Scientists use Hubble and Webb to confirm there are as yet no planets forming in Vega’s accretion disk
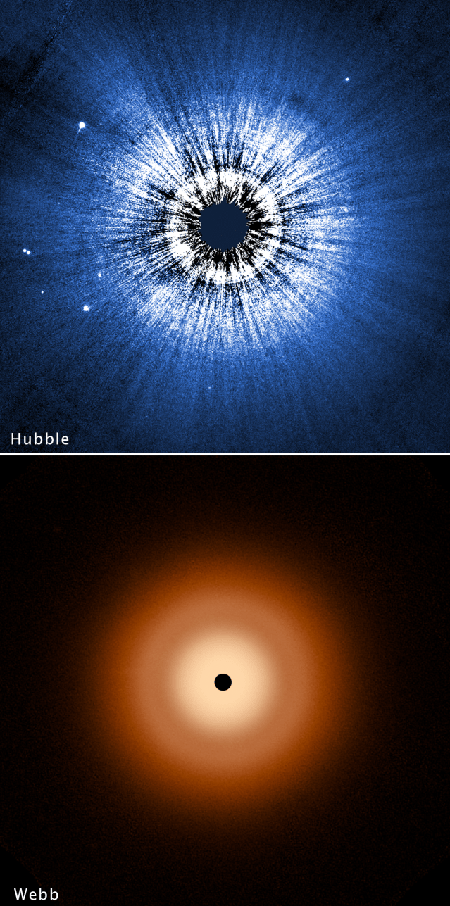
Using both the Hubble and Webb space telescopes, scientists have now confirmed, to their surprise, that the accretioni disk that surrounds the nearby star Vega is very smooth with almost no gaps, and thus apparently has not new exoplanets forming within it.
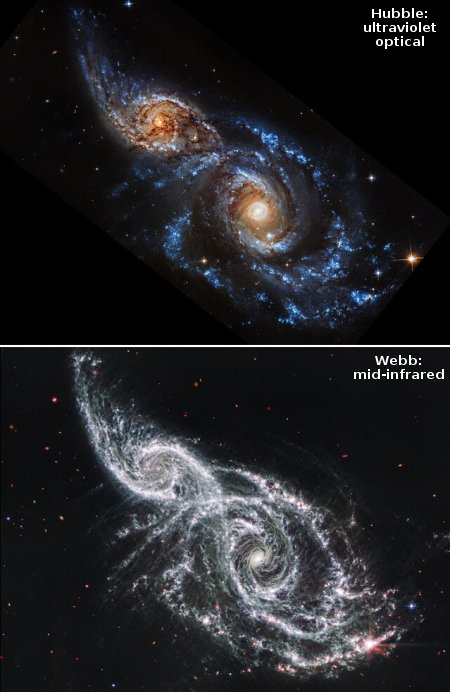
The two pictures to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, come from two different papers. The Hubble paper is here [pdf] while the Webb paper is here [pdf]. From the press release:
Webb sees the infrared glow from a disk of particles the size of sand swirling around the sizzling blue-white star that is 40 times brighter than our Sun. Hubble captures an outer halo of this disk, with particles no bigger than the consistency of smoke that are reflecting starlight.
The distribution of dust in the Vega debris disk is layered because the pressure of starlight pushes out the smaller grains faster than larger grains. “Different types of physics will locate different-sized particles at different locations,” said Schuyler Wolff of the University of Arizona team, lead author of the paper presenting the Hubble findings. “The fact that we’re seeing dust particle sizes sorted out can help us understand the underlying dynamics in circumstellar disks.”
The Vega disk does have a subtle gap, around 60 AU (astronomical units) from the star (twice the distance of Neptune from the Sun), but otherwise is very smooth all the way in until it is lost in the glare of the star. This shows that there are no planets down at least to Neptune-mass circulating in large orbits, as in our solar system, say the researchers.
At the moment astronomers consider the very smooth accretion disk surrounding Vega to be rare and exception to the rule, with most debris disks having gaps that suggest the presence of newly formed exoplanets within them. That Vega breaks the rule however suggests the rule might not be right in the first place.
Using both the Hubble and Webb space telescopes, scientists have now confirmed, to their surprise, that the accretioni disk that surrounds the nearby star Vega is very smooth with almost no gaps, and thus apparently has not new exoplanets forming within it.
The two pictures to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, come from two different papers. The Hubble paper is here [pdf] while the Webb paper is here [pdf]. From the press release:
Webb sees the infrared glow from a disk of particles the size of sand swirling around the sizzling blue-white star that is 40 times brighter than our Sun. Hubble captures an outer halo of this disk, with particles no bigger than the consistency of smoke that are reflecting starlight.
The distribution of dust in the Vega debris disk is layered because the pressure of starlight pushes out the smaller grains faster than larger grains. “Different types of physics will locate different-sized particles at different locations,” said Schuyler Wolff of the University of Arizona team, lead author of the paper presenting the Hubble findings. “The fact that we’re seeing dust particle sizes sorted out can help us understand the underlying dynamics in circumstellar disks.”
The Vega disk does have a subtle gap, around 60 AU (astronomical units) from the star (twice the distance of Neptune from the Sun), but otherwise is very smooth all the way in until it is lost in the glare of the star. This shows that there are no planets down at least to Neptune-mass circulating in large orbits, as in our solar system, say the researchers.
At the moment astronomers consider the very smooth accretion disk surrounding Vega to be rare and exception to the rule, with most debris disks having gaps that suggest the presence of newly formed exoplanets within them. That Vega breaks the rule however suggests the rule might not be right in the first place.