Author: Robert Zimmerman
October 15, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast shows off the two Haven-1 primary structures, the qualification and flight article, side by side
The company is once again pitching the fact that its work is entirely American-made.
- Geologists analyzing old rocks on Earth find they contain potassium isotopes they claim come from very early in Earth’s history
The press release makes even more outlandish claims. I have tried to distill the claims to their basic form, which tells us they haven’t really found anything significant at all.
- A low-density, puffy planet orbiting relatively far from a young star in a nearly perpendicular orbit
Or maybe not. It is too far from the star for heat to puff it up, so maybe it isn’t as puffy as first thought.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast shows off the two Haven-1 primary structures, the qualification and flight article, side by side
The company is once again pitching the fact that its work is entirely American-made.
- Geologists analyzing old rocks on Earth find they contain potassium isotopes they claim come from very early in Earth’s history
The press release makes even more outlandish claims. I have tried to distill the claims to their basic form, which tells us they haven’t really found anything significant at all.
- A low-density, puffy planet orbiting relatively far from a young star in a nearly perpendicular orbit
Or maybe not. It is too far from the star for heat to puff it up, so maybe it isn’t as puffy as first thought.
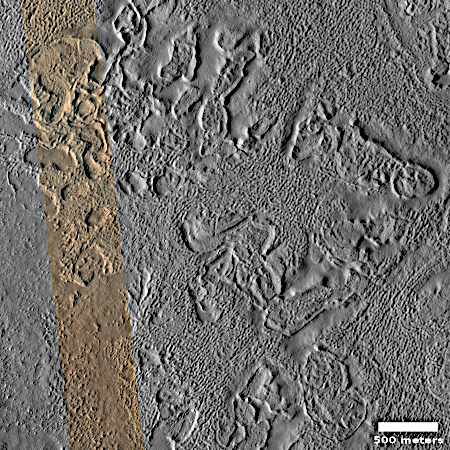
Peeling brain terrain in Martian crater
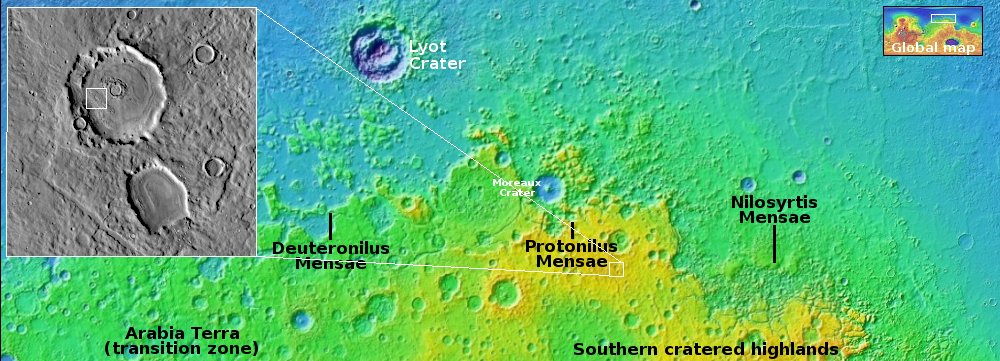
Today’s cool image takes us once again back to Mars’ glacier country, the 2,000 mile-long mid-latitude strip in the northern hemisphere where almost every image shows glacier features. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 4, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. It shows a small section of the floor of an unnamed 13-mile-wide crater, highlighting what the science team labels vaguely as “features.”
Those features appear to be glacial debris whose surface alternates between peeling gaps and the unique Martian geology dubbed “brain terrain”, whose formation is not yet understood but is believed to be associated with near surface ice.
The location is indicated by the white rectangle on the overview map above. At 36 degrees north latitude, this crater is deep within that mid-latitude strip where a lot of glacial features are routinely found. If you look at the inset, you can see that all the nearby craters appear to have formed in what appears to be slushy ground, their rims not very pronounced or distorted and their floors shallow, as if the ground melted like ice upon impact but very quickly solidified.
Mars is not a dry place. Future colonists will likely build their first cities around 30 degrees latitude, close enough to the equator to get warmer temperatures, but close enough to the near-surface ice found just a few degrees poleward, in a place such as this.

Today’s cool image takes us once again back to Mars’ glacier country, the 2,000 mile-long mid-latitude strip in the northern hemisphere where almost every image shows glacier features. The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 4, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. It shows a small section of the floor of an unnamed 13-mile-wide crater, highlighting what the science team labels vaguely as “features.”
Those features appear to be glacial debris whose surface alternates between peeling gaps and the unique Martian geology dubbed “brain terrain”, whose formation is not yet understood but is believed to be associated with near surface ice.
The location is indicated by the white rectangle on the overview map above. At 36 degrees north latitude, this crater is deep within that mid-latitude strip where a lot of glacial features are routinely found. If you look at the inset, you can see that all the nearby craters appear to have formed in what appears to be slushy ground, their rims not very pronounced or distorted and their floors shallow, as if the ground melted like ice upon impact but very quickly solidified.
Mars is not a dry place. Future colonists will likely build their first cities around 30 degrees latitude, close enough to the equator to get warmer temperatures, but close enough to the near-surface ice found just a few degrees poleward, in a place such as this.
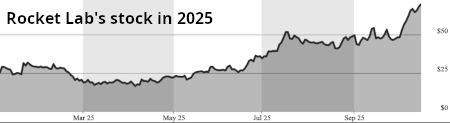
New Morgan Stanley report reflects Wall Street’s generally optimistic view of Rocket Lab
Though Rocket Lab is still not in the black, a new positive analysis of the company this week from Morgan Stanley reflects Wall Street’s generally optimistic view of Rocket Lab during the past year.
Rocket Lab (NASDAQ:RKLB) had its price target raised by equities researchers at Morgan Stanley from $20.00 to $68.00 in a research report issued on Monday, Benzinga reports. The brokerage presently has an “equal weight” rating on the rocket manufacturer’s stock. Morgan Stanley’s price target would suggest a potential upside of 1.63% from the company’s current price.
The article at the link also notes that Morgan Stanley is not alone in giving Rocket Lab a positive report, and in fact in the past year it shows that the recommendations from many analysts to buy its stock have risen considerably. These positive reviews have been reflected in a steady rise in the company’s stock price in 2025, as shown by the graph on the right.
Nor are these reports written in a vacuum. In recent weeks Rocket Lab has signed a bunch of new launch contracts, some extending deals with old customers, some with new customers of some note.
Buying the stock of a startup like Rocket Lab always carries risk, but it appears Wall Street is beginning to see the future of this particular startup as very promising.
Though Rocket Lab is still not in the black, a new positive analysis of the company this week from Morgan Stanley reflects Wall Street’s generally optimistic view of Rocket Lab during the past year.
Rocket Lab (NASDAQ:RKLB) had its price target raised by equities researchers at Morgan Stanley from $20.00 to $68.00 in a research report issued on Monday, Benzinga reports. The brokerage presently has an “equal weight” rating on the rocket manufacturer’s stock. Morgan Stanley’s price target would suggest a potential upside of 1.63% from the company’s current price.
The article at the link also notes that Morgan Stanley is not alone in giving Rocket Lab a positive report, and in fact in the past year it shows that the recommendations from many analysts to buy its stock have risen considerably. These positive reviews have been reflected in a steady rise in the company’s stock price in 2025, as shown by the graph on the right.
Nor are these reports written in a vacuum. In recent weeks Rocket Lab has signed a bunch of new launch contracts, some extending deals with old customers, some with new customers of some note.
Buying the stock of a startup like Rocket Lab always carries risk, but it appears Wall Street is beginning to see the future of this particular startup as very promising.
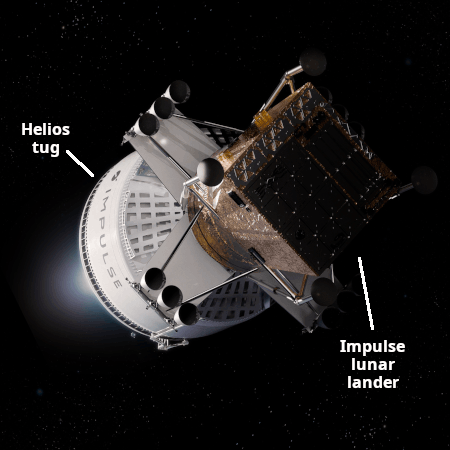
Orbital tug startup Impulse Space to develop its own unmanned lunar lander
The orbital tug startup Impulse Space, founded by Tom Mueller (one of SpaceX’s first engineers), is now proposing to build its own unmanned lunar lander, with a target for delivering six tons of cargo on two missions, starting in 2028.
