Sunspot update December 2018: Decline to solar minimum continues
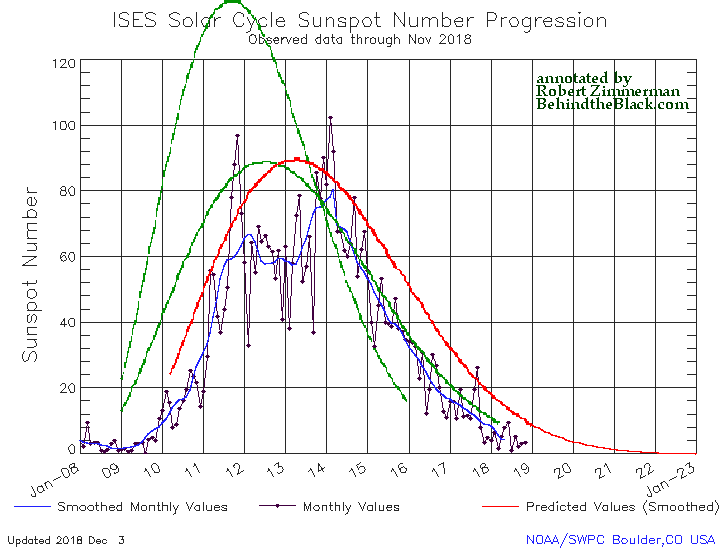
Time for the monthly solar cycle update! NOAA today posted its monthly update of the solar cycle, covering sunspot activity for December 2018. As I do every month, I am posting it below, annotated to give it some context.
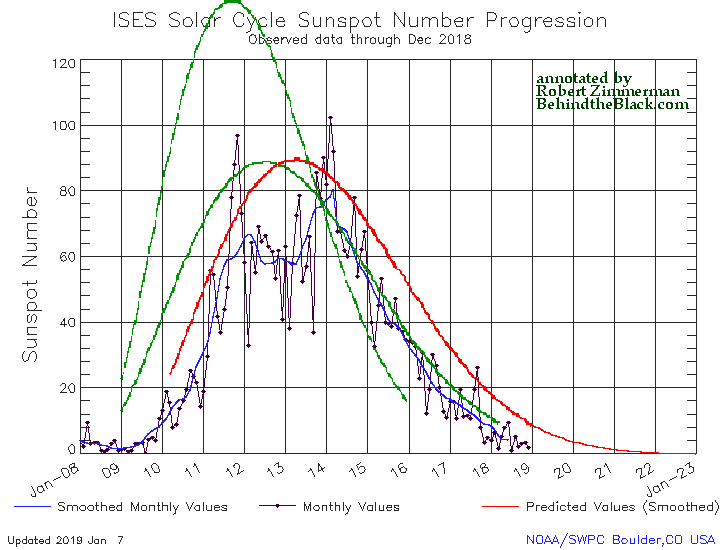
The graph above has been modified to show the predictions of the solar science community. The green curves show the community’s two original predictions from April 2007, with half the scientists predicting a very strong maximum and half predicting a weak one. The red curve is their revised May 2009 prediction.
There really isn’t much to say about the sunspot activity in December. It continued to show a steady decline to solar minimum, exhibiting activity very comparable to what we saw in mid-2008 when the previous unusually long and extended solar minimum began.
One interested detail however: When NOAA issued this graph last month, it finally extended it out beyond the end of 2019 to the end of 2022. In doing so, it also extended out the 2009 prediction of the solar science community, as indicated by the red curve. I hadn’t commented on this last month, but if you look at that curve it drops to zero and then flatlines for the entire year of 2022.
If this is what the solar science community now expects for this upcoming minimum, it means that community is now expecting a record-breaking minimum, lasting far longer than any previous minimum, two to three years at least. It also means that they have not dismissed the possibility that the Sun is about to enter a Grand Minimum, where no significant sunspot activity is seen for literally decades.
Should such a grand minimum occur, it bodes ill for global warming advocates. The track record of the Earth’s climate consistently shows that when sunspot activity declines, the global climate gets colder. Why this happens is not clearly understood, though there is at least one theory backed up by good experimental data. Should this happen, we shall discover that global cooling is a far worse thing to fear than global warming.