Author: Robert Zimmerman
February 6, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Isaacman: NASA astronauts can now use their smartphones on ISS and Orion
It appears Isaacman is slashing some old hidebound NASA rules about using commercial store-bought equipment.
- Boeing is shifting 787 Dreamliner work from Washington state to South Carolina
This accelerated this shift, which began five years ago. The flight from Democratic Party strongholds continues.
- EU’s European Commission awards consortium led by French rocket startup HyPrSpace the contract to develop a fast launch capability
At present this appears to just be an initial design study, not an actual launch contract.
- Starlink now available in the former Soviet Republic of Tajikistan
Everyone’s getting it but Russia. It seems invading your neighbors is bad for business in all ways.
- Senate committee delays consideration of bill to streamline FCC satellite licensing
More shenanigans by stupid members of the swamp. In this case the delay is caused by senator Maria Cantwell (D-Washington), who appears to want to flex her muscles.
- On this day in 1974 Mariner 10 reached Venus and returned the first close-up photo of the planet
The image, using an ultraviolet filter, revealed the dark absorption streaks caused by some material in Venus’ atmosphere that still remains unknown. The spacecraft also discovered the super-rotation of that atmosphere, 60 times faster than the planet’s rotation.
- Documentary describing the maiden flight of the space shuttle Challenger in 1983
I haven’t watched it so I cannot vouch for it. It does appear to be assembled from historic footage.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Isaacman: NASA astronauts can now use their smartphones on ISS and Orion
It appears Isaacman is slashing some old hidebound NASA rules about using commercial store-bought equipment.
- Boeing is shifting 787 Dreamliner work from Washington state to South Carolina
This accelerated this shift, which began five years ago. The flight from Democratic Party strongholds continues.
- EU’s European Commission awards consortium led by French rocket startup HyPrSpace the contract to develop a fast launch capability
At present this appears to just be an initial design study, not an actual launch contract.
- Starlink now available in the former Soviet Republic of Tajikistan
Everyone’s getting it but Russia. It seems invading your neighbors is bad for business in all ways.
- Senate committee delays consideration of bill to streamline FCC satellite licensing
More shenanigans by stupid members of the swamp. In this case the delay is caused by senator Maria Cantwell (D-Washington), who appears to want to flex her muscles.
- On this day in 1974 Mariner 10 reached Venus and returned the first close-up photo of the planet
The image, using an ultraviolet filter, revealed the dark absorption streaks caused by some material in Venus’ atmosphere that still remains unknown. The spacecraft also discovered the super-rotation of that atmosphere, 60 times faster than the planet’s rotation.
- Documentary describing the maiden flight of the space shuttle Challenger in 1983
I haven’t watched it so I cannot vouch for it. It does appear to be assembled from historic footage.
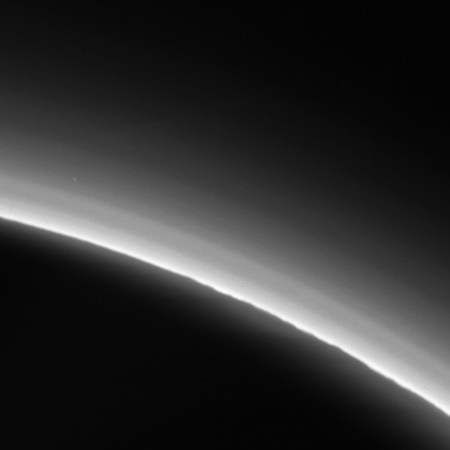
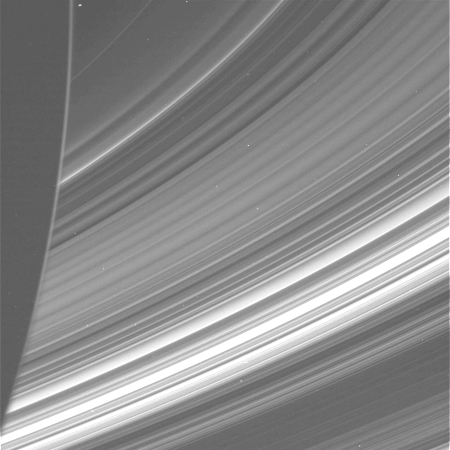
One of Cassini’s first close-up images of Saturn’s rings
Cool image time! My exploration of the Cassini image archive continues. The picture to the right, reduced and enhanced to post here, was taken on May 2, 2005 by Cassini soon after it moved into a close orbit of Saturn where it could get high resolution images of Saturn’s rings. This is one of the first.
This is also a raw image that has not been calibrated or validated, to use the science team’s terms. Thus, the white dots scattered across the image could be artifacts that need to be cleaned up, not examples of Saturn’s many moons.
Regardless, the image illustrates the incredible delicacy of these rings, despite the fact that they are gigantic, spanning almost 45,000 miles in width, with a thickness ranging from 30 to 1,000 feet. And yet, there are so many distinct rings they almost resemble an old-fashioned vinyl record.
Cool image time! My exploration of the Cassini image archive continues. The picture to the right, reduced and enhanced to post here, was taken on May 2, 2005 by Cassini soon after it moved into a close orbit of Saturn where it could get high resolution images of Saturn’s rings. This is one of the first.
This is also a raw image that has not been calibrated or validated, to use the science team’s terms. Thus, the white dots scattered across the image could be artifacts that need to be cleaned up, not examples of Saturn’s many moons.
Regardless, the image illustrates the incredible delicacy of these rings, despite the fact that they are gigantic, spanning almost 45,000 miles in width, with a thickness ranging from 30 to 1,000 feet. And yet, there are so many distinct rings they almost resemble an old-fashioned vinyl record.
A new American satellite constellation gets FCC approval
The satellite startup Logos has won approval from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for its proposed 4,178 satellite internet constellation.
The Federal Communications Commission partially granted the Redwood City, California-based venture’s constellation proposal Jan. 30, clearing operations in K-, Q- and V-band spectrum under certain conditions while deferring and denying parts of its higher-frequency requests. The satellites would operate across seven orbital shells ranging from 870 kilometers to 925 kilometers above Earth, with inclinations spanning 28 to 90 degrees.
Under FCC rules, Logos must deploy and operate half of the constellation within seven years, with the remainder in place by Jan. 30, 2035.
The company last year raised $50 million in private investment capital, and hopes to launch its first satellite by 2027.
It seems this constellation is coming to the game very late.
The satellite startup Logos has won approval from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for its proposed 4,178 satellite internet constellation.
The Federal Communications Commission partially granted the Redwood City, California-based venture’s constellation proposal Jan. 30, clearing operations in K-, Q- and V-band spectrum under certain conditions while deferring and denying parts of its higher-frequency requests. The satellites would operate across seven orbital shells ranging from 870 kilometers to 925 kilometers above Earth, with inclinations spanning 28 to 90 degrees.
Under FCC rules, Logos must deploy and operate half of the constellation within seven years, with the remainder in place by Jan. 30, 2035.
The company last year raised $50 million in private investment capital, and hopes to launch its first satellite by 2027.
It seems this constellation is coming to the game very late.
Has the FAA officially approved Starship launches for Kennedy Space Center in Florida?
