Clashing layers in Mars’ largest canyon
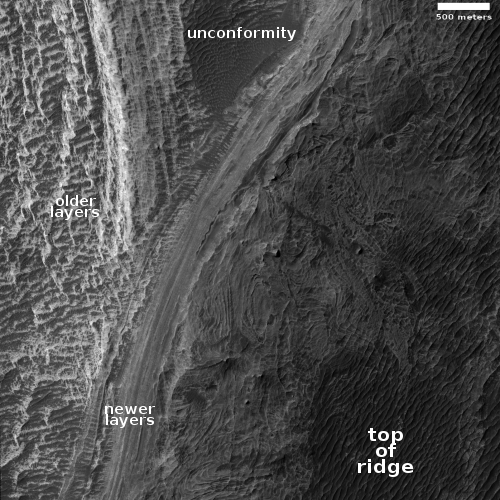
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on May 27, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows the clash of different layers on the western slope of a mountain within Mars’ largest canyon, Valles Marineris.
The scientist have labeled this a “possible angular unconformity.” In geology an unconformity generally refers to a gap in a series of layers, a period when instead of the layers being deposited they are being eroded away, leaving no record for that time period. An angular unconformity adds tilting to the older layers, which after erosion are then covered by new layers that are oriented somewhat differently.
Based on these definitions, what the scientists suspect is that the brighter layers to the left and lower down the mountain are older. After a period of erosion new layers were deposited on top at a different angle, forming the stripe of layers going from center left up to center right.
The swirly nature of the material on the top of the ridge suggests to me that these layers might be volcanic in nature, but that’s a pure uneducated guess. What some scientists do believe (but have not yet conclusively proven) is that the lower older layers are sediments laid down by an ancient lake that once filled the canyon here.
The overview map below provides a wider view and some context.
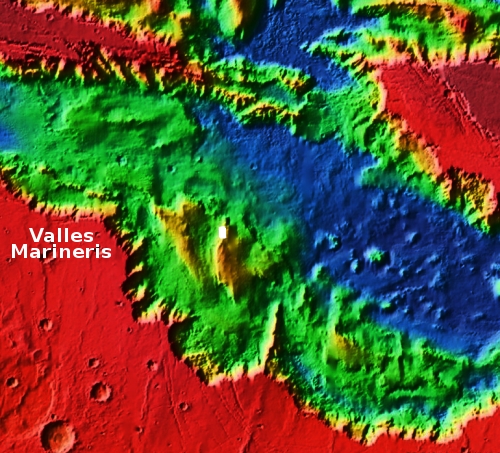
The white box marks the location of this image. This particular part of Valles Marineris is also its widest, and is dubbed Melas Chasma.
From this mountain slope the rims of Valles Marineris are a hundred miles away in both directions. The canyon itself is about 29,000 feet deep at this point, which means if placed at the canyon’s bottom the peak of Mount Everest would still be below the rim.
This particular mountain is itself somewhere between 16,000 to 19,000 feet high. If it was in the U.S. it would be among the nation’s highest peaks.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, was taken on May 27, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows the clash of different layers on the western slope of a mountain within Mars’ largest canyon, Valles Marineris.
The scientist have labeled this a “possible angular unconformity.” In geology an unconformity generally refers to a gap in a series of layers, a period when instead of the layers being deposited they are being eroded away, leaving no record for that time period. An angular unconformity adds tilting to the older layers, which after erosion are then covered by new layers that are oriented somewhat differently.
Based on these definitions, what the scientists suspect is that the brighter layers to the left and lower down the mountain are older. After a period of erosion new layers were deposited on top at a different angle, forming the stripe of layers going from center left up to center right.
The swirly nature of the material on the top of the ridge suggests to me that these layers might be volcanic in nature, but that’s a pure uneducated guess. What some scientists do believe (but have not yet conclusively proven) is that the lower older layers are sediments laid down by an ancient lake that once filled the canyon here.
The overview map below provides a wider view and some context.

The white box marks the location of this image. This particular part of Valles Marineris is also its widest, and is dubbed Melas Chasma.
From this mountain slope the rims of Valles Marineris are a hundred miles away in both directions. The canyon itself is about 29,000 feet deep at this point, which means if placed at the canyon’s bottom the peak of Mount Everest would still be below the rim.
This particular mountain is itself somewhere between 16,000 to 19,000 feet high. If it was in the U.S. it would be among the nation’s highest peaks.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News



“The canyon itself is about 29,000 feet deep at this point, which means if placed at the canyon’s bottom the peak of Mount Everest would still be below the rim.”
The generally accepted value for the height above sea level of Everest is 29,029 feet. I don’t mean to fuss over 29 whole feet, but you categorically state the peak would be below the rim, when it clearly would not be.
True, there is much discussion about the height of various mountains as measured along their own flanks. For example by this standard, Mt. Chimborazo of Ecuador is often cited as the “tallest” mountain.