I wrote this essay last year, to celebrate the fiftieth anniversary of the Apollo 8 mission to the Moon. I think it worth reposting, especially because stories about Apollo 8 still refuse to show the Earthrise image as Bill Anders took it. Note that they took the picture on Christmas Eve, not Christmas day.
———————————————
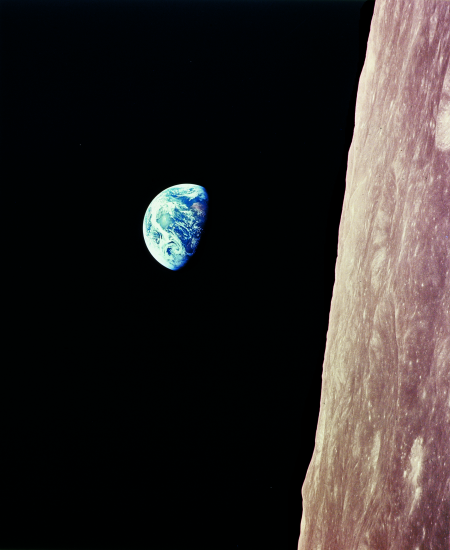

Today is the fiftieth anniversary of the moment when the three astronauts on Apollo 8 witnessed their first Earthrise while in orbit around the Moon, and Bill Anders snapped the picture of that Earthrise that has been been called “the most influential environmental picture ever taken.”
The last few days have seen numerous articles celebrating this iconic image. While all have captured in varying degrees the significance and influence of that picture on human society on Earth, all have failed to depict this image as Bill Anders, the photographer, took it. He did not frame the shot, in his mind, with the horizon on the bottom of the frame, as it has been depicted repeatedly in practically every article about this image, since the day it was published back in 1968.
Instead, Anders saw himself as an spaceman in a capsule orbiting the waist of the Moon. He also saw the Earth as merely another space object, now appearing from behind the waist of that Moon. As a result, he framed the shot with the horizon to the right, with the Earth moving from right to left as it moved out from behind the Moon, as shown on the right.
His perspective was that of a spacefarer, an explorer of the universe that sees the planets around him as objects within that universe in which he floats.
When we here are on Earth frame the image with the horizon on the bottom, we immediately reveal our limited planet-bound perspective. We automatically see ourselves on a planet’s surface, watching another planet rise above the distant horizon line.
This difference in perspective is to me the real meaning of this picture. On one hand we see the perspective of the past. On the other we see the perspective the future, for as long humanity can remain alive.
I prefer the future perspective, which is why I framed this image on the cover of Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8 the way Bill Anders took it. I prefer to align myself with that space-faring future.
And it was that space-faring future that spoke when they read from Genesis that evening. They had made the first human leap to another world, and they wished to describe and capture the majesty of that leap to the world. They succeeded beyond their wildest dreams.
Yet, they were also still mostly Earth-bound in mind, which is why Frank Borman’s concluding words during that Christmas eve telecast were so heartfelt. He was a spaceman in a delicate vehicle talking to his home of Earth, 240,000 miles away. “And from the crew of Apollo 8, we close with good night, good luck, a Merry Christmas, and God bless all of you — all of you on the good Earth.” They longed deeply to return, a wish that at that moment, in that vehicle, was quite reasonable.
Someday that desire to return to Earth will be gone. People will live and work and grow up in space, and see the Earth as Bill Anders saw it in his photograph fifty years ago.
And it is for that time that I long. It will be a future of majesty we can only imagine.
Merry Christmas to all, all of us still pinned down here on “the good Earth.”