According to the budget data that was leaked anonymous last week, the Trump administration is proposing a major restructuring of NOAA’s satellite operations, shifting from building geosynchronous weather/climate satellites in partnership with NASA to focusing on buying weather data from commercial smallsats.
The plan would initially reduce NOAA’s program by two-thirds.
The document suggests NOAA’s National Environmental Satellite, Data and Information Service (NESDIS) “immediately cancel all major instrument and spacecraft contracts on the GeoXO program,” saying the projected costs are “unstainable, lack support of Congress, and are out of step with international peers.”
GeoXO is a $19.6 billion program that includes six satellites and ground infrastructure to significantly enhance NOAA’s ability to monitor weather, map lightning, and track ocean and atmospheric conditions over decades. To maintain observations from geostationary orbit at the conclusion of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-R Series, the White House memo calls on NOAA to “immediately institute a major overhaul to lower lifecycle costs by 50 percent” with annual costs below $500 million, while remaining on schedule to launch the first satellite in 2032.
Rather than expanding the geostationary constellation to include satellites over the East, West and Central United States, the proposal includes only East and West satellites like the GOES-R Series. OMB also recommends an immediate end to NOAA relying on NASA to help it acquire weather satellites.
Maybe the most controversial recommendation calls for NOAA to focus on gathering daily weather data while ending its monitoring of long term ocean and atmospheric climate trends.
The shift from NOAA-built satellites to purchasing weather data from commercially launched and built satellites makes great sense, and is the most likely part of this plan to get implemented. Similarly, ending NOAA’s reliance on NASA will help streamline the fat from both agencies.
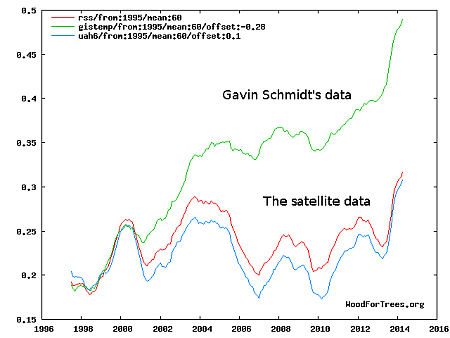
Whether the Trump administration can force an end to NOAA’s climate gathering operations is less clear. The politics suggest this will be difficult. The realities however suggest that a major house-cleaning in this area is in order, as there is ample evidence that the scientists running this work have been playing games with the data, manipulating it in order to support their theories of human-caused global warming.