Our proposed architecture combines our existing Helios kick stage and a new lunar lander, to be developed by our team in-house. Helios would launch on a standard medium- or heavy-lift rocket. Our lunar lander would ride as a payload on Helios. Once Helios and the lander are deployed in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Helios serves as a cruise stage, transporting the lander to low lunar orbit within one week. The lunar lander then separates from Helios and descends to the surface of the Moon. By taking advantage of Helios’s high delta-v capabilities, this mission architecture doesn’t require in-space refueling.
This solution can bridge the existing cargo delivery gap by offering direct transportation of the necessary mass to kickstart infrastructure, resource utilization, and economic activities on the Moon. We’ve already begun engine development for our lunar lander solution, and we stand ready to execute as dictated by industry demand and interest.
With this Helios and Impulse-made lander combination, we estimate delivering up to 6 tons of payload mass to the Moon (across two missions) per year starting in 2028 at a cost-effective price point. Each Helios + lander combo would take approximately 3 tons of cargo to the Moon.
It appears the company has identified a need (transporting cargo to the Moon cheaply and quickly) that no one (including NASA) is presently considering. SpaceX will be able to do it with Starship. Blue Origin is also proposing to do it with various versions of its Blue Moon manned lander. Impulse has decided however that both of those spacecraft are too large and tied to SLS and Lunar Gateway, with Starship requiring refueling, that makes their cargo missions more costly than a direct mission. Impulse proposes a simpler option.
This decision is also another indication that the demand for low orbital tugs is not developing as expected. It appears satellite companies and the available rocket companies have worked out ways to get most of their satellites to the orbits they require without tugs.
It will be interesting to watch if this proposal gains traction. If it does, than it will likely encourage other orbital tug as well as the other lunar lander companies to propose their own alternatives.
The orbital tug startup Impulse Space, founded by Tom Mueller (one of SpaceX’s first engineers), is now proposing to build its own unmanned lunar lander, with a target for delivering six tons of cargo on two missions, starting in 2028.
Our proposed architecture combines our existing Helios kick stage and a new lunar lander, to be developed by our team in-house. Helios would launch on a standard medium- or heavy-lift rocket. Our lunar lander would ride as a payload on Helios. Once Helios and the lander are deployed in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Helios serves as a cruise stage, transporting the lander to low lunar orbit within one week. The lunar lander then separates from Helios and descends to the surface of the Moon. By taking advantage of Helios’s high delta-v capabilities, this mission architecture doesn’t require in-space refueling.
This solution can bridge the existing cargo delivery gap by offering direct transportation of the necessary mass to kickstart infrastructure, resource utilization, and economic activities on the Moon. We’ve already begun engine development for our lunar lander solution, and we stand ready to execute as dictated by industry demand and interest.
With this Helios and Impulse-made lander combination, we estimate delivering up to 6 tons of payload mass to the Moon (across two missions) per year starting in 2028 at a cost-effective price point. Each Helios + lander combo would take approximately 3 tons of cargo to the Moon.
It appears the company has identified a need (transporting cargo to the Moon cheaply and quickly) that no one (including NASA) is presently considering. SpaceX will be able to do it with Starship. Blue Origin is also proposing to do it with various versions of its Blue Moon manned lander. Impulse has decided however that both of those spacecraft are too large and tied to SLS and Lunar Gateway, with Starship requiring refueling, that makes their cargo missions more costly than a direct mission. Impulse proposes a simpler option.
This decision is also another indication that the demand for low orbital tugs is not developing as expected. It appears satellite companies and the available rocket companies have worked out ways to get most of their satellites to the orbits they require without tugs.
It will be interesting to watch if this proposal gains traction. If it does, than it will likely encourage other orbital tug as well as the other lunar lander companies to propose their own alternatives.
Space Force approves Vandenberg environmental assessment, allowing SpaceX’s to launch as much as 100 times annually
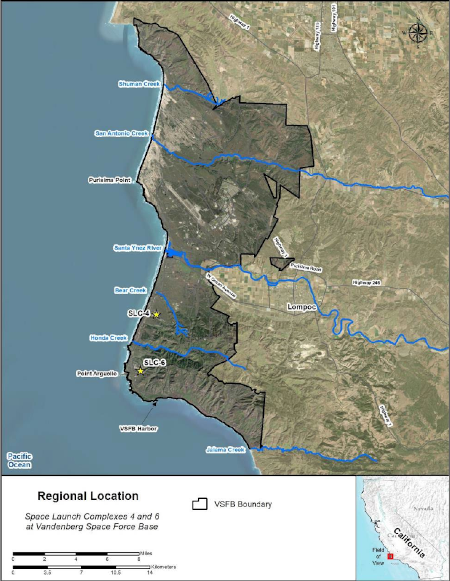
Figure 2.1-1 of the final environmental assessment report
The Space Force on October 10, 2025 announced it has now finalized and approved the environmental assessment that will permit SpaceX’s to increase its launch rate at Vandenberg to as much as 100 times per year.
The DAF [Air Force] has decided to increase the annual Falcon launch cadence at VSFB [Vandenberg] through launch and landing operations at SLC-4 and SLC-6 [the two SpaceX launchpads], including modification of SLC-6 for Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles to support future U.S. Government and commercial launch service needs. The overall launch cadence will increase from 50 Falcon 9 launches per year at SLC-4 to up to 100 launches per year for Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy at both SLCs combined. Falcon Heavy, which has not previously launched from VSFB, would launch and land up to five times per year from and at SLC-6. The DAF will authorize SpaceX to construct a new hangar south of the HIF [SpaceX’s horizontal integration facility] and north of SLC-6 to support Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy integration and processing.
You can read the full environmental assessment here [pdf]. The map to the right, from the assessment, shows the location at Vandenberg of the two SpaceX launch sites. SLC-4 (pronounced “slick-four”) is the pad SpaceX has been using for years to launch Falcon 9s. SLC-6 was originally built for the space shuttle but never used for that purpose. Subsequently ULA leased it to launch its Delta family of rockets. When that rocket was retired SpaceX won the lease to reconfigure the site for both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches.
The Space Force apparently decided to ignore the objections of the California Coastal Commission as well as a number of anti-Musk leftwing activist groups. And its decision is well grounded in facts. The report documents at length the lack of any consequential environmental impacts from the increase of launches, which is further supported by almost three quarters of a century of actual use.
The decision is also well founded in basic American culture and law. The Space Force as a government agency must act as a servant of the American people, in this case represented by the private company SpaceX. It must therefore do whatever it can to aid and support that company, not put up roadblocks because it doesn’t like what the company proposes.
At least under Trump, this is the approach the Space Force is taking. I fear what will happen if a Democrat regains the presidency, based on the radical and enthused communist make-up of that party today.

Figure 2.1-1 of the final environmental assessment report
The Space Force on October 10, 2025 announced it has now finalized and approved the environmental assessment that will permit SpaceX’s to increase its launch rate at Vandenberg to as much as 100 times per year.
The DAF [Air Force] has decided to increase the annual Falcon launch cadence at VSFB [Vandenberg] through launch and landing operations at SLC-4 and SLC-6 [the two SpaceX launchpads], including modification of SLC-6 for Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles to support future U.S. Government and commercial launch service needs. The overall launch cadence will increase from 50 Falcon 9 launches per year at SLC-4 to up to 100 launches per year for Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy at both SLCs combined. Falcon Heavy, which has not previously launched from VSFB, would launch and land up to five times per year from and at SLC-6. The DAF will authorize SpaceX to construct a new hangar south of the HIF [SpaceX’s horizontal integration facility] and north of SLC-6 to support Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy integration and processing.
You can read the full environmental assessment here [pdf]. The map to the right, from the assessment, shows the location at Vandenberg of the two SpaceX launch sites. SLC-4 (pronounced “slick-four”) is the pad SpaceX has been using for years to launch Falcon 9s. SLC-6 was originally built for the space shuttle but never used for that purpose. Subsequently ULA leased it to launch its Delta family of rockets. When that rocket was retired SpaceX won the lease to reconfigure the site for both Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches.
The Space Force apparently decided to ignore the objections of the California Coastal Commission as well as a number of anti-Musk leftwing activist groups. And its decision is well grounded in facts. The report documents at length the lack of any consequential environmental impacts from the increase of launches, which is further supported by almost three quarters of a century of actual use.
The decision is also well founded in basic American culture and law. The Space Force as a government agency must act as a servant of the American people, in this case represented by the private company SpaceX. It must therefore do whatever it can to aid and support that company, not put up roadblocks because it doesn’t like what the company proposes.
At least under Trump, this is the approach the Space Force is taking. I fear what will happen if a Democrat regains the presidency, based on the radical and enthused communist make-up of that party today.
Lena Haarberg – Fall Into You
October 14, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Thirteen years ago today the space shuttle Endeavour’s was moved from the airport to the California Science Center
Took 11 hours to go 12 miles, which Jay notes “is pretty typical traffic for LA.”