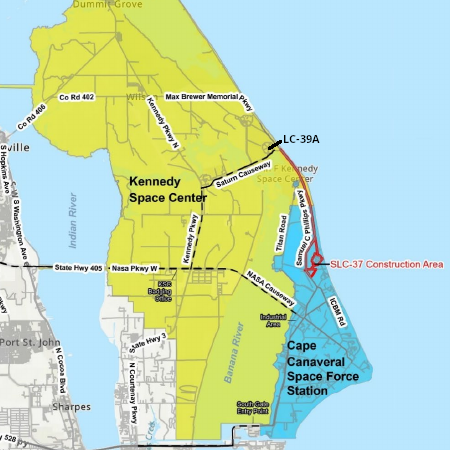
Proposed Starship/Superheavy launchsites at
Kennedy (LC-39A) and Cape Canaveral (SLC-37)
It appears that though the FAA’s preliminary summary that it issued on January 30, 2026 only suggested it was leaning to approve Starship/Superheavy launches at SpaceX’s LC-39A launchpad at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, it now appears that SpaceX is treating it as an official approval, and has begun work re-configuring LC-39A from the launchpad used for manned Falcon 9 launches to a facility for launching both Falcon Heavy and Starship/Superheavy.
The launch pad has seen a pause in action due to SpaceX working to finalize the Starship tower and launch pad on the site. Then on Wednesday, Feb. 4, a crane appeared next to the Falcon 9 launch tower, attaching to the crew access arm.
“For our manifest going forward, we’re planning to launch most of our Falcon 9 launches off of Space Launch Complex 40. That will include all Dragon missions going forward,” said Lee Echerd, senior mission manager of Human Spaceflight Mission Management at SpaceX during the Crew-12 prelaunch press briefing. “That will allow our Cape team to focus 39A on Falcon Heavy launches and hopefully our first Starship launches later this year.”
This Space News article today claims the FAA has issued a final approval for Starship/Superheavy at LC-39A, but it links to that preliminary summary from January 30th, which as far as I can tell is still preliminary and does not include an official approval.
Not that it matters. The FAA appears quite prepared to okay Starship/Superheavy launches at LC-39A, and it now appears SpaceX is proceeding under that assumption.

Proposed Starship/Superheavy launchsites at
Kennedy (LC-39A) and Cape Canaveral (SLC-37)
It appears that though the FAA’s preliminary summary that it issued on January 30, 2026 only suggested it was leaning to approve Starship/Superheavy launches at SpaceX’s LC-39A launchpad at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, it now appears that SpaceX is treating it as an official approval, and has begun work re-configuring LC-39A from the launchpad used for manned Falcon 9 launches to a facility for launching both Falcon Heavy and Starship/Superheavy.
The launch pad has seen a pause in action due to SpaceX working to finalize the Starship tower and launch pad on the site. Then on Wednesday, Feb. 4, a crane appeared next to the Falcon 9 launch tower, attaching to the crew access arm.
“For our manifest going forward, we’re planning to launch most of our Falcon 9 launches off of Space Launch Complex 40. That will include all Dragon missions going forward,” said Lee Echerd, senior mission manager of Human Spaceflight Mission Management at SpaceX during the Crew-12 prelaunch press briefing. “That will allow our Cape team to focus 39A on Falcon Heavy launches and hopefully our first Starship launches later this year.”
This Space News article today claims the FAA has issued a final approval for Starship/Superheavy at LC-39A, but it links to that preliminary summary from January 30th, which as far as I can tell is still preliminary and does not include an official approval.
Not that it matters. The FAA appears quite prepared to okay Starship/Superheavy launches at LC-39A, and it now appears SpaceX is proceeding under that assumption.
Russia launches classified nine satellites
Russia yesterday successfully placed nine classified military satellites into orbit, its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from its Plesetsk spaceport in northeast Russia.
The rocket’s flight path took it over the Arctic, where all its lower stages fell harmlessly. As for the satellites:
Based on these orbital parameters, it appeared that upon forming its initial near-circular orbit at an altitude just below 330 kilometers, the Fregat released one (main) payload (Object 2026-023A). The space tug then maneuvered to a near 500-kilometer orbit, where it released the rest of its passengers (Objects B, C, D, E, F, G, H and J).
The 2026 launch race:
14 SpaceX
6 China
2 Rocket Lab
1 Russia
Launches in the past week have dropped practically to zero, for what appear to be technical and political reasons. SpaceX has paused launches as it investigates why the upper stage on its last launch on February 2, 2025 did not correctly do its de-orbit burn. China meanwhile seems to have partly done the same after losing two rockets in launches in mid-January, a Long March 3B and the Ceres-2. There have been no launches of its workhorse Long March 3B rocket since then, while the Ceres-2 launch was that rocket’s maiden flight for the pseudo-company Galactic Energy. Since then there have been no launches by any of China’s pseudo-companies. It could be the new government agency in charge of all these fake companies has imposed its will and paused them all while the Ceres-2 failure is investigated.
Russia yesterday successfully placed nine classified military satellites into orbit, its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from its Plesetsk spaceport in northeast Russia.
The rocket’s flight path took it over the Arctic, where all its lower stages fell harmlessly. As for the satellites:
Based on these orbital parameters, it appeared that upon forming its initial near-circular orbit at an altitude just below 330 kilometers, the Fregat released one (main) payload (Object 2026-023A). The space tug then maneuvered to a near 500-kilometer orbit, where it released the rest of its passengers (Objects B, C, D, E, F, G, H and J).
The 2026 launch race:
14 SpaceX
6 China
2 Rocket Lab
1 Russia
Launches in the past week have dropped practically to zero, for what appear to be technical and political reasons. SpaceX has paused launches as it investigates why the upper stage on its last launch on February 2, 2025 did not correctly do its de-orbit burn. China meanwhile seems to have partly done the same after losing two rockets in launches in mid-January, a Long March 3B and the Ceres-2. There have been no launches of its workhorse Long March 3B rocket since then, while the Ceres-2 launch was that rocket’s maiden flight for the pseudo-company Galactic Energy. Since then there have been no launches by any of China’s pseudo-companies. It could be the new government agency in charge of all these fake companies has imposed its will and paused them all while the Ceres-2 failure is investigated.
Voyager Technologies and Max Space team up to develop inflatable planetary structures
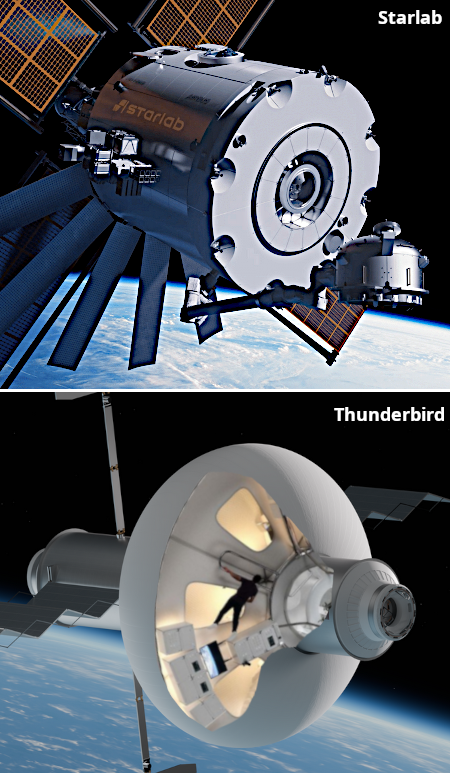
The station designs as of the end of 2025
The space station startups Voyager Technologies, which is leading the consortium developing Starlab, and Max Space, which is developing its own inflatable Thunderbird station, have now partnered to use their combined talents to develop inflatable planetary structures for habitation and cargo.
In terms of their space stations, they are similar but different. Voyager’s Starlab station will be a single giant module launched on Starship. The consortium building this module had hired the interior decoration company Journey to design the interior, and yesterday showed off a mock-up of that interior.
Max Space’s Thunderbird is an equally large single module but because it uses inflatable technology it will launch on a Falcon 9. The company plans to launch a smaller demo module in ’27 to prove this technology.
Both companies will now use their skills together to begin design work on inflatable habitats that both NASA and SpaceX could use on the planned lunar and Mars colonies.
