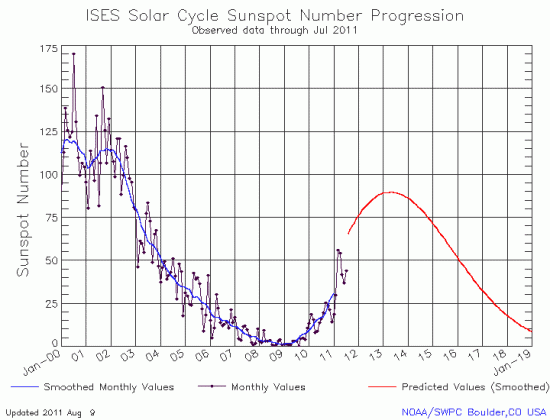
The sun’s weak maximum continues
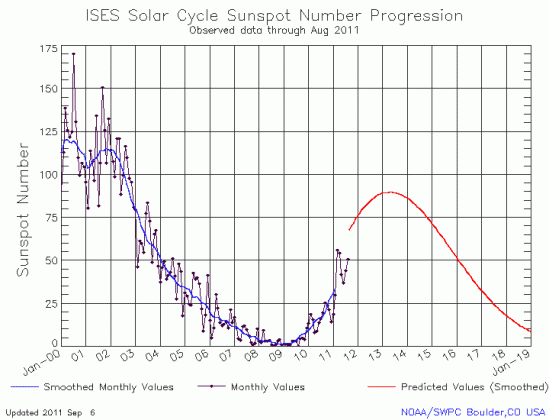
The monthly graph from NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center of the Sun’s solar cycle sunspot activity is out and I have posted it below. Though activity increased for the second month in a row, the totals are still below the activity levels of March and April 2011.
I am beginning to think that I sound like a broken record. This monthly graph once again suggests that the next solar maximum will be weak, possibly weaker than the most up-to-date predictions for the next solar maximum. And even if that prediction is correct, the data continues to point towards a quieter Sun, with the likelihood of a long period of no sunspots beginning in the next decade.
Based on past history, the consequences of a long Maunder-type minimum, where there are no sunspots for decades, should be very profound. Every time the Sun has gone this quiet in the past, the Earth’s climate has cooled. Furthermore, new results just released add weight to this conclusion. A less active Sun allows more intergalactic cosmic rays to hit the atmosphere, and the CLOUD experiment at CERN strongly suggests that the higher rate of cosmic rays could in turn increase the atmosphere’s cloudiness, thereby reflecting more light and energy and making the Earth colder.