- Astronomers detect lowest mass dark object ever measured using gravitational lensing
I remain very skeptical of any claim that relies on gravitational lensing, because though it is a real phenomenon the uncertainties are so great any detailed conclusions from the data — such as this one — are always suspect. That it was further used to detect a “dark matter” object makes me even more skeptical.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Thirteen years ago today the space shuttle Endeavour’s was moved from the airport to the California Science Center
Took 11 hours to go 12 miles, which Jay notes “is pretty typical traffic for LA.”
- Astronomers detect lowest mass dark object ever measured using gravitational lensing
I remain very skeptical of any claim that relies on gravitational lensing, because though it is a real phenomenon the uncertainties are so great any detailed conclusions from the data — such as this one — are always suspect. That it was further used to detect a “dark matter” object makes me even more skeptical.
The hurricane season in 2024 confounded the predictions again
The uncertainty of science: Though the climate science community had predicted that last year’s hurricane season was going to be one of the most active ever, a new study published two weeks ago in Geophysical Research Letters of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) found that the 2024 season did not behave as predicted. It ended up producing about the predicted number of hurricanes, but did so only because of a sudden rise in activity near the end of the season, after a long lull with almost no activity. From the study’s conclusion:
As has been noted throughout this study, the lull was immediately followed by one of the busiest ends to an Atlantic hurricane season on record, including two major hurricane landfalls in Florida (Helene and Milton), resulting in more than 250 fatalities and $100 billion in damage (National Centers for Environmental Information, 2025). Though the final overall number of hurricanes and major hurricanes were aligned with the seasonal forecasts, the extremely busy beginning and end to the season and marked lull in the middle highlight just how unusual the season was.
Last year’s prediction was not the first to be incorrect, though this time the error was in how the season unfolded instead of the total numbers. In the past two decades — since Al Gore prophesied that global warming would cause a gigantic increase in violent storms — NOAA has repeatedly called for very active hurricane seasons, and repeatedly those predictions have turned out wrong. In fact, from 2006 until 2018 there were almost no major hurricanes at all, the exact opposite to what Gore had foretold. Since then the seasons have returned to more normal numbers, but the predictions of the scientists have continued to be no better than throwing a dart at a wall while wearing a blindfold.
The ongoing 2025 hurricane season is following this same pattern. In May 2025 NOAA predicted this year would be a very active hurricane season. Instead, this season has matched those from 2006 to 2016, in which no hurricanes made landfall in the U.S. and the number of strong hurricanes was almost nil.
The season of course is not yet over. We could see a burst of activity in the next few months, similar to what happened in 2024. Nonetheless, the important takeaway from this story is that the scientists who claim to know what is going to happen simply don’t know anything. They are guessing, because as the paper above admits, the Earth’s weather and climate are incredibly complex, and our understanding of it is still in its infancy.
Remember this when you read the next “We’re all gonna die!” prediction touted in the propaganda press.

The uncertainty of science: Though the climate science community had predicted that last year’s hurricane season was going to be one of the most active ever, a new study published two weeks ago in Geophysical Research Letters of the American Geophysical Union (AGU) found that the 2024 season did not behave as predicted. It ended up producing about the predicted number of hurricanes, but did so only because of a sudden rise in activity near the end of the season, after a long lull with almost no activity. From the study’s conclusion:
As has been noted throughout this study, the lull was immediately followed by one of the busiest ends to an Atlantic hurricane season on record, including two major hurricane landfalls in Florida (Helene and Milton), resulting in more than 250 fatalities and $100 billion in damage (National Centers for Environmental Information, 2025). Though the final overall number of hurricanes and major hurricanes were aligned with the seasonal forecasts, the extremely busy beginning and end to the season and marked lull in the middle highlight just how unusual the season was.
Last year’s prediction was not the first to be incorrect, though this time the error was in how the season unfolded instead of the total numbers. In the past two decades — since Al Gore prophesied that global warming would cause a gigantic increase in violent storms — NOAA has repeatedly called for very active hurricane seasons, and repeatedly those predictions have turned out wrong. In fact, from 2006 until 2018 there were almost no major hurricanes at all, the exact opposite to what Gore had foretold. Since then the seasons have returned to more normal numbers, but the predictions of the scientists have continued to be no better than throwing a dart at a wall while wearing a blindfold.
The ongoing 2025 hurricane season is following this same pattern. In May 2025 NOAA predicted this year would be a very active hurricane season. Instead, this season has matched those from 2006 to 2016, in which no hurricanes made landfall in the U.S. and the number of strong hurricanes was almost nil.
The season of course is not yet over. We could see a burst of activity in the next few months, similar to what happened in 2024. Nonetheless, the important takeaway from this story is that the scientists who claim to know what is going to happen simply don’t know anything. They are guessing, because as the paper above admits, the Earth’s weather and climate are incredibly complex, and our understanding of it is still in its infancy.
Remember this when you read the next “We’re all gonna die!” prediction touted in the propaganda press.
Three launches in the past day
Even as all eyes focused on SpaceX’s 11th test launch of Starship/Superheavy yesterday, there were three other launches in the past fourteen hours taking place on three different continents by China and two different American companies.
First, China placed a technology test satellite into orbit, its Long March 2D rocket lifting off from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China. The only information about the satellite is that it will test “new optical imaging.” No information at all was released on where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
Next, SpaceX placed 24 of Amazon’s Kuiper satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida. The first stage completed its second flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
With this launch, Amazon now has 154 satellites in orbit, out of a planned constellation of about 3,200. Its FCC license requires it to have about 1,600 in orbit by July of ’26, but that goal seems increasingly unlikely to be met. With this launch SpaceX completed its three-launch contract for Amazon. It has contracts with ULA for 46 launches (having so far completed three in 2025), and that company appears ready to launch regularly in the coming months. Amazon’s other launch contracts with Blue Origin’s New Glenn (27 launches) and ArianeGroup’s Ariane-6 (18 launches) however are more uncertain. Neither company has achieved any launches on their contracts, and it is not clear when either company, especially Blue Origin, will ever begin regular launches.
Finally, this morning Rocket Lab placed the seventh radar satellite into orbit for the company Synspective, its Electron rocket lifting off from one of its two launchpads in New Zealand. Rocket Lab has a contract for another twenty Synspective launches over the next few years. The launch also featured a larger fairing that will give the company the ability to launch bigger-sized satellites with Electron.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race, now including yesterday’s Starship/Superheavy launch:
131 SpaceX
60 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 131 to 101.
Even as all eyes focused on SpaceX’s 11th test launch of Starship/Superheavy yesterday, there were three other launches in the past fourteen hours taking place on three different continents by China and two different American companies.
First, China placed a technology test satellite into orbit, its Long March 2D rocket lifting off from its Jiuquan spaceport in northwest China. The only information about the satellite is that it will test “new optical imaging.” No information at all was released on where the rocket’s lower stages, using very toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed inside China.
Next, SpaceX placed 24 of Amazon’s Kuiper satellites into orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida. The first stage completed its second flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
With this launch, Amazon now has 154 satellites in orbit, out of a planned constellation of about 3,200. Its FCC license requires it to have about 1,600 in orbit by July of ’26, but that goal seems increasingly unlikely to be met. With this launch SpaceX completed its three-launch contract for Amazon. It has contracts with ULA for 46 launches (having so far completed three in 2025), and that company appears ready to launch regularly in the coming months. Amazon’s other launch contracts with Blue Origin’s New Glenn (27 launches) and ArianeGroup’s Ariane-6 (18 launches) however are more uncertain. Neither company has achieved any launches on their contracts, and it is not clear when either company, especially Blue Origin, will ever begin regular launches.
Finally, this morning Rocket Lab placed the seventh radar satellite into orbit for the company Synspective, its Electron rocket lifting off from one of its two launchpads in New Zealand. Rocket Lab has a contract for another twenty Synspective launches over the next few years. The launch also featured a larger fairing that will give the company the ability to launch bigger-sized satellites with Electron.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race, now including yesterday’s Starship/Superheavy launch:
131 SpaceX
60 China
13 Russia
13 Rocket Lab
SpaceX now leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 131 to 101.
PLD issues detailed update on its preparations for first launch in 2026
The Spanish rocket startup PLD today released a detailed video update outlining the work it is doing designing and building its Miura-5 rocket for its first launch, now targeting 2026.
I have embedded that video below. Its engineers and managers describe and show in detail the hard metal they are cutting. Their goal is to produce one upper stage engine every two weeks by the end of this year. The company has already build eight tanks for both stages, and has even tested one tank to failure. PLD has also started construction of its launch site in French Guiana.
All in all, PLD seems moving aggressively towards that first launch, making it one of three European rocket startups on the brink of operations. The other two are Isar Aerospace and Rocket Factory Augsburg, both from Germany.