The phased development path includes ground validation and in-space demonstrations later this decade, with the goal of enabling operational lunar and Mars capabilities aligned with NASA’s exploration timelines. The partnership emphasizes early risk retirement, interoperability and commercial scalability as guiding principles.
In other words, these companies are expanding their business model to sell their products across a wider range of uses. This deal does not change my rankings of the five space stations currently under development, as shown below, but it is an interesting data point that suggests the technology of these space stations can be marketed in many other space-related areas.
» Read more

The station designs as of the end of 2025
The space station startups Voyager Technologies, which is leading the consortium developing Starlab, and Max Space, which is developing its own inflatable Thunderbird station, have now partnered to use their combined talents to develop inflatable planetary structures for habitation and cargo.
In terms of their space stations, they are similar but different. Voyager’s Starlab station will be a single giant module launched on Starship. The consortium building this module had hired the interior decoration company Journey to design the interior, and yesterday showed off a mock-up of that interior.
Max Space’s Thunderbird is an equally large single module but because it uses inflatable technology it will launch on a Falcon 9. The company plans to launch a smaller demo module in ’27 to prove this technology.
Both companies will now use their skills together to begin design work on inflatable habitats that both NASA and SpaceX could use on the planned lunar and Mars colonies.
The phased development path includes ground validation and in-space demonstrations later this decade, with the goal of enabling operational lunar and Mars capabilities aligned with NASA’s exploration timelines. The partnership emphasizes early risk retirement, interoperability and commercial scalability as guiding principles.
In other words, these companies are expanding their business model to sell their products across a wider range of uses. This deal does not change my rankings of the five space stations currently under development, as shown below, but it is an interesting data point that suggests the technology of these space stations can be marketed in many other space-related areas.
» Read more
Stephen Sondheim – Someone in a Tree
An evening pause: For my birthday, a repost of a 2010 evening pause of one of my favorite Broadway songs, from Stephen Sondheim’s Pacific Overtures, which I only recently learned was his favorite song as well.
It tells the story of a significant moment in history, the moment when Japan’s leaders signed their first international treaty in 1852 with the United States, but from the point of view of outside witnesses. Its point is profound, that history is not just made by the leaders who sign the deals, but by every individual who makes up the whole of human society.
It’s the fragment, not the day
It’s the pebble, not the stream
It’s the ripple, not the sea
That is happening.
Not the building but the beam
Not the garden but the stone
Only cups of tea
And history
And someone in a tree.
Pluto’s implausible atmosphere, as seen in 2015 by New Horizons
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on July 14, 2015 by the camera on the New Horizons probe as it flew past Pluto, the only time a human craft has gotten close to this distant planet. From the link:
These high phase angle images show many artifacts associated with scattered sunlight; the Sun was less then 15 degrees from the center of the LORRI frame for these observations. But the outline of Pluto and its hazy atmosphere are also visible.
To see the atmosphere the light from the planet itself has been blocked out.
What is implausible about Pluto’s atmosphere is the location of the planet, about 3.7 billion miles from the Sun, out in the nether reaches of the solar system. At that distance sunlight is very weak, and produces very little energy. And yet, there is enough energy here to produce an atmosphere of mostly nitrogen gas, with trace amounts of metane and carbon monoxide. Scientists think this atmosphere only exists when Pluto is closer to the Sun in its somewhat oblong orbit, and freezes out the rest of the time. As Pluto was just retreating in 2015 from that closest approach in the last two decades of the 20th century, New Horizons could detect its presence.
But then, we really can’t be sure if this atmosphere truly vanishes when the planet is farthest from the Sun, as we have only so far observed 96 years in Pluto’s 248-year orbit.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on July 14, 2015 by the camera on the New Horizons probe as it flew past Pluto, the only time a human craft has gotten close to this distant planet. From the link:
These high phase angle images show many artifacts associated with scattered sunlight; the Sun was less then 15 degrees from the center of the LORRI frame for these observations. But the outline of Pluto and its hazy atmosphere are also visible.
To see the atmosphere the light from the planet itself has been blocked out.
What is implausible about Pluto’s atmosphere is the location of the planet, about 3.7 billion miles from the Sun, out in the nether reaches of the solar system. At that distance sunlight is very weak, and produces very little energy. And yet, there is enough energy here to produce an atmosphere of mostly nitrogen gas, with trace amounts of metane and carbon monoxide. Scientists think this atmosphere only exists when Pluto is closer to the Sun in its somewhat oblong orbit, and freezes out the rest of the time. As Pluto was just retreating in 2015 from that closest approach in the last two decades of the 20th century, New Horizons could detect its presence.
But then, we really can’t be sure if this atmosphere truly vanishes when the planet is farthest from the Sun, as we have only so far observed 96 years in Pluto’s 248-year orbit.
French startup The Exploration Company completes first splashdown tests of Nyx capsule prototype
The French cargo capsule startup, The Exploration Company, has successfully completed the first splashdown tests of a smallscate prototype model of its proposed Nyx capsule.
On 5 February, The Exploration Company announced that it had successfully completed a splashdown test campaign at the National Research Council’s Institute of Marine Engineering (CNR-INM) in Rome.
A 1:4-scale mockup of Nyx, with a mass of around 135 kilograms, was built for the test campaign by Poli Model, a small Turin-based model builder. For reference, the full-scale capsule will be 4 metres wide and stand at 7 metres tall. The subscale model’s exterior was fitted with pressure sensors, accelerometers, and a gyroscope.
The tests were conducted in the CNR-INM facility’s Umberto Pugliese towing tank, a 470-metre-long pool measuring 13.5 metres across and 6.5 metres deep. Between 13 and 28 January, a total of 20 drops were conducted at varying heights and speeds in calm water, which the company explained maximised repeatability.
The company hopes to fly a fullscale demo mission to ISS in 2028, and wants to upgrade Nyx to manned capabilities in the 2030s.
The French cargo capsule startup, The Exploration Company, has successfully completed the first splashdown tests of a smallscate prototype model of its proposed Nyx capsule.
On 5 February, The Exploration Company announced that it had successfully completed a splashdown test campaign at the National Research Council’s Institute of Marine Engineering (CNR-INM) in Rome.
A 1:4-scale mockup of Nyx, with a mass of around 135 kilograms, was built for the test campaign by Poli Model, a small Turin-based model builder. For reference, the full-scale capsule will be 4 metres wide and stand at 7 metres tall. The subscale model’s exterior was fitted with pressure sensors, accelerometers, and a gyroscope.
The tests were conducted in the CNR-INM facility’s Umberto Pugliese towing tank, a 470-metre-long pool measuring 13.5 metres across and 6.5 metres deep. Between 13 and 28 January, a total of 20 drops were conducted at varying heights and speeds in calm water, which the company explained maximised repeatability.
The company hopes to fly a fullscale demo mission to ISS in 2028, and wants to upgrade Nyx to manned capabilities in the 2030s.
Israeli weather satellite startup raises $175 million in investment capital
An Israeli weather satellite startup, dubbed Tomorrow.io, has now raised $175 million in investment capital to build an AI-driven constellation of satellites to supplement the smallsat constellation it has already launched.
This financing builds on a proven foundation of execution. Tomorrow.io has completed the full deployment of its first satellite constellation, having launched 13 satellites to space, achieving 60-minute global revisit, while scaling an AI-driven intelligence platform now embedded across critical industries. DeepSky extends this foundation into the next phase of the company’s roadmap, supporting continued commercial growth, expanding data coverage, and unlocking new high-frequency sensing capabilities.
I find amusing this new desire to label all computer programming “AI”, when in many cases it is simply the same software slightly upgraded that these companies have been using for years.
Nonetheless, this story signals the continuing transition in the weather satellite industry from the government/Soviet-style model, where all weather satellites are built and operated by governments, to the capitalism model, where governments and industry buy weather data from privately built, launched, and maintained commercial constellations.
