Craters in the soft Martian northern lowland plains
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was a featured image today from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The caption, written by Carol Weitz of the Planetary Science Institute in Arizona, focused on the wind patterns created within these craters.
These impact craters in the northern middle latitudes have interesting interiors: all of them have wind-blown (aeolian) ripples.
Outside of the craters and along the crater floors, the ripples are all oriented in the same direction. However, along the walls of some of the larger craters, the ripples are situated radially away from the center, indicating the winds moving inside the larger craters can be influenced by the topography of the crater wall.
Additionally, many of the larger craters have layered mesas along their floors that are likely sedimentary deposits laid down after the craters formed but prior to the development of the aeolian ripples.
I am further intrigued by the rimless nature of these craters, as well as the lack of significant rocky debris at their edges. They all look like the bolides that created them impacted into a relatively soft surface that, rather than break up into rocks and boulders, melted, flowed, and then quickly refroze into these depressions.
The location, as always, provides us a possible explanation.
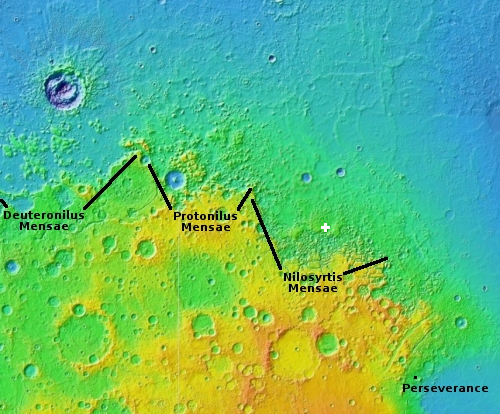
The white cross indicates the location of these craters, in an area just north of the region of chaos terrain dubbed Nilosyrtis Mensae, the easternmost part of that 2,000 mile long mid-latitude strip of chaos I dub glacier country because every image taken of the landscape there seems to exhibit glacial features.
Thus, it is very likely that there is a lot of ice very close to the surface at this location. In fact, that ice layer could be dominant, and its presence could easily explain the nature of these craters.
Obviously, that can’t be the whole story. We don’t know how long ago these impacts occurred, and in the interim erosion processes could have reshaped things by quite a lot. Moreover, the data is still somewhat sparse.
Below is a global map of Mars, indicating where scientists have found a lot of evidence of ice. The two lines at 30 degrees latitude indicate the range of detected persistent ice, near the surface. The equatorial regions have so far been found to be dry, though underground ice might still exist.
The regions outlined in white are those where extensive glacial and ice features have been detected as well. For the full resolution version click on the map.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was a featured image today from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The caption, written by Carol Weitz of the Planetary Science Institute in Arizona, focused on the wind patterns created within these craters.
These impact craters in the northern middle latitudes have interesting interiors: all of them have wind-blown (aeolian) ripples.
Outside of the craters and along the crater floors, the ripples are all oriented in the same direction. However, along the walls of some of the larger craters, the ripples are situated radially away from the center, indicating the winds moving inside the larger craters can be influenced by the topography of the crater wall.
Additionally, many of the larger craters have layered mesas along their floors that are likely sedimentary deposits laid down after the craters formed but prior to the development of the aeolian ripples.
I am further intrigued by the rimless nature of these craters, as well as the lack of significant rocky debris at their edges. They all look like the bolides that created them impacted into a relatively soft surface that, rather than break up into rocks and boulders, melted, flowed, and then quickly refroze into these depressions.
The location, as always, provides us a possible explanation.

The white cross indicates the location of these craters, in an area just north of the region of chaos terrain dubbed Nilosyrtis Mensae, the easternmost part of that 2,000 mile long mid-latitude strip of chaos I dub glacier country because every image taken of the landscape there seems to exhibit glacial features.
Thus, it is very likely that there is a lot of ice very close to the surface at this location. In fact, that ice layer could be dominant, and its presence could easily explain the nature of these craters.
Obviously, that can’t be the whole story. We don’t know how long ago these impacts occurred, and in the interim erosion processes could have reshaped things by quite a lot. Moreover, the data is still somewhat sparse.
Below is a global map of Mars, indicating where scientists have found a lot of evidence of ice. The two lines at 30 degrees latitude indicate the range of detected persistent ice, near the surface. The equatorial regions have so far been found to be dry, though underground ice might still exist.
The regions outlined in white are those where extensive glacial and ice features have been detected as well. For the full resolution version click on the map.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or from any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit. If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
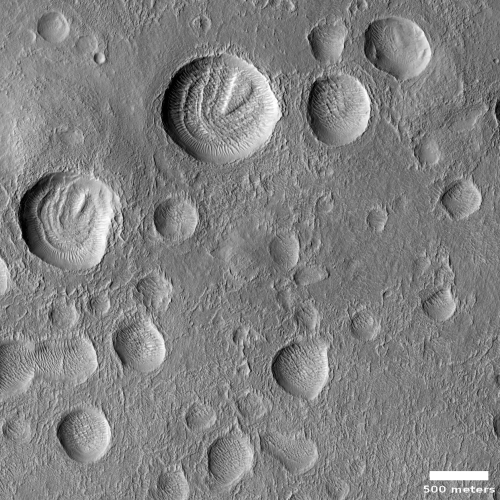




If you had not indicated they were impact “Craters”, I would guess something similar to the mounds in the arctic where ice has been a factor in the uplift.
Agreed the edges don’t have an ejecta rim. The craters also don’t seem to have a central peak – interior topography covered by eolian debris, or not there in the first place?