The Spanish rocket startup PLD today released a detailed video update outlining the work it is doing designing and building its Miura-5 rocket for its first launch, now targeting 2026.
I have embedded that video below. Its engineers and managers describe and show in detail the hard metal they are cutting. Their goal is to produce one upper stage engine every two weeks by the end of this year. The company has already build eight tanks for both stages, and has even tested one tank to failure. PLD has also started construction of its launch site in French Guiana.
All in all, PLD seems moving aggressively towards that first launch, making it one of three European rocket startups on the brink of operations. The other two are Isar Aerospace and Rocket Factory Augsburg, both from Germany.
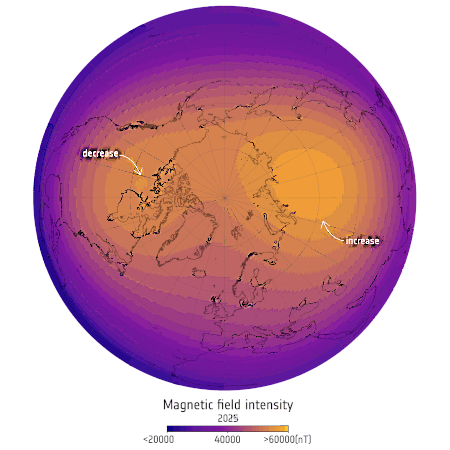
Swarm satellite constellation detects changes in the Earth’s magnetic field during the past decade
The European Space Agency’s three-satellite Swarm constellation, designed to measure the strength of the Earth’s magnetic field at high resolution, has found that the field’s weak and strong regions have shifted and changed in the past eleven years, since the constellation was launched.
The map to the right shows the changes over the northern hemisphere, related to the movement of the north magnetic pole towards Siberia.
[S]ince Swarm has been in orbit the magnetic field over Siberia has strengthened while it has weakened over Canada. The Canadian strong field region has shrunk by 0.65% of Earth’s surface area, which is almost the size of India, while the Siberian region has grown by 0.42% of Earth’s surface area, which is comparable to the size of Greenland.
Similarly, the Swarm data has shown the South Atlantic Anomaly, a major weak area of the field above South America near the equator, has grown significantly eastward towards Africa. That change is important for satellite operations, as spacecraft passing through it experience higher levels of radiation.
All these changes are thought to be because of shifts within the Earth’s molten core from which the dynamo of the magnetic field is generated.
The European Space Agency’s three-satellite Swarm constellation, designed to measure the strength of the Earth’s magnetic field at high resolution, has found that the field’s weak and strong regions have shifted and changed in the past eleven years, since the constellation was launched.
The map to the right shows the changes over the northern hemisphere, related to the movement of the north magnetic pole towards Siberia.
[S]ince Swarm has been in orbit the magnetic field over Siberia has strengthened while it has weakened over Canada. The Canadian strong field region has shrunk by 0.65% of Earth’s surface area, which is almost the size of India, while the Siberian region has grown by 0.42% of Earth’s surface area, which is comparable to the size of Greenland.
Similarly, the Swarm data has shown the South Atlantic Anomaly, a major weak area of the field above South America near the equator, has grown significantly eastward towards Africa. That change is important for satellite operations, as spacecraft passing through it experience higher levels of radiation.
All these changes are thought to be because of shifts within the Earth’s molten core from which the dynamo of the magnetic field is generated.
Eleventh Starship/Superheavy a complete success

Starship and Superheavy during ascent today.
On the eleventh orbital test flight today of Starship/Superheavy, SpaceX basically achieved all its engineering goals, with both Superheavy and Starship completing their flights as planned, with Superheavy doing a soft vertical splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico, and Starship doing a soft vertical splashdown in the Indian Ocean.
The Superheavy flown was on its second flight, having flown on test flight #8. Of its 33 Raptor engines, 24 had flown previously. In returning, it successfully used a new configuration of engine burns, first firing thirteen engines, then six, then three.
More significant was Starship’s flight. The engineers had purposely left tiles off in some locations that would experience the greatest heat during re-entry, to find out if the ship could survive a loss of those tiles. It did, and did so in a truly remarkable manner, always flying in a controlled manner, even as it attempted a radical and previously untried banking maneuver as it approached the ocean in order to simulate a return to the launch tower chopsticks at Boca Chica.
Prior to splashdown and during its coast phase, Starship once again successfully tested the deployment of eight dummy Starlink satellites, as well as a relight of one of its Raptor engines to demonstrate it will be able to do a planned de-orbit burn once it enters a full orbit on future test flights.
Once again, the word to describe this flight is remarkable. While no else has yet been able to recover a first stage and reuse it, SpaceX has been doing it with its Falcon 9 for almost a decade, and doing it hundreds of times.
And now it has twice reused a Superheavy booster, out of only eleven test launches. Based on this and the last test flight, the company will almost certainly begin reusing Starship prototypes during next year’s orbital test flights, when it will begin flying full orbits using its third version of Starship, including returns to Boca Chica for chopstick tower catches. Furthermore, expect the deployment of real Starlink satellites on those missions.
The next mission should likely take place close to the end of this year, and it should likely be followed by additional flights about every two months.

“Proclaim liberty throughout all the land unto all
the inhabitants thereof.” Photo credit: William Zhang
While politicians and media swamp creatures focus on the relatively inconsequential race to do an Apollo-like manned landing on the Moon, the real American space program is being run privately by SpaceX, and its goal is to not only go to Mars, but to do so in a manner that will quickly establish a human colony. Along the way the company will help facilitate that government space program, but only as it helps SpaceX learn better how to get humans to Mars.
Most significantly, SpaceX is doing its space program entirely on its own dime. It is being financed by the revenues coming in to the company from the now more than seven million subscribers to Starlink. And those numbers will only rise with time, as Starship begins launching the next generation of satellites with capabilities that will dwarf all of SpaceX’s competitors.
Once again, freedom, private enterprise, and the American dream wins. May all humans someday live under rules that will allow them the same possibilities.
I love love love my toy chicken!!!
An evening pause: Something wholesome to start the week. And stay with it, it gets better and better.
Hat tip Mike Nelson.
This woman gives a chicken toy to this donkey. He loves it, brays with utters of joy, & funnily plays with it. No innocent being stays indifferent to love.pic.twitter.com/7jCzHa4UZP
— Hakan Kapucu (@1hakankapucu) September 3, 2025
Another round of layoffs at JPL
The management at the Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) in California today announced it will be laying off 550 people this week, about 11% of its work force.
As part of this effort, JPL is undergoing a realignment of its workforce, including a reduction in staff. This reduction — part of a reorganization that began in July and not related to the current government shutdown — will affect approximately 550 of our colleagues across technical, business, and support areas. Employees will be notified of their status on Tuesday, Oct. 14.
As the statement makes clear, this reduction is unrelated to the government shutdown, and is also mostly unrelated directly to the 24% budget cut the Trump administration wishes to impose on NASA. JPL has had major management issues in the last few years, including two previous rounds of layoffs of similar amounts. Much of these budget issues stem from the cancellation by NASA of the Mars sample return mission, which JPL was to play a major part. That money is gone, and even if the mission is resurrected, JPL is almost certainly not going to play a major part.
The management at the Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) in California today announced it will be laying off 550 people this week, about 11% of its work force.
As part of this effort, JPL is undergoing a realignment of its workforce, including a reduction in staff. This reduction — part of a reorganization that began in July and not related to the current government shutdown — will affect approximately 550 of our colleagues across technical, business, and support areas. Employees will be notified of their status on Tuesday, Oct. 14.
As the statement makes clear, this reduction is unrelated to the government shutdown, and is also mostly unrelated directly to the 24% budget cut the Trump administration wishes to impose on NASA. JPL has had major management issues in the last few years, including two previous rounds of layoffs of similar amounts. Much of these budget issues stem from the cancellation by NASA of the Mars sample return mission, which JPL was to play a major part. That money is gone, and even if the mission is resurrected, JPL is almost certainly not going to play a major part.
Michael Knowles – Celebrating Columbus
A mid-day pause: I posted twice in the past, but think it should be seen again. As I wrote in 2021,
On this day when all should be celebrating Christopher Columbus and his willingness “sail beyond the sunset,” to use a phrase from Tennyson, this short video give us an accurate picture of the man, his times, and his achievements. It also puts the lie to the bigoted, hateful, leftist slanders that have been used in recent years to poison his legacy.
A mid-day pause: I posted twice in the past, but think it should be seen again. As I wrote in 2021,
On this day when all should be celebrating Christopher Columbus and his willingness “sail beyond the sunset,” to use a phrase from Tennyson, this short video give us an accurate picture of the man, his times, and his achievements. It also puts the lie to the bigoted, hateful, leftist slanders that have been used in recent years to poison his legacy.