An Israeli weather satellite startup, dubbed Tomorrow.io, has now raised $175 million in investment capital to build an AI-driven constellation of satellites to supplement the smallsat constellation it has already launched.
This financing builds on a proven foundation of execution. Tomorrow.io has completed the full deployment of its first satellite constellation, having launched 13 satellites to space, achieving 60-minute global revisit, while scaling an AI-driven intelligence platform now embedded across critical industries. DeepSky extends this foundation into the next phase of the company’s roadmap, supporting continued commercial growth, expanding data coverage, and unlocking new high-frequency sensing capabilities.
I find amusing this new desire to label all computer programming “AI”, when in many cases it is simply the same software slightly upgraded that these companies have been using for years.
Nonetheless, this story signals the continuing transition in the weather satellite industry from the government/Soviet-style model, where all weather satellites are built and operated by governments, to the capitalism model, where governments and industry buy weather data from privately built, launched, and maintained commercial constellations.
Astronomers use SphereX infrared space telescope to study interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas

False color images of SphereX infrared data.
Click for original.
Using NASA’s SphereX infrared space telescope, astronomers have now detected a range of new molecules in the coma surround interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas as that coma brightened and grew in December 2025 following the comet’s closest approach to the Sun in the fall.
You can read the research paper here. From the press release:
In a new research note, mission scientists describe the detection of organic molecules, such as methanol, cyanide, and methane. On Earth, organic molecules are the foundation for biological processes but can be created by non-biological processes as well. The researchers also note a dramatic increase in brightness two months after the icy body had passed its closest distance to the Sun, a phenomenon associated with comets as they vent water, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide into space.
In every way this interstellar object continues to behave like an ordinary comet, which is actually quite profound. It tells us the rest of the universe is not that different than our solar system.

False color images of SphereX infrared data.
Click for original.
Using NASA’s SphereX infrared space telescope, astronomers have now detected a range of new molecules in the coma surround interstellar Comet 3I/Atlas as that coma brightened and grew in December 2025 following the comet’s closest approach to the Sun in the fall.
You can read the research paper here. From the press release:
In a new research note, mission scientists describe the detection of organic molecules, such as methanol, cyanide, and methane. On Earth, organic molecules are the foundation for biological processes but can be created by non-biological processes as well. The researchers also note a dramatic increase in brightness two months after the icy body had passed its closest distance to the Sun, a phenomenon associated with comets as they vent water, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide into space.
In every way this interstellar object continues to behave like an ordinary comet, which is actually quite profound. It tells us the rest of the universe is not that different than our solar system.
German rocket startup Isar Aerospace opens new rocket testing facility at Esrange spaceport

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
Though the German rocket startup Isar Aerospace is using Norway’s Andoya spaceport to launch its Spectrum rocket, it is now expanding significantly its testing facilities at Sweden’s Esrange spaceport to the east.
European space company Isar Aerospace is significantly expanding their testing operations with SSC Space at Esrange Space Center in Sweden, opening a second test site to support the development and production of its ‘Spectrum’ rocket. The new facility will enable testing of 30+ engines per month, along with expanded integrated stage testing capabilities, increasing testing capacity and enabling faster development.
Launching from Esrange is a problem because of its interior location, but testing engines there, close to Germany and the Andoya spaceport makes great sense.
Isar had hoped to make its second attempt to complete the first orbital launch of Spectrum in January, but postponed the launch until March to deal with a valve issue.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay.

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
Though the German rocket startup Isar Aerospace is using Norway’s Andoya spaceport to launch its Spectrum rocket, it is now expanding significantly its testing facilities at Sweden’s Esrange spaceport to the east.
European space company Isar Aerospace is significantly expanding their testing operations with SSC Space at Esrange Space Center in Sweden, opening a second test site to support the development and production of its ‘Spectrum’ rocket. The new facility will enable testing of 30+ engines per month, along with expanded integrated stage testing capabilities, increasing testing capacity and enabling faster development.
Launching from Esrange is a problem because of its interior location, but testing engines there, close to Germany and the Andoya spaceport makes great sense.
Isar had hoped to make its second attempt to complete the first orbital launch of Spectrum in January, but postponed the launch until March to deal with a valve issue.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay.
Midnight repost: Truth, Justice, and the American Way
Tonight Diane and I decided to watch again the 1978 Richard Donner movie, Superman. The overall film is lighthearted entertainment that captures the myth of this super-hero perfectly. However, it has two scenes that remain among the best moments in movie history (which you can watch here and here). The first captures the myth in every way. The second shows us that Superman truly stood for the best in America.
In watching the movie tonight again and reliving the myth I grew up with — that great things are possible if you believe and follow sincerely Superman’s motto of “truth, justice, and the American way” — I decided to repost my essay from 2020 where I attempted to explain what that motto really meant.
Enjoy!
———————

George Reeves as the heroic Superman as envisioned
in the 1950s television show, emulated later by Richard
Donner in his 1978 movie. Click for show’s opening credits.
Truth, Justice, and the American Way
The words spoken during the opening credits of a 1950s children’s television show:
Faster than a speeding bullet.
More powerful than a locomotive.
Able to leap tall buildings in a single bound.
Look up in the sky!
It’s a bird.
It’s a plane.
It’s Superman!
Yes, it’s Superman, strange visitor from another planet who came to Earth with powers and abilities far beyond those of mortal men.
Superman, who can change the course of mighty rivers, bend steel in his bare hands, and who, disguised as Clark Kent, mild-mannered reporter for a great metropolitan newspaper, fights a never-ending battle for truth, justice, and the American Way.
That television show was obviously Superman, starring George Reeves, and these opening words expressed the mythology and basic ideals by which this most popular of all comic-book super-heroes lived.
I grew up with those words. They had been bequeathed to me by the American generation that had fought and won World War II against the genocidal Nazis, and expressed the fundamental ideals of that generation.
Much of the meaning of these fundamental ideals is outright and clear.
» Read more
February 4, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Uncovered Past – Traditional charcoal making
An evening pause: It always amazes me the level of engineering sophistication that one finds in all human endeavor, even from centuries past.
Hat tip Cotour.
SpaceX wants revisions to federal rural grant program that has awarded it $733 million
SpaceX is presently asking for changes in the Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program that awards grants to companies that provide internet in rural areas and has already awarded the company $733 million in grants.
BEAD was part of the Biden administration’s bipartisan infrastructure act – originally a $42 billion program to bring broadband internet to areas of the country with little or no broadband access. The Trump administration eliminated other infrastructure act programs, and cut BEAD outlays to $21 billion, along with rule changes to allow satellite providers.
SpaceX applied for BEAD funds in 2025. The company won $733 million worth of BEAD projects nationwide, including $109 million in Texas.
Initially the Biden administration awarded SpaceX almost a billion dollar grant, because its Starlink constellation was the only broadband outlet actually doing the job. Then Musk began to campaign for Republicans, and suddenly the Biden administration pulled that grant, saying absurdly that SpaceX was failing to provide its service to rural areas, when that was exactly what it was doing.
Now SpaceX wants BEAD to ease some of its requirements, and wants these grant funds upfront.
I say, this whole BEAD program is a waste of taxpayer money and a perfect example of crony capitalism. I’m glad Trump cut it in half, but that wasn’t good enough. It should be shut down entirely. SpaceX doesn’t need this handout. It is making money hand-over-fist on its own.
SpaceX is presently asking for changes in the Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) program that awards grants to companies that provide internet in rural areas and has already awarded the company $733 million in grants.
