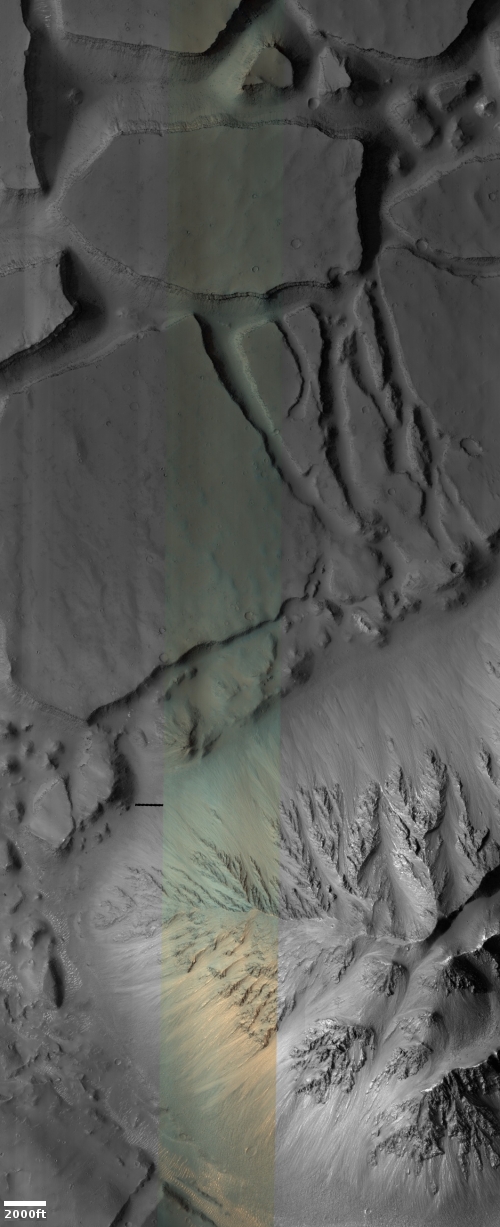
Second on the right, cropped and sharpened to post here, is a high resolution photo taken by Perseverance on May 15, 2022 of one of the cliff faces seen by the rover looking up into the delta in Jezero Crater. Here again we see many layers and jagged, pointy rocks, illustrating again the many cycles in the past that formed the delta as it flowed into the crater.
The smoothness on the surface of the leftmost pointy rock suggests that it has stood in this position for a long very time, allowing the wind of Mars’ very thin atmosphere to erode its rough surface.
We have two cool images today from both of America’s rovers on Mars, each of which illustrates the alien nature of the red planet.
First on the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, is a close-up taken by Curiosity’s high resolution camera on May 14, 2022 of the rightmost jagged boulder in yesterday’s navigation panorama. The number of layers is astonishing, though hardly a unique phenomenon as seen by Curiosity in its travels. Each likely marks one of many climate and geological cycles, each laying down another unique stratum for a relatively short period of geological time. Some might be volcanic ash or lava layers. Some might be layers caused by climatic changes.
The ability of these thin layers to extend outward so much, almost like they were floating, illustrates the weak Martian gravity, as well as the thinness of its atmosphere. On Earth, if the wind and weather didn’t cause these flakes to break, the gravity would.
Second on the right, cropped and sharpened to post here, is a high resolution photo taken by Perseverance on May 15, 2022 of one of the cliff faces seen by the rover looking up into the delta in Jezero Crater. Here again we see many layers and jagged, pointy rocks, illustrating again the many cycles in the past that formed the delta as it flowed into the crater.
The smoothness on the surface of the leftmost pointy rock suggests that it has stood in this position for a long very time, allowing the wind of Mars’ very thin atmosphere to erode its rough surface.