Welsh university delivers spectometer for Europe’s Franklin Mars rover
Aberystwyth University in Wales this week delivered the spectometer instrument, dubbed Enfys, to be installed on Franklin Mars rover being built by the European Space Agency (ESA) and now scheduled for launch in 2028.
Enfys will work in tandem with PanCam – a camera system led by UCL’s Mullard Space Science Laboratory – to pinpoint mineral targets. These insights will enable the rover to select optimal drilling sites on the Martian surface, with samples analysed by other onboard instruments. The instrument being shipped today will be installed on the rover’s ‘Earth twin’ known as the Ground Test Model located at the Aerospace Logistics Technology Engineering Company in Turin.
Since the Franklin rover was initially supposed to launch in 2020, it is puzzling this instrument is only being delivered now. It could be that the original spectrometer was supposed to be provided by ESA’s original partner in the project Russia, but became unavailable when that partnership broke up due to Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine.
Or it could be the instrument’s development was simply late and behind schedule, as so many ESA’s projects routinely are. For example, the mission’s launch was first delayed from ’20 to ’22 because the parachutes weren’t ready. Then it was delayed until ’28 because of the break-up with Russia. Even now it remains uncertain it will meet this new date.
Aberystwyth University in Wales this week delivered the spectometer instrument, dubbed Enfys, to be installed on Franklin Mars rover being built by the European Space Agency (ESA) and now scheduled for launch in 2028.
Enfys will work in tandem with PanCam – a camera system led by UCL’s Mullard Space Science Laboratory – to pinpoint mineral targets. These insights will enable the rover to select optimal drilling sites on the Martian surface, with samples analysed by other onboard instruments. The instrument being shipped today will be installed on the rover’s ‘Earth twin’ known as the Ground Test Model located at the Aerospace Logistics Technology Engineering Company in Turin.
Since the Franklin rover was initially supposed to launch in 2020, it is puzzling this instrument is only being delivered now. It could be that the original spectrometer was supposed to be provided by ESA’s original partner in the project Russia, but became unavailable when that partnership broke up due to Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine.
Or it could be the instrument’s development was simply late and behind schedule, as so many ESA’s projects routinely are. For example, the mission’s launch was first delayed from ’20 to ’22 because the parachutes weren’t ready. Then it was delayed until ’28 because of the break-up with Russia. Even now it remains uncertain it will meet this new date.
Faced with loss of the federal gravy train, Lowell Observatory makes major changes
According to a press release last week, the Lowell Observatory in Arizona is now making major changes to it management and operations due to “declines in federal research funding.”
The new framework centers on two defining pursuits: Planetary Defense, safeguarding our world from cosmic hazards, and Exoplanetary Research, seeking to understand distant worlds and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Declines in federal research funding, coupled with uncertainty about future national priorities, have impacted research institutions across the country. At the same time, Lowell’s historic reliance on internal funding to sustain research is no longer a viable long-term model. To ensure stability and growth, the Observatory will focus its efforts on key scientific areas while building new endowments to support the scientists and technology that drive discovery.
Essentially, it can no longer depend on easy federal cash (thank you Donald Trump!), and thus needs to actually do real research work in fields that others consider important. It will also abandon its “traditional academic tenure system.” Scientists who use the facility will now have to earn that right, in a case-by-case basis. And such researchers will have to be funded by “private, endowed support.”
In other words, Lowell is returning to the model that had been used by American researchers for most of the nation’s history, until World War II, getting their funding from private sources rather than the federal teat.
We should expect therefore the work at Lowell to become more effective and focused, something it has not been for decades.
According to a press release last week, the Lowell Observatory in Arizona is now making major changes to it management and operations due to “declines in federal research funding.”
The new framework centers on two defining pursuits: Planetary Defense, safeguarding our world from cosmic hazards, and Exoplanetary Research, seeking to understand distant worlds and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Declines in federal research funding, coupled with uncertainty about future national priorities, have impacted research institutions across the country. At the same time, Lowell’s historic reliance on internal funding to sustain research is no longer a viable long-term model. To ensure stability and growth, the Observatory will focus its efforts on key scientific areas while building new endowments to support the scientists and technology that drive discovery.
Essentially, it can no longer depend on easy federal cash (thank you Donald Trump!), and thus needs to actually do real research work in fields that others consider important. It will also abandon its “traditional academic tenure system.” Scientists who use the facility will now have to earn that right, in a case-by-case basis. And such researchers will have to be funded by “private, endowed support.”
In other words, Lowell is returning to the model that had been used by American researchers for most of the nation’s history, until World War II, getting their funding from private sources rather than the federal teat.
We should expect therefore the work at Lowell to become more effective and focused, something it has not been for decades.
Germany’s space agency DLR delivers one prototype leg for Europe’s Callisto grasshopper
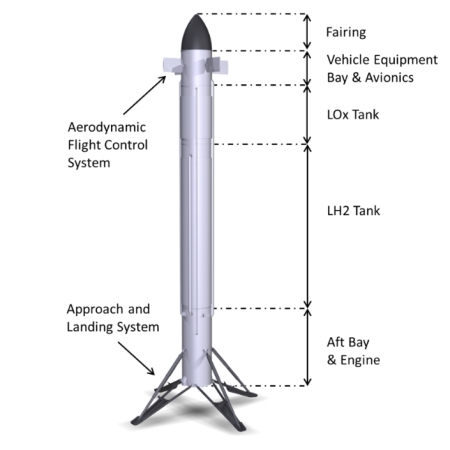
Callisto’s basic design
Government in-action: After a decade of work, the German space agency DLR this week finally delivered for testing a prototype leg of the Callisto grasshopper-type demo rocket, intended by the European Space Agency (ESA) to demonstrate vertical take-off and landing.
On 9 October, the Institute of Structures and Design announced that it had delivered a qualification model of the demonstrator’s landing leg to the Institute of Space Systems in Bremen. According to a 3 December 2024 update, the leg will now undergo a series of tests at the Institute’s Landing and Mobility Facility, including deployment, touchdown, and vibration testing.
Once the qualification test campaign is complete and the landing leg design has been validated, the Institute of Structures and Design will proceed with the construction of the four flight-ready legs.
Note again that Callisto, as shown to the right, was proposed as a joint ESA and JAXA project in 2015. Only now, a decade later, as DLR delivered one prototype leg. The first test hop has been repeatedly delayed, so that now it is now not expected to happen until 2027, and that rocket will not even be an operational version, it will simply be a small scale prototype.
Meanwhile, SpaceX has landed its Falcon 9 first stage hundreds of times, and reused them dozens of times. Other companies are flying or building their own reusable rockets, and hope to fly operational versions next year.
The contrast between this government project and the private sector is quite embarrassing. What makes it even more embarrassing is that it is par for the course, and yet so many people still look to the government as the god who can get things done. When will people learn?

Callisto’s basic design
Government in-action: After a decade of work, the German space agency DLR this week finally delivered for testing a prototype leg of the Callisto grasshopper-type demo rocket, intended by the European Space Agency (ESA) to demonstrate vertical take-off and landing.
On 9 October, the Institute of Structures and Design announced that it had delivered a qualification model of the demonstrator’s landing leg to the Institute of Space Systems in Bremen. According to a 3 December 2024 update, the leg will now undergo a series of tests at the Institute’s Landing and Mobility Facility, including deployment, touchdown, and vibration testing.
Once the qualification test campaign is complete and the landing leg design has been validated, the Institute of Structures and Design will proceed with the construction of the four flight-ready legs.
Note again that Callisto, as shown to the right, was proposed as a joint ESA and JAXA project in 2015. Only now, a decade later, as DLR delivered one prototype leg. The first test hop has been repeatedly delayed, so that now it is now not expected to happen until 2027, and that rocket will not even be an operational version, it will simply be a small scale prototype.
Meanwhile, SpaceX has landed its Falcon 9 first stage hundreds of times, and reused them dozens of times. Other companies are flying or building their own reusable rockets, and hope to fly operational versions next year.
The contrast between this government project and the private sector is quite embarrassing. What makes it even more embarrassing is that it is par for the course, and yet so many people still look to the government as the god who can get things done. When will people learn?
Watch the eleventh orbital test flight of SpaceX’s Starship/Superheavy rocket
The eleventh orbital test launch of Starship/Superheavy is scheduled for 6:15 (Central) today. It will be the last flight for version 2 of Starship, and will also include the second reuse of a Superheavy booster.
Starship will repeat its flight plan from the previous flight, testing the deployment of dummy Starlink satellites, the relighting of its Raptor engines once in orbit, and various new configurations of its thermal protection system. It will come down in the Indian Ocean, either controlled or not. Future flights will use version three, and quickly move towards orbital flights and a return to Boca Chica for a tower chopstick capture and later reuse.