BEAD was part of the Biden administration’s bipartisan infrastructure act – originally a $42 billion program to bring broadband internet to areas of the country with little or no broadband access. The Trump administration eliminated other infrastructure act programs, and cut BEAD outlays to $21 billion, along with rule changes to allow satellite providers.
SpaceX applied for BEAD funds in 2025. The company won $733 million worth of BEAD projects nationwide, including $109 million in Texas.
Initially the Biden administration awarded SpaceX almost a billion dollar grant, because its Starlink constellation was the only broadband outlet actually doing the job. Then Musk began to campaign for Republicans, and suddenly the Biden administration pulled that grant, saying absurdly that SpaceX was failing to provide its service to rural areas, when that was exactly what it was doing.
Now SpaceX wants BEAD to ease some of its requirements, and wants these grant funds upfront.
I say, this whole BEAD program is a waste of taxpayer money and a perfect example of crony capitalism. I’m glad Trump cut it in half, but that wasn’t good enough. It should be shut down entirely. SpaceX doesn’t need this handout. It is making money hand-over-fist on its own.
February 4, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast’s Haven Demo satellite successfully completes initial de-orbit burn
Video at the link. The burn proves the company’s technology for doing these kinds of maneuvers on its upcoming Haven-1 station
- Space Forge’s ForgeStar-1 orbiting furnace generates plasma
This is demonstration technology for manufacturing pure products in space for sale on Earth that can only be made in weightlessness, such as advanced crystals and semiconductor chips
- An image of China’s next generation Mengzhou manned capsule being lifted up onto a Long March 10A test stage
China hopes to do a test orbital launch of the rocket and capsule this year.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast’s Haven Demo satellite successfully completes initial de-orbit burn
Video at the link. The burn proves the company’s technology for doing these kinds of maneuvers on its upcoming Haven-1 station
- Space Forge’s ForgeStar-1 orbiting furnace generates plasma
This is demonstration technology for manufacturing pure products in space for sale on Earth that can only be made in weightlessness, such as advanced crystals and semiconductor chips
- An image of China’s next generation Mengzhou manned capsule being lifted up onto a Long March 10A test stage
China hopes to do a test orbital launch of the rocket and capsule this year.
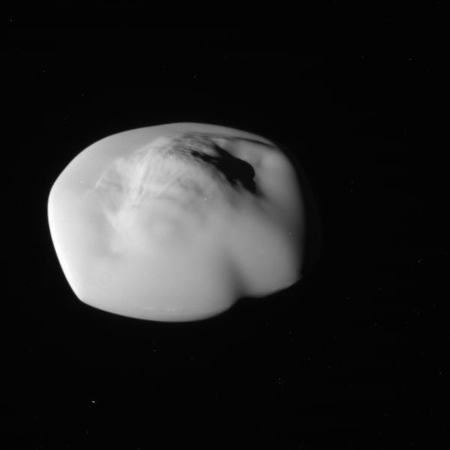
One of Saturn’s many weird moons
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 13, 2017 by the orbiter Cassini as it began it last close loops around Saturn before diving into its atmosphere to burn up.
Those close loops allowed it to get good close-up images of a few of the tiny moons that orbit in or close to the gas giant’s rings. On the right is one of those pictures, of the moon Atlas, taken from a distance of about 10,000 miles.
The moon’s weird ravioli shape is thought to be caused by the accretion of dust and ice from the nearby rings along Atlas’s equator.
Scientists also found the moon surfaces to be highly porous, further confirming that they were formed in multiple stages as ring material settled onto denser cores that might be remnants of a larger object that broke apart. The porosity also helps explain their shape: Rather than being spherical, they are blobby and ravioli-like, with material stuck around their equators. “We found these moons are scooping up particles of ice and dust from the rings to form the little skirts around their equators,” Buratti said. “A denser body would be more ball-shaped because gravity would pull the material in.”
Atlas itself is about 25 miles wide and about 11.5 miles thick, at its thickest point. I suspect if you tried to walk on it you would sink into the accumulated dust and ice, as it is likely no more dense as newly fallen snow.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 13, 2017 by the orbiter Cassini as it began it last close loops around Saturn before diving into its atmosphere to burn up.
Those close loops allowed it to get good close-up images of a few of the tiny moons that orbit in or close to the gas giant’s rings. On the right is one of those pictures, of the moon Atlas, taken from a distance of about 10,000 miles.
The moon’s weird ravioli shape is thought to be caused by the accretion of dust and ice from the nearby rings along Atlas’s equator.
Scientists also found the moon surfaces to be highly porous, further confirming that they were formed in multiple stages as ring material settled onto denser cores that might be remnants of a larger object that broke apart. The porosity also helps explain their shape: Rather than being spherical, they are blobby and ravioli-like, with material stuck around their equators. “We found these moons are scooping up particles of ice and dust from the rings to form the little skirts around their equators,” Buratti said. “A denser body would be more ball-shaped because gravity would pull the material in.”
Atlas itself is about 25 miles wide and about 11.5 miles thick, at its thickest point. I suspect if you tried to walk on it you would sink into the accumulated dust and ice, as it is likely no more dense as newly fallen snow.
A nice summary of all space-based research of reproduction in space
Link here to the press release. The paper itself can be read here.
The paper is an excellent summary of practically all the research that has been done in space and on the ground studying the impact of the harsh environment of space on reproduction. It notes above all that we really know very little despite this research, because the risks to the newborn have precluded direct study. From the paper’s abstract:
Despite over 65 years of human spaceflight activities, little is known of the impact of the space environment on the human reproductive systems during long-duration missions. Extended time in space poses potential hazards to the reproductive function of female and male astronauts, including exposure to cosmic radiation, altered gravity, psychological and physical stress, and disruption to circadian rhythm.
This review encapsulates current understanding of the effects of spaceflight on reproductive physiology, incorporating findings from animal studies, a recent experiment on sperm motility, and omics-based insights from astronaut physiology. Female reproductive systems appear to be especially vulnerable, with implications for oogenesis and embryonic development in microgravity. Male reproductive function reveals compromised DNA integrity, even when motility appears to be preserved. This review examines the limited embryogenesis studies in space, which show frequent abnormal cell division and impaired development in rodents.
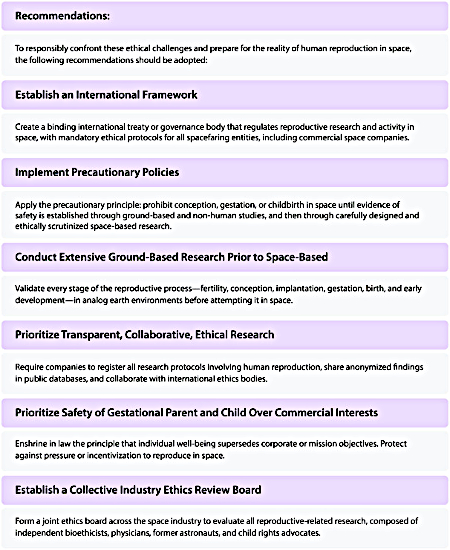
In the paper’s conclusion, these academics sadly revert to type, and propose the establishment of an international regulatory framework for controlling this issue, as shown in the graphic to the right. This is empty foolishness, because such regulations will only do more harm than good, stifling research while failing to accomplish anything.
Link here to the press release. The paper itself can be read here.
The paper is an excellent summary of practically all the research that has been done in space and on the ground studying the impact of the harsh environment of space on reproduction. It notes above all that we really know very little despite this research, because the risks to the newborn have precluded direct study. From the paper’s abstract:
Despite over 65 years of human spaceflight activities, little is known of the impact of the space environment on the human reproductive systems during long-duration missions. Extended time in space poses potential hazards to the reproductive function of female and male astronauts, including exposure to cosmic radiation, altered gravity, psychological and physical stress, and disruption to circadian rhythm.