Superheavy, which flew previously on the eighth test flight, will do more engine configuration tests on its return, and will attempt a soft vertical splashdown in the Gulf.
You can watch SpaceX’s X live stream at the link above. I have also embedded Space Affairs youtube feed below.
» Read more
The eleventh orbital test launch of Starship/Superheavy is scheduled for 6:15 (Central) today. It will be the last flight for version 2 of Starship, and will also include the second reuse of a Superheavy booster.
Starship will repeat its flight plan from the previous flight, testing the deployment of dummy Starlink satellites, the relighting of its Raptor engines once in orbit, and various new configurations of its thermal protection system. It will come down in the Indian Ocean, either controlled or not. Future flights will use version three, and quickly move towards orbital flights and a return to Boca Chica for a tower chopstick capture and later reuse.
Superheavy, which flew previously on the eighth test flight, will do more engine configuration tests on its return, and will attempt a soft vertical splashdown in the Gulf.
You can watch SpaceX’s X live stream at the link above. I have also embedded Space Affairs youtube feed below.
» Read more
Rocket Lab gets two-launch contract from Japan’s space agency JAXA
In what appears to be a significant slap at its own rockets (especially its delayed Epsilon-S rocket), Japan’s space agency JAXA this week signed a two-launch deal with the American rocket company Rocket Lab.
Launching from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in New Zealand, the two Electron missions will deploy satellites for JAXA’s Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration Program. The first launch, scheduled from December 2025, will deploy the agency’s RApid Innovative payload demonstration SatellitE-4 (RAISE-4) spacecraft, a single satellite that will demonstrate eight technologies developed by private companies, universities, and research institutions throughout Japan.
The second launch, scheduled for 2026, is a JAXA-manifested rideshare of eight separate spacecraft that includes educational small sats, an ocean monitoring satellite, a demonstration satellite for ultra-small multispectral cameras, and a deployable antenna that can be packed tightly using origami folding techniques and unfurled to 25 times its size.
Rocket Lab has previously won contracts from several private Japanese satellite companies (Q-Shu, Astroscale, ALE), but this I think is the first JAXA contract it has won. What makes it significant is that JAXA has always focused on using its own rockets, the large retired H2A and the new H3 as well as the smaller Epsilon-S. To go to an American company is somewhat unprecedented.
Though larger than Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket, Epsilon-S was being developed to compete for the same market. That development however has been plagued by failure, including explosions of engines during tests of both its upper and first stages in ’23 and ’24 respectively. After the second explosion JAXA announced in December 2024 the rocket’s first launch would not occur in the spring of 2025 as planned, but provided no additional information. Since then there have been no updates.
This Rocket Lab deal suggests the Epsilon program is in big trouble. In the long run however this might be a very good thing for both JAXA and Japan’s own nascent rocket industry. JAXA might finally be recognizing that building and owning its own rockets is not the best plan, that it would be better to use the capitalism model and simply be a customer buying the services from the private sector. At the moment Japan doesn’t yet have a viable commercial rocket sector, with only Mitsubishi having an operational commercial rocket, the H3 (mostly controlled by JAXA). There are a number of new startups however, including Interstellar, Honda, Space One, and Tispace, all of which have done tests of one kind or another. If JAXA is ready to abandon its own government rockets and buy the service from the private sector, those Japanese startups will start to prosper.
In what appears to be a significant slap at its own rockets (especially its delayed Epsilon-S rocket), Japan’s space agency JAXA this week signed a two-launch deal with the American rocket company Rocket Lab.
Launching from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1 in New Zealand, the two Electron missions will deploy satellites for JAXA’s Innovative Satellite Technology Demonstration Program. The first launch, scheduled from December 2025, will deploy the agency’s RApid Innovative payload demonstration SatellitE-4 (RAISE-4) spacecraft, a single satellite that will demonstrate eight technologies developed by private companies, universities, and research institutions throughout Japan.
The second launch, scheduled for 2026, is a JAXA-manifested rideshare of eight separate spacecraft that includes educational small sats, an ocean monitoring satellite, a demonstration satellite for ultra-small multispectral cameras, and a deployable antenna that can be packed tightly using origami folding techniques and unfurled to 25 times its size.
Rocket Lab has previously won contracts from several private Japanese satellite companies (Q-Shu, Astroscale, ALE), but this I think is the first JAXA contract it has won. What makes it significant is that JAXA has always focused on using its own rockets, the large retired H2A and the new H3 as well as the smaller Epsilon-S. To go to an American company is somewhat unprecedented.
Though larger than Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket, Epsilon-S was being developed to compete for the same market. That development however has been plagued by failure, including explosions of engines during tests of both its upper and first stages in ’23 and ’24 respectively. After the second explosion JAXA announced in December 2024 the rocket’s first launch would not occur in the spring of 2025 as planned, but provided no additional information. Since then there have been no updates.
This Rocket Lab deal suggests the Epsilon program is in big trouble. In the long run however this might be a very good thing for both JAXA and Japan’s own nascent rocket industry. JAXA might finally be recognizing that building and owning its own rockets is not the best plan, that it would be better to use the capitalism model and simply be a customer buying the services from the private sector. At the moment Japan doesn’t yet have a viable commercial rocket sector, with only Mitsubishi having an operational commercial rocket, the H3 (mostly controlled by JAXA). There are a number of new startups however, including Interstellar, Honda, Space One, and Tispace, all of which have done tests of one kind or another. If JAXA is ready to abandon its own government rockets and buy the service from the private sector, those Japanese startups will start to prosper.
China launches three satellites from ocean platform
The Chinese pseudo-company Orienspace yesterday successfully placed three satellites into orbit, its solid-fueled Gravity-1 rocket lifting off from an ocean platform off the country’s northeast coast.
This was Orienspace’s second launch, both using its Gravity-1 rocket from the ocean. Of the three satellites, one was an Earth observation satellite, and the other two were part of the pseudo-company Geespace’s Geely constellation of satellites, though it is not clear if these are for its Internet-of-Things (IoT) constellation or for general communications. The IoT constellation already has 64 satellites in orbit out of a planned 240.
Another launch of China’s Long March 8A rocket was supposed to happen yesterday, but there is no indication in China’s state-run that it took place, nor any information about a rescheduled launch date. That state-run press also illustrated the pseudo nature of these Chinese companies by only mentioning Orienspace as an afterthought at the end of the article.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
129 SpaceX
59 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 129 to 99. The company will try again this evening to launch its third mission for Amazon, placing a set of Kuiper satellites into orbit. Weather has scrubbed the past two attempts in the previous few days.
The Chinese pseudo-company Orienspace yesterday successfully placed three satellites into orbit, its solid-fueled Gravity-1 rocket lifting off from an ocean platform off the country’s northeast coast.
This was Orienspace’s second launch, both using its Gravity-1 rocket from the ocean. Of the three satellites, one was an Earth observation satellite, and the other two were part of the pseudo-company Geespace’s Geely constellation of satellites, though it is not clear if these are for its Internet-of-Things (IoT) constellation or for general communications. The IoT constellation already has 64 satellites in orbit out of a planned 240.
Another launch of China’s Long March 8A rocket was supposed to happen yesterday, but there is no indication in China’s state-run that it took place, nor any information about a rescheduled launch date. That state-run press also illustrated the pseudo nature of these Chinese companies by only mentioning Orienspace as an afterthought at the end of the article.
The leaders in the 2025 launch race:
129 SpaceX
59 China
13 Russia
12 Rocket Lab
SpaceX still leads the rest of the world in successful launches, 129 to 99. The company will try again this evening to launch its third mission for Amazon, placing a set of Kuiper satellites into orbit. Weather has scrubbed the past two attempts in the previous few days.
October 10, 2025 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Business Insider – The Rise And Fall Of The American Diner
An evening pause: This remains the place that Americans go to after church.
Enjoy the weekend. And find a great diner to eat at!
Hat tip Cotour.
October 10, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Inversion Space shows off video of a helicopter drop test of a prototype engineering test vehicle of its proposed Arc recoverable orbiting capsule
The American company has raised $44 million in private investment capital. It has also won financial grants from the Space Force. The prototype resembled a lifting body design, similar to Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser.
- Space Force picks Blue Origin for satellite processing at Cape Canaveral
Essentially Blue Origin will provide the facilities for integrating satellites prior to launch, whether or not they are launched by Blue Origin.
- Law firm begins investigation in behalf of stockholders against Firefly because its stock dropped after its rocket exploded during a static fire test in September
It appears to both Jay and I that this law firm, Glancy Prongay & Murray, is fishing for a nuisance lawsuit to shake Firefly down for money. No one has grounds to sue just because a stock lost value because something went wrong. It’s called buyer beware.
- Ispace press conference showing off engineering test prototype of its 2nd generation lunar lander
After two landing failures with its first generation design, the upgrade will be bigger and will be used on its fourth mission in ’28, for Japan’s space agency JAXA. This prototype has already undergone thermal, radiation, and vibration testing.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Inversion Space shows off video of a helicopter drop test of a prototype engineering test vehicle of its proposed Arc recoverable orbiting capsule
The American company has raised $44 million in private investment capital. It has also won financial grants from the Space Force. The prototype resembled a lifting body design, similar to Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser.
- Space Force picks Blue Origin for satellite processing at Cape Canaveral
Essentially Blue Origin will provide the facilities for integrating satellites prior to launch, whether or not they are launched by Blue Origin.
- Law firm begins investigation in behalf of stockholders against Firefly because its stock dropped after its rocket exploded during a static fire test in September
It appears to both Jay and I that this law firm, Glancy Prongay & Murray, is fishing for a nuisance lawsuit to shake Firefly down for money. No one has grounds to sue just because a stock lost value because something went wrong. It’s called buyer beware.
- Ispace press conference showing off engineering test prototype of its 2nd generation lunar lander
After two landing failures with its first generation design, the upgrade will be bigger and will be used on its fourth mission in ’28, for Japan’s space agency JAXA. This prototype has already undergone thermal, radiation, and vibration testing.
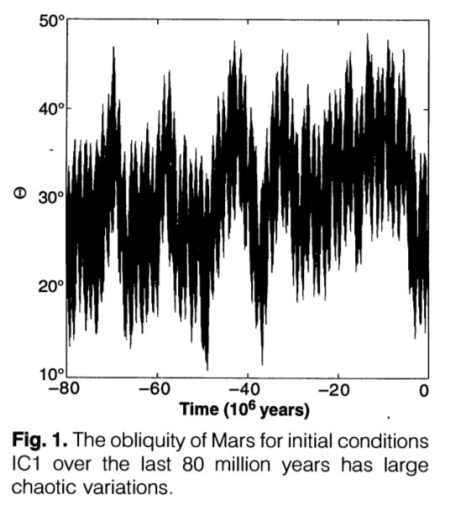
New research confirms the steady decline of Martian ice with each glacial cycle
Using orbital data from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of glaciers inside mid-latitude craters, scientists have concluded that there was a steady decline in the growth of those glaciers with each new glacial cycle.
They focused on craters with indicative signs of glaciation, such as ridges, moraines (piles of debris left behind by glaciers), and brain terrain (a pitted, maze-like surface formed by ice-rich landforms). By comparing the shapes and orientations of these features with climate models, they found that ice consistently clustered in the colder, shadowed southwestern walls of craters. This trend was consistent across various glacial periods, ranging from approximately 640 million to 98 million years ago.
The results show that Mars didn’t just freeze once—it went through a series of ice ages driven by shifts in its axial tilt, also known as obliquity. Unlike Earth, Mars’ tilt can swing dramatically over millions of years, redistributing sunlight and triggering cycles of ice build-up and melting. These changes shaped where water ice could survive on the planet’s surface. Over time, however, each cycle stored less ice, pointing to a gradual planetary drying. [emphasis mine]
You can read the paper here [pdf]. This result is not new. Based on the orbital data scientists have theorized now for almost a decade that as Mars’ rotational tilt (its obliquity) swings from 11 to 60 degrees, it produces extreme climate cycles on the planet. Those swings are shown on the graph to the right, taken from this 1993 paper [pdf]. When the obliquity is low, the mid-latitudes are warm and the glaciers there shrink, with the snow falling at the poles. When obliquity is high, the poles are warmer and its ice sublimates away to fall as snow in the mid-latitudes, thus causing those glaciers to grow instead.
The orbital data has consistently shown that with each new cycle, the glaciers grew less, suggesting that less global water was available on the planet. This new study further confirms these conclusions.
One last point: Though the amount of water ice on Mars has declined, we mustn’t think the red planet now has none. The orbital data shows that there is a lot of near surface ice on Mars, covering the planet from 30 degrees latitude poleward. As I’ve noted numerous times, Mars is a desert like Antarctica.

Using orbital data from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) of glaciers inside mid-latitude craters, scientists have concluded that there was a steady decline in the growth of those glaciers with each new glacial cycle.
They focused on craters with indicative signs of glaciation, such as ridges, moraines (piles of debris left behind by glaciers), and brain terrain (a pitted, maze-like surface formed by ice-rich landforms). By comparing the shapes and orientations of these features with climate models, they found that ice consistently clustered in the colder, shadowed southwestern walls of craters. This trend was consistent across various glacial periods, ranging from approximately 640 million to 98 million years ago.
The results show that Mars didn’t just freeze once—it went through a series of ice ages driven by shifts in its axial tilt, also known as obliquity. Unlike Earth, Mars’ tilt can swing dramatically over millions of years, redistributing sunlight and triggering cycles of ice build-up and melting. These changes shaped where water ice could survive on the planet’s surface. Over time, however, each cycle stored less ice, pointing to a gradual planetary drying. [emphasis mine]
You can read the paper here [pdf]. This result is not new. Based on the orbital data scientists have theorized now for almost a decade that as Mars’ rotational tilt (its obliquity) swings from 11 to 60 degrees, it produces extreme climate cycles on the planet. Those swings are shown on the graph to the right, taken from this 1993 paper [pdf]. When the obliquity is low, the mid-latitudes are warm and the glaciers there shrink, with the snow falling at the poles. When obliquity is high, the poles are warmer and its ice sublimates away to fall as snow in the mid-latitudes, thus causing those glaciers to grow instead.
The orbital data has consistently shown that with each new cycle, the glaciers grew less, suggesting that less global water was available on the planet. This new study further confirms these conclusions.
One last point: Though the amount of water ice on Mars has declined, we mustn’t think the red planet now has none. The orbital data shows that there is a lot of near surface ice on Mars, covering the planet from 30 degrees latitude poleward. As I’ve noted numerous times, Mars is a desert like Antarctica.
Orbital tug company Momentus gets two NASA contracts
The orbital tug startup Momentus yesterday announced that NASA has awarded it two contracts worth $7.6 million total to fly two experimental NASA payloads on its Vigoride tug.
One payload will test “test the ability to make semiconductor crystals in microgravity”, while the second will “test a rotating detonation rocket engine, a propulsion system designed to provide higher efficiency than traditional engines.” In this case the propellants used will be nitrous oxide and ethane.
Both will fly on the same Vigoride tug on a mission to be launched no earlier than October 2026. Momentus also says there is room for additional payloads on that mission.
It appears the increase in the number and launches of rockets has actually hurt the orbital tug business:
Momentus is among several companies that developed orbital transfer vehicles, or OTVs, like Vigoride to ferry spacecraft between orbits. They are designed to provide last-mile delivery to specific orbits for spacecraft launched on rideshare missions such as [SpaceX’s] Transporter [launches]. However, demand for such services has been slower to materialize than expected. “Candidly, that part of the market has not developed as much as people thought, say, five years ago,” [said John Rood, Momentus’ chief executive] during a panel at World Space Business Week in September. “The reason is many small manufacturers are multi-manifesting satellites to deploy a single plane with a single launcher.”
As a result, Momentus has focused on getting technology demonstration contracts such as the two above, with the tug acting more like a service module.
The orbital tug startup Momentus yesterday announced that NASA has awarded it two contracts worth $7.6 million total to fly two experimental NASA payloads on its Vigoride tug.
One payload will test “test the ability to make semiconductor crystals in microgravity”, while the second will “test a rotating detonation rocket engine, a propulsion system designed to provide higher efficiency than traditional engines.” In this case the propellants used will be nitrous oxide and ethane.
Both will fly on the same Vigoride tug on a mission to be launched no earlier than October 2026. Momentus also says there is room for additional payloads on that mission.
It appears the increase in the number and launches of rockets has actually hurt the orbital tug business:
Momentus is among several companies that developed orbital transfer vehicles, or OTVs, like Vigoride to ferry spacecraft between orbits. They are designed to provide last-mile delivery to specific orbits for spacecraft launched on rideshare missions such as [SpaceX’s] Transporter [launches]. However, demand for such services has been slower to materialize than expected. “Candidly, that part of the market has not developed as much as people thought, say, five years ago,” [said John Rood, Momentus’ chief executive] during a panel at World Space Business Week in September. “The reason is many small manufacturers are multi-manifesting satellites to deploy a single plane with a single launcher.”
As a result, Momentus has focused on getting technology demonstration contracts such as the two above, with the tug acting more like a service module.