This review encapsulates current understanding of the effects of spaceflight on reproductive physiology, incorporating findings from animal studies, a recent experiment on sperm motility, and omics-based insights from astronaut physiology. Female reproductive systems appear to be especially vulnerable, with implications for oogenesis and embryonic development in microgravity. Male reproductive function reveals compromised DNA integrity, even when motility appears to be preserved. This review examines the limited embryogenesis studies in space, which show frequent abnormal cell division and impaired development in rodents.
In the paper’s conclusion, these academics sadly revert to type, and propose the establishment of an international regulatory framework for controlling this issue, as shown in the graphic to the right. This is empty foolishness, because such regulations will only do more harm than good, stifling research while failing to accomplish anything.
Commercial changes at France’s French Guiana spaceport
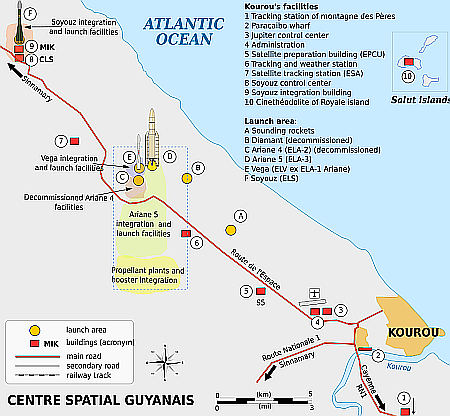
The French Guiana spaceport. The Diamant launchsite is labeled “B.”
Click for full resolution image. (Note: The Ariane-5 pad is now the
Ariane-6 pad.)
Once France’s space agency CNES regained control of its spaceport in French Guiana several years ago from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial pseudo-company Arianespace, it has moved aggressively to make that spaceport attractive to the new European rocket startups.
Beginning in 2022, it began to sign deals with every one of those rocket startups to allow them to establish launch facilities at the spaceport using several long abandoned pads, including the French Diamant rocket site not used for decades as well as the Soyuz launch site unused due to Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine.
CNES decided to standardize Diamant for multiple rocket companies, while leasing the Soyuz site to one.
In a news story today, it appears the startup MaiaSpace, a wholly owned subsidiary of the much larger aerospace company ArianeGroupk, has shifted its launch plans at French Guiana. Initially it was going to launch its rocket from the Diamant pad. In 2024 however it won the contract to use the Soyuz pad, and it has now withdrawn its plans to use Diamant entirely.
CNES has therefore put out a call to the European rocket industry to fill this slot at Diamant. At present Isar Aerospace, PLD Space, Rocket Factory Augsburg, and Latitude have agreements to use Diamant, though only Latitude and PLD had done any development work on their facilities there.
As far as I know, these companies comprise the entire cadre of new European rocket startups, so I don’t know what other users CNES hopes to find. Furthermore, CNES had wanted to standardize the launch site for everyone, and the companies had balked at that idea. PLD got a deal to use its own pad at Diamant. I suspect the reason Isar and Rocket Factory have done little there is because they want their own facilities as well.
Either way, French Guiana is moving the direction of supporting competitive commercial operations, and that is a very good thing.

The French Guiana spaceport. The Diamant launchsite is labeled “B.”
Click for full resolution image. (Note: The Ariane-5 pad is now the
Ariane-6 pad.)
Once France’s space agency CNES regained control of its spaceport in French Guiana several years ago from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) commercial pseudo-company Arianespace, it has moved aggressively to make that spaceport attractive to the new European rocket startups.
Beginning in 2022, it began to sign deals with every one of those rocket startups to allow them to establish launch facilities at the spaceport using several long abandoned pads, including the French Diamant rocket site not used for decades as well as the Soyuz launch site unused due to Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine.
CNES decided to standardize Diamant for multiple rocket companies, while leasing the Soyuz site to one.
In a news story today, it appears the startup MaiaSpace, a wholly owned subsidiary of the much larger aerospace company ArianeGroupk, has shifted its launch plans at French Guiana. Initially it was going to launch its rocket from the Diamant pad. In 2024 however it won the contract to use the Soyuz pad, and it has now withdrawn its plans to use Diamant entirely.
CNES has therefore put out a call to the European rocket industry to fill this slot at Diamant. At present Isar Aerospace, PLD Space, Rocket Factory Augsburg, and Latitude have agreements to use Diamant, though only Latitude and PLD had done any development work on their facilities there.
As far as I know, these companies comprise the entire cadre of new European rocket startups, so I don’t know what other users CNES hopes to find. Furthermore, CNES had wanted to standardize the launch site for everyone, and the companies had balked at that idea. PLD got a deal to use its own pad at Diamant. I suspect the reason Isar and Rocket Factory have done little there is because they want their own facilities as well.
Either way, French Guiana is moving the direction of supporting competitive commercial operations, and that is a very good thing.
Midnight repost: Genocide is coming to America
Today I came across this tweet:
The comparison between the tactics of the Nazi storm troopers and our modern Antifa thugs is apt. It illustrates the time we now live in. It also immediately made me want to repost my 2020 essay, Genocide is coming to America. That essay sadly remains pertinent, because the same unwillingness of decent Germans to believe the Nazis were a threat is the same unwillingness of too many modern Americans to believe the same thing about Antifa and the Democratic Party (which now enthusiastically uses Antifa as its storm troopers).
Worse, we now have a large minority of Americans who support this violent behavior. To them, violence is wholly justified against those who disagree with them. The proof of this horrible fact was demonstrated in the 2025 elections, where in Virginia a Democrat won his election despite openly wishing death not only on a Republican but on that Republican’s children, while in New York an anti-Semitic communist won election as mayor.
————————-
Genocide is coming to America
In my last visit to Israel in 2018, my brother and sister-in-law took me sight-seeing to the northern parts of Israel near the Sea of Galilee. On our first night, we stayed at the home of one of their older friends, a man in his seventies.
That night we sat around their kitchen table so that they could catch up on family matters. At one point in the conversation our host reminisced about an older woman, now gone, who he had known in his childhood in the 1950s who had lived in Germany before and during World War II and had survived a concentration camp.
» Read more
Judy Garland -Trolley Song
An evening pause: From the 1944 film, Meet me in St. Louis. I posted this in July 2010 as one of the very first evening pauses. As I wrote then, “The last line of the song says it all, about life and love.”
Hat tip to Judd Clark, who suggested it, which convinced me it was time to post it again.
February 3, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast touts its full-scale life support testing for its Haven-1 single module space station
It is my understanding that some of these life support functions will be handled by the Dragon capsule that brings up the crew.
- House NASA authorization bill demands numerous reports and paperwork
While it is good Congress wants to maintain oversight, this bill simply forces NASA to write seven reports (essentially paperwork) that will add little knowledge not already in public domain and that no one will read.
- On this day in 1956 the Soviet Union launched the world’s first ballistic missile carrying a nuclear warhead
The R-5M rocket flew 740 miles in 10.5 minutes, delivering a nuclear warhead to the Aral Karakum region with a yield of 300 tons of TNT.
- On this day in 1966 the Soviet Union’s Luna 9 became the world’s first spacecraft to land on the Moon and function thereafter
It returned data for three days. The landing was not soft, as the spacecraft used giant airbags to protect it as it hit the ground hard and bounced several times.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Vast touts its full-scale life support testing for its Haven-1 single module space station
It is my understanding that some of these life support functions will be handled by the Dragon capsule that brings up the crew.
- House NASA authorization bill demands numerous reports and paperwork
While it is good Congress wants to maintain oversight, this bill simply forces NASA to write seven reports (essentially paperwork) that will add little knowledge not already in public domain and that no one will read.