Astronomers take first radio image of the supermassive binary system OJ287
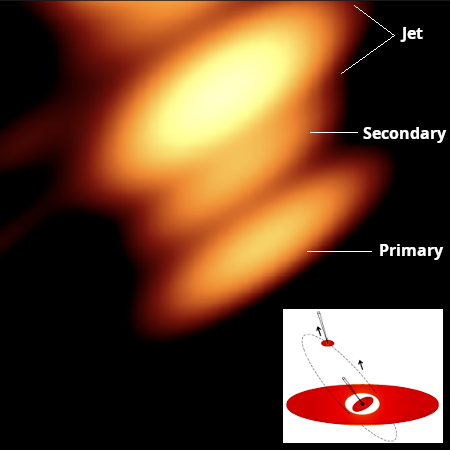
Using archive data from the now retired Russian orbiting radio telescope RadioAstron, scientists have now obtained the first image of the binary supermassive black hole system OJ287 that was previously detected flaring as predicted when the smaller black hole (150 million solar masses) circled near the larger (18 billion solar masses).
That image is to the right, cropped and annotated to post here. The cartoon in the lower right shows the theorized orientation of the system, taken from figure 2 of the published paper [pdf]. According to the paper the elongation of the three objects is an artifact of the data and is “not real.” From the press release:
In this latest study, the astronomers compared the earlier theoretical calculations with a radio image. The two black holes were there in the image, just where they were expected to be. This gave the researchers an answer to a question that has been open for 40 years: whether black-hole pairs exist in the first place. “For the first time, we managed to get an image of two black holes circling each other. In the image, the black holes are identified by the intense particle jets they emit. The black holes themselves are perfectly black, but they can be detected by these particle jets or by the glowing gas surrounding the hole,” Valtonen says.
The researchers also identified a completely new kind of a jet emanating from a black hole. The jet coming out of the smaller black hole is twisted like a jet of a rotating garden hose. This is because the smaller black hole moves fast around the primary black hole of OJ287, and its jet is diverted depending on its current motion. The researches liken it to “a wagging tail” which should be seen twisting in different directions in the coming years when the smaller black hole changes its speed and direction of motion.
This image is cropped from the full dataset. The jet continues upward and then curves to the right as it “wags” away.
This incredible black hole binary system, estimated to be about 3.5 billion light years away, has been posited since 1982, when one astronomer noticed that it repeatedly flared every twelve years. Since then scientists have successfully predicted several flares, based on the system’s theorized orbit. These images further confirm the system’s shape.

Using archive data from the now retired Russian orbiting radio telescope RadioAstron, scientists have now obtained the first image of the binary supermassive black hole system OJ287 that was previously detected flaring as predicted when the smaller black hole (150 million solar masses) circled near the larger (18 billion solar masses).
That image is to the right, cropped and annotated to post here. The cartoon in the lower right shows the theorized orientation of the system, taken from figure 2 of the published paper [pdf]. According to the paper the elongation of the three objects is an artifact of the data and is “not real.” From the press release:
In this latest study, the astronomers compared the earlier theoretical calculations with a radio image. The two black holes were there in the image, just where they were expected to be. This gave the researchers an answer to a question that has been open for 40 years: whether black-hole pairs exist in the first place. “For the first time, we managed to get an image of two black holes circling each other. In the image, the black holes are identified by the intense particle jets they emit. The black holes themselves are perfectly black, but they can be detected by these particle jets or by the glowing gas surrounding the hole,” Valtonen says.
The researchers also identified a completely new kind of a jet emanating from a black hole. The jet coming out of the smaller black hole is twisted like a jet of a rotating garden hose. This is because the smaller black hole moves fast around the primary black hole of OJ287, and its jet is diverted depending on its current motion. The researches liken it to “a wagging tail” which should be seen twisting in different directions in the coming years when the smaller black hole changes its speed and direction of motion.
This image is cropped from the full dataset. The jet continues upward and then curves to the right as it “wags” away.
This incredible black hole binary system, estimated to be about 3.5 billion light years away, has been posited since 1982, when one astronomer noticed that it repeatedly flared every twelve years. Since then scientists have successfully predicted several flares, based on the system’s theorized orbit. These images further confirm the system’s shape.
Canadian rocket startup Nordspace signs deal for its mission control center

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The Canadian rocket startup Nordspace, which earlier this week signed a deal for another company to establish ground stations for its proposed Atlantic Spaceport, today signed an agreement with the company Kongsberg Geospatial to provide software for running its mission control center.
According to the news release TerraLens “will ingest data from multiple sensors to deliver real-time three-dimensional (3D) visualization of launch operations, range safety, decision support, and vehicle tracking. This will help streamline launch operations and enable deployment of critical space missions to orbit in under 48 hours.” Kongsberg said TerraLens builds on their “experience supporting range safety and mission-critical visualization for the Andøya Space and Defence project in Norway.”
Andøya is Norway’s new commercial spaceport that has been launching suborbital government rockets for decades.
Nordspace continues to move forward quickly, having been established only three years ago. It is putting the pieces together for its spaceport, and is testing both a small suborbital rocket and the engines for its proposed orbital Tundra rocket. Though the race is certainly not over, it does appear Nordspace will get to orbit ahead of the Nova Scotia spaceport that was first proposed in 2016.

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The Canadian rocket startup Nordspace, which earlier this week signed a deal for another company to establish ground stations for its proposed Atlantic Spaceport, today signed an agreement with the company Kongsberg Geospatial to provide software for running its mission control center.
According to the news release TerraLens “will ingest data from multiple sensors to deliver real-time three-dimensional (3D) visualization of launch operations, range safety, decision support, and vehicle tracking. This will help streamline launch operations and enable deployment of critical space missions to orbit in under 48 hours.” Kongsberg said TerraLens builds on their “experience supporting range safety and mission-critical visualization for the Andøya Space and Defence project in Norway.”
Andøya is Norway’s new commercial spaceport that has been launching suborbital government rockets for decades.
Nordspace continues to move forward quickly, having been established only three years ago. It is putting the pieces together for its spaceport, and is testing both a small suborbital rocket and the engines for its proposed orbital Tundra rocket. Though the race is certainly not over, it does appear Nordspace will get to orbit ahead of the Nova Scotia spaceport that was first proposed in 2016.
Is Trump considering re-nominating Jared Isaacman for NASA administrator?

Billionaire Jared Isaacman
According to a report late today (based on anonymous sources), President Trump has held several face-to-face meetings in the past few weeks with billionaire Jared Isaacman, and those meetings have raised the possibility of Trump re-nominating him for NASA administrator.
According to Bloomberg News, President Trump has reportedly met with Isaacman several times in recent weeks to discuss NASA’s operational plans and future plans. Isaacman is the founder of fintech company Shift4 Payments and a private astronaut at SpaceX who has had a longstanding relationship with Elon Musk.
Isaacman, who has flown two private missions in space (and done one spacewalk), had been nominated by Trump for NASA administrator in December 2024, and was only days away from a Senate confirmation vote when Trump suddenly withdrew the nomination on May 31, 2025. Though it has never been clear why Trump withdrew the nomination, Isaacman’s past support of Democrats and his close links to Musk have been raised as issues, especially because of the Trump-Musk kerfuffle in the spring. Isaacman has also expressed some opinions since then about NASA and what it should do that might not have fit with Trump’s plans.
At the same time, NASA is presently without its own administrator, with Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy holding down the job as an interim head. It appears Trump might be reconsidering his earlier decision in order to get someone in charge of NASA who isn’t distracted by other responsibilities.
Note however that this report is solely from anonymous sources, and we all know how unreliable those are. The whole story could be fantasy cooked up by someone in DC for any number of devious political purposes.

Billionaire Jared Isaacman
According to a report late today (based on anonymous sources), President Trump has held several face-to-face meetings in the past few weeks with billionaire Jared Isaacman, and those meetings have raised the possibility of Trump re-nominating him for NASA administrator.
According to Bloomberg News, President Trump has reportedly met with Isaacman several times in recent weeks to discuss NASA’s operational plans and future plans. Isaacman is the founder of fintech company Shift4 Payments and a private astronaut at SpaceX who has had a longstanding relationship with Elon Musk.
Isaacman, who has flown two private missions in space (and done one spacewalk), had been nominated by Trump for NASA administrator in December 2024, and was only days away from a Senate confirmation vote when Trump suddenly withdrew the nomination on May 31, 2025. Though it has never been clear why Trump withdrew the nomination, Isaacman’s past support of Democrats and his close links to Musk have been raised as issues, especially because of the Trump-Musk kerfuffle in the spring. Isaacman has also expressed some opinions since then about NASA and what it should do that might not have fit with Trump’s plans.
At the same time, NASA is presently without its own administrator, with Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy holding down the job as an interim head. It appears Trump might be reconsidering his earlier decision in order to get someone in charge of NASA who isn’t distracted by other responsibilities.
Note however that this report is solely from anonymous sources, and we all know how unreliable those are. The whole story could be fantasy cooked up by someone in DC for any number of devious political purposes.