- On this day in 1956 the Soviet Union launched the world’s first ballistic missile carrying a nuclear warhead
The R-5M rocket flew 740 miles in 10.5 minutes, delivering a nuclear warhead to the Aral Karakum region with a yield of 300 tons of TNT.
- On this day in 1966 the Soviet Union’s Luna 9 became the world’s first spacecraft to land on the Moon and function thereafter
It returned data for three days. The landing was not soft, as the spacecraft used giant airbags to protect it as it hit the ground hard and bounced several times.
Isaacman: SLS stands on very thin ice
Though NASA administration Jared Isaacman continues to support unequivocally NASA’s planned Artemis-2 ten-day manned mission around the Moon — presently targeting a March launch date — in a statement today on X he revealed that he also recognizes the serious limitations of the SLS rocket.
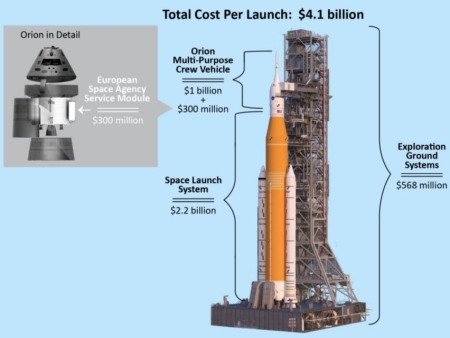
And it also takes two-plus years between launches
The Artemis vision began with President Trump, but the SLS architecture and its components long predate his administration, with much of the heritage clearly traced back to the Shuttle era. As I stated during my hearings, and will say again, this is the fastest path to return humans to the Moon and achieve our near-term objectives through at least Artemis V, but it is not the most economic path and certainly not the forever path.
The flight rate is the lowest of any NASA-designed vehicle, and that should be a topic of discussion. It is why we undertake wet dress rehearsals, Pre-FRR, and FRR, and why we will not press to launch until we are absolutely ready.
These comments were also in connection with the first wet dress rehearsal countdown that NASA performed with SLS/Orion in the past few days, a rehearsal that had to be terminated early because of fuel leaks. NASA now plans to do another wet dress rehearsal, requiring it to push back the Artemis-2 launch until March.
I think there is more going on here than meets the eye.
» Read more
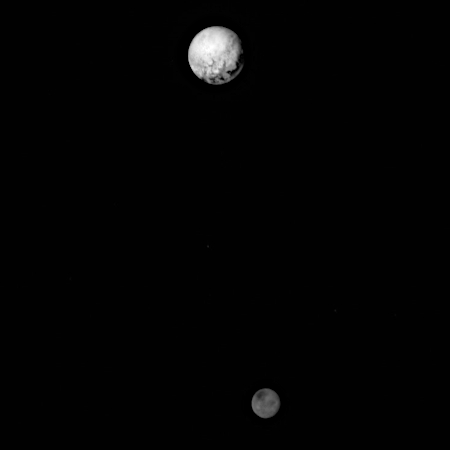
Pluto and Charon come out of the dark
Cool image time! I have decided to start delving into the archives of some of the older planetary missions, because there is value there that is often forgotten now years later, that should not be forgotten.
In looking through the archive of images from the main camera on New Horizons as it sped past Pluto in July 2015, I found the picture to the right, taken on July 10, 2015 when New Horizons was still about three million miles away.
This is the raw image from that camera, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. It is also the first time in human history we had a sharp look at these two planets that sit at the outer fringes of the solar system. The science team that day released a version that they enhanced to bring out the details, which I immediately posted. They then noted the following:
A high-contrast array of bright and dark features covers Pluto’s surface, while on Charon, only a dark polar region interrupts a generally more uniform light gray terrain. The reddish materials that color Pluto are absent on Charon. Pluto has a significant atmosphere; Charon does not. On Pluto, exotic ices like frozen nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide have been found, while Charon’s surface is made of frozen water and ammonia compounds. The interior of Pluto is mostly rock, while Charon contains equal measures of rock and water ice. “These two objects have been together for billions of years, in the same orbit, but they are totally different,” said Principal Investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, Colorado.
This difference is quite clear in the raw image, with Charon markedly dimmer than Pluto even though they are getting the same amount of light from the Sun.
More than any other objects in the solar system, the double planet system of Pluto-Charon demonstrates how uniquely different every object in the solar system is from every other object. Even when formed together, as these two planets were, they formed in a manner that made them drastically different.
Cool image time! I have decided to start delving into the archives of some of the older planetary missions, because there is value there that is often forgotten now years later, that should not be forgotten.
In looking through the archive of images from the main camera on New Horizons as it sped past Pluto in July 2015, I found the picture to the right, taken on July 10, 2015 when New Horizons was still about three million miles away.
This is the raw image from that camera, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. It is also the first time in human history we had a sharp look at these two planets that sit at the outer fringes of the solar system. The science team that day released a version that they enhanced to bring out the details, which I immediately posted. They then noted the following:
A high-contrast array of bright and dark features covers Pluto’s surface, while on Charon, only a dark polar region interrupts a generally more uniform light gray terrain. The reddish materials that color Pluto are absent on Charon. Pluto has a significant atmosphere; Charon does not. On Pluto, exotic ices like frozen nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide have been found, while Charon’s surface is made of frozen water and ammonia compounds. The interior of Pluto is mostly rock, while Charon contains equal measures of rock and water ice. “These two objects have been together for billions of years, in the same orbit, but they are totally different,” said Principal Investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, Colorado.
This difference is quite clear in the raw image, with Charon markedly dimmer than Pluto even though they are getting the same amount of light from the Sun.
More than any other objects in the solar system, the double planet system of Pluto-Charon demonstrates how uniquely different every object in the solar system is from every other object. Even when formed together, as these two planets were, they formed in a manner that made them drastically different.
Lawrence of Arabia: Truth is sometimes stranger than fiction
One of the 20th century’s greatest movies is David Lean’s 1962 epic Lawrence of Arabia. The story it tells — of the clash of cultures, of war, and of colonization — combined with the personal story of T.E. Lawrence during World War I, is one of high drama that is unforgettable to anyone who has ever seen it.
Yet, the events it tells seem too dramatic to be believed. Did Lawrence actually rescue a man in the desert, by himself and against the advice of his Arab allies who knew better? Did he actually later execute that man coldly to prevent a tribal war that would have destroyed the Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire? Did he actually lead those Arab tribes across a deadly desert to take the town of Aqaba from the rear?
And did he actually lead that Arab revolt so successfully that it took Damascus ahead of the British, only to lose it because that medieval tribal culture knew nothing about modern technology?
For years I wondered about these questions and tried to find out. I read T.E. Lawrence’s own memoir of his time there, The Seven Pillars of Wisdom, and found it to be unclear and obscure, answering none of my questions. Other histories about World War I merely touched upon these events, treating them as a minor side show. And histories about the Middle East during that time seemed uninterested in telling this part of the story.
So, the questions remained: Did these events really happen? They seemed too good to be true.
I have now discovered that these stories are not only largely true, the reality of T.E. Lawrence’s life and his time in Arabia was even stranger than I could suppose. I learned this from Scott Anderson’s fine biography of Lawrence, Lawrence in Arabia: War, Deceit, Imperial Folly, and the Making of the Modern Middle East. Anderson not only unveiled Lawrence in all his inexplicable glory in this book, he made clear the complex political background that shaped the Middle East, and made it as we know it today.
» Read more
Dumb science: Researchers claim Jupiter is 0.0028% thinner than previously measured
Stupidity on display: According to researchers using data from the Jupiter orbiter Juno, Jupiter is a tiny bit thinner at the equator and flatter at the poles than previously measured.
Leading an international team from Italy, the United States, France and Switzerland, Weizmann Institute of Science researchers [Israel] have produced more precise measurements of Jupiter’s size and shape than ever before, using new data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
The peer-reviewed research, published today in Nature Astronomy, shows that the radius of Jupiter is about four kilometers (2.5 miles) thinner at its equator and 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) flatter at the poles than believed in earlier assessments. The scientists determined the planet has a radius of 71,484 kilometers (44,418 miles). Earlier data measured it at 71,492 kilometers (44,423 miles).
The absurdity of this research is galling. The revision they claim is tiny, a mere 0.0028% difference at the equator, and 0.0084% at the poles. These numbers are insignificant. Moreover, Jupiter is a gas giant. It has no precisely known surface. Instead, it has an atmosphere that gradually thins as you go up. To claim any precise diameter is absurd, especially because seasonally and over time that atmosphere will expand and shrink.
And of course, at least two mainstream news outlets, Scientific American and The Times of Israel (linked above), report this story without any skepticism, as if this is a Earth-shaking discovery. All that tells me is that when it comes to science, both are incompetent sources of information.
Stupidity on display: According to researchers using data from the Jupiter orbiter Juno, Jupiter is a tiny bit thinner at the equator and flatter at the poles than previously measured.
Leading an international team from Italy, the United States, France and Switzerland, Weizmann Institute of Science researchers [Israel] have produced more precise measurements of Jupiter’s size and shape than ever before, using new data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft.
The peer-reviewed research, published today in Nature Astronomy, shows that the radius of Jupiter is about four kilometers (2.5 miles) thinner at its equator and 12 kilometers (7.5 miles) flatter at the poles than believed in earlier assessments. The scientists determined the planet has a radius of 71,484 kilometers (44,418 miles). Earlier data measured it at 71,492 kilometers (44,423 miles).
The absurdity of this research is galling. The revision they claim is tiny, a mere 0.0028% difference at the equator, and 0.0084% at the poles. These numbers are insignificant. Moreover, Jupiter is a gas giant. It has no precisely known surface. Instead, it has an atmosphere that gradually thins as you go up. To claim any precise diameter is absurd, especially because seasonally and over time that atmosphere will expand and shrink.
And of course, at least two mainstream news outlets, Scientific American and The Times of Israel (linked above), report this story without any skepticism, as if this is a Earth-shaking discovery. All that tells me is that when it comes to science, both are incompetent sources of information.
India schedules next PSLV launch for June, claims it knows cause of January launch failure

India’s space agency ISRO,
as transparent as mud
According to a statement by a government minister yesterday, India’s space agency ISRO now knows what caused the January launch failure of its PSLV rocket, and has thus scheduled its next launch for June 2026.
This had been the second PSLV launch failure in a row, both of which occurred with the rocket’s third stage at almost the exact same time. With the first failure, ISRO never outlined publicly the cause, though it claimed it had solved the issue. According to the minister’s statement, the failure of the second launch was unrelated to the first.
The minister also said that the two PSLV missions that had failed—PSLV-C61 in May 2025 and PSLV-C62 in January this year—were unrelated. “It wasn’t the same problem. When the first mission failed, there was a detailed assessment, and the problem was fixed. Both the issues were different,” Singh said.
He also added that separate internal and external failure assessment committees have been set up to analyse what went wrong in each of the missions.
No word however as to the cause of the failure has yet been released. Though he also claimed the PSLV has not lost its customers due to these issues, ISRO’s lack of transparency says otherwise. If it claims the two failures came from different causes, it should provide the details in order to reassure potential customers.

India’s space agency ISRO,
as transparent as mud
According to a statement by a government minister yesterday, India’s space agency ISRO now knows what caused the January launch failure of its PSLV rocket, and has thus scheduled its next launch for June 2026.
This had been the second PSLV launch failure in a row, both of which occurred with the rocket’s third stage at almost the exact same time. With the first failure, ISRO never outlined publicly the cause, though it claimed it had solved the issue. According to the minister’s statement, the failure of the second launch was unrelated to the first.
The minister also said that the two PSLV missions that had failed—PSLV-C61 in May 2025 and PSLV-C62 in January this year—were unrelated. “It wasn’t the same problem. When the first mission failed, there was a detailed assessment, and the problem was fixed. Both the issues were different,” Singh said.
He also added that separate internal and external failure assessment committees have been set up to analyse what went wrong in each of the missions.
No word however as to the cause of the failure has yet been released. Though he also claimed the PSLV has not lost its customers due to these issues, ISRO’s lack of transparency says otherwise. If it claims the two failures came from different causes, it should provide the details in order to reassure potential customers.
NASA makes right decision and delays Artemis-2 launch to do a 2nd dress rehearsal countdown

NASA management announced today that it has decided to postpone the launch of the manned Artemis-2 mission around the Moon until March in order to give it time to do a second wet dress rehearsal countdown of the rocket and fix the hydrogen fuel leaks that occurred in yesterday’s rehearsal.
Engineers pushed through several challenges during the two-day test and met many of the planned objectives. To allow teams to review data and conduct a second wet dress rehearsal, NASA now will target March as the earliest possible launch opportunity for the flight test.
Moving off a February launch window also means the Artemis II astronauts will be released from quarantine, which they entered in Houston on Jan. 21. As a result, they will not travel to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida Tuesday as tentatively planned. Crew will enter quarantine again about two weeks out from the next targeted launch opportunity.
It should be understood that these hydrogen leaks have been systemic to SLS’s core stage rocket engines, which come from the shuttle era. Shuttle launches were routinely delayed due to similar leaks. This was partly because hydrogen is extremely difficult to control, as its atom is so small and light, and partly because of the engine design. This was the first rocket system ever to use hydrogen as fuel, and was thus cutting edge, in the 1970s. We should not be surprised by such issues.
Newer hydrogen-fueled designs have apparently overcome the problem. For example, Blue Origin uses hydrogen as a fuel in the upper stage of its New Glenn rocket, and though it has only launched twice, it has not had such issues on either launch.
In its announcement NASA also noted a bunch of other issues that occurred during this first rehearsal, all of which suggest that a delay is called for. There was a valve issue in the Orion capsule, some audio communication channels kept dropping out, and the cold weather affected some equipment. Waiting until warmer weather will help alleviate some of this.

NASA management announced today that it has decided to postpone the launch of the manned Artemis-2 mission around the Moon until March in order to give it time to do a second wet dress rehearsal countdown of the rocket and fix the hydrogen fuel leaks that occurred in yesterday’s rehearsal.
Engineers pushed through several challenges during the two-day test and met many of the planned objectives. To allow teams to review data and conduct a second wet dress rehearsal, NASA now will target March as the earliest possible launch opportunity for the flight test.
Moving off a February launch window also means the Artemis II astronauts will be released from quarantine, which they entered in Houston on Jan. 21. As a result, they will not travel to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida Tuesday as tentatively planned. Crew will enter quarantine again about two weeks out from the next targeted launch opportunity.
It should be understood that these hydrogen leaks have been systemic to SLS’s core stage rocket engines, which come from the shuttle era. Shuttle launches were routinely delayed due to similar leaks. This was partly because hydrogen is extremely difficult to control, as its atom is so small and light, and partly because of the engine design. This was the first rocket system ever to use hydrogen as fuel, and was thus cutting edge, in the 1970s. We should not be surprised by such issues.
Newer hydrogen-fueled designs have apparently overcome the problem. For example, Blue Origin uses hydrogen as a fuel in the upper stage of its New Glenn rocket, and though it has only launched twice, it has not had such issues on either launch.
In its announcement NASA also noted a bunch of other issues that occurred during this first rehearsal, all of which suggest that a delay is called for. There was a valve issue in the Orion capsule, some audio communication channels kept dropping out, and the cold weather affected some equipment. Waiting until warmer weather will help alleviate some of this.