Japanese tsunami set record at 132.5 feet high
The March 11th Japanese tsunami was the highest on record, 132.5 feet high.
The March 11th Japanese tsunami was the highest on record, 132.5 feet high.
The March 11th Japanese tsunami was the highest on record, 132.5 feet high.
That’s so nice of them: Russia vows not to exploit its manned space flight monopoly.
Actually, this isn’t really news. Since the fall of the Soviet Union the Russians have always driven a hard bargain when they have sold tickets to get crew or cargo into space. However, once the contract has been signed they have also honored those contracts, to the letter. As the U.S. already has a signed contract to get its astronauts to ISS using Russian rockets and capsules, there won’t be any opportunities for Russian exploitation — until that contract expires.
In other words, the U.S. had better get some manned launch capability on line before too long. And on that note, see this article: NASA considers man-rating the Atlas V.
Finding out what’s in it: More than 400 companies in the medical industry are demanding repeal of an excise tax imposed by Obamacare.
Some good news: Dawn has returned its first sharp close-up image of Vesta.
The image to below the fold is to me a relief, as it shows that the spacecraft’s camera is fine and that my engineering friends were correct in telling me so. Forgive me for being a skeptical and nervous reporter.
» Read more
Ten signs that Americans have begun freaking out about the state of the economy.
Here’s another: Bank Of America is tanking again, as the firm may need $50 billion in fresh capital.
NASA to announce on Friday the landing site of Curiousity, the next Mars rover.
Our government in action: The National Relations Labor Board under the Obama administration has prosecuted a dead person for not responding to a union complaint, made after the person died.
The Russians yesterday successfully launched their first space telescope since the fall of the Soviet Union. Here is a Google translation of a Russian article describing Spektr-R’s research goals:
[Spektr-R is] designed to study galaxies and quasars in the radio, the study of black holes and neutron stars in the Milky Way, as well as the regions immediately adjacent to the massive black holes. In addition, using the observatory, scientists expect to receive information about pulsars and the interstellar plasma. It is planned that the “Spektr-R” will work in orbit for at least 5 years.
Though this particular space telescope is probably not going to rewrite the science of astrophysics, its launch is historically significant. It indicates that Russia has just about recovered from the seventy-plus years of bankrupt communist rule that ended in 1990.
» Read more
Now here’s a useful data point: A new poll finds that nearly one-fourth of those polled would give up sex if it meant that they could avoid a PowerPoint presentation.
Dawn enters orbit around Vesta.
Two wrongs don’t make a right: A Colorado woman who refused a TSA patdown has been accused of groping a TSA agent.
Though her behavior appears to have been an assault and therefore the arrest apparently justified, why is it that this woman gets charged with a crime while all around her TSA agents freely do exactly the same thing repeatedly to innocent Americans and are never charged as well?
The answer has to do with power, wielded by the government to dominate its citizens, and done so in a complete defiance of the Constitution and the Bill of Rights.
We need more elected officials like this:
“Re-election is the farthest thing from my mind,” said Representative Tom Reed, a freshman Republican from upstate New York. “Like many of my colleagues in the freshman class, I came down here to get our fiscal house in order and take care of the threat to national security that we see in the federal debt. We came here not to have long careers. We came here to do something. We don’t care about re-election.”
In a paper published today in Geophysical Research Letters, climate scientists have estimated the distribution and trends for the Arctic icecap from 1980 through March 2011. What they have found is a significant decline in older ice on top of an overall declining trend that showed a strong but partial recovery since 2008. The graph below, from the paper, illustrates clearly these trends.
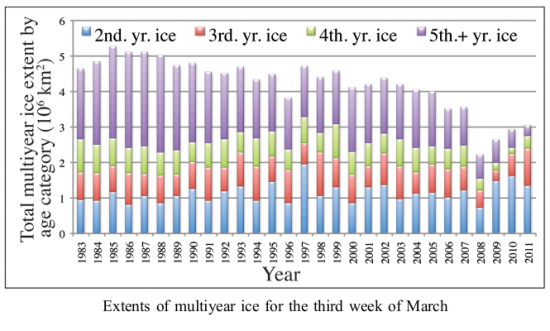
What this means for the icecap itself remains unclear. As the scientists themselves note in their conclusion:
» Read more
The Obama Administration granted 39 new waivers last month from Obamacare, bringing the total to just under 1,500.
“Dominate. Intimidate. Control.”
Now, thanks to TSA Chief John Pistole’s determination to “take the TSA to the next level,” there will soon be no place safe from the TSA’s groping searches. Only this time, the “ritualized humiliation” is being meted out by the serpentine-labeled Visible Intermodal Prevention and Response (VIPR) task forces, comprised of federal air marshals, surface transportation security inspectors, transportation security officers, behavior detection officers and explosive detection canine teams. At a cost of $30 million in 2009, VIPR relies on 25 teams of agents, in addition to assistance from local law enforcement agencies as well as immigration agents. And as a sign of where things are headed, Pistole, himself a former FBI agent, wants to turn the TSA into a “national-security, counterterrorism organization, fully integrated into U.S. government efforts.” To accomplish this, Pistole has requested funding for an additional 12 teams for fiscal year 2012, bringing VIPR’s operating budget close to $110 million.
Our government at work: A New Jersey Township has threatened to fine a diner owner if he doesn’t remove a string of American flags.
Lost for 87 years, the Bornean rainbow toad has been rediscovered.
Leftwing civility: Environmental terrorists destroy genetically modified test plots of wheat and potatoes.
On the night of 9 July, half a dozen masked attackers overpowered the security guard watching over test fields in Gross Lüsewitz, near Rostock. They then destroyed a field of wheat resistant to fungal diseases and a field of potatoes engineered to produce cyanophycin, an amino acid polymer that could potentially be used to make plastics. . . . Two nights later, a dozen attackers threatened guards with pepper spray and bats at a demonstration garden in Üplingen, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. They destroyed a field of potatoes and trampled wheat and maize.
SpaceX has broken ground on its Falcon Heavy launch site.
Our government at work: Georgia police shut down a girls’ lemonade stand because they lacked a business license, peddler’s permit and food permit.
The day of reckoning looms: The U.S. might still lose its top credit rating even if a debt limit agreement is reached.
How did Al Gore miss this important fact? Cats cause global warming!
A new analysis of the orbits of Ceres and Vesta says that in a surprisingly short time those orbits become chaotic and therefore unpredictable. More significantly, those orbits interact with the Earth’s and also make its long term orbit chaotic and unpredictable. From the abstract:
Although small, Ceres and Vesta gravitationally interact together and with the other planets of the Solar System. Because of these interactions, they are continuously pulled or pushed slightly out of their initial orbit. Calculations show that, after some time, these effects do not average out. Consequently, the bodies leave their initial orbits and, more importantly, their orbits are chaotic, meaning that we cannot predict their positions. The two bodies also have a significant probability of impacting each other, estimated at 0.2% per billion year. Last but not least, Ceres and Vesta gravitationally interact with the Earth, whose orbit also becomes unpredictable after only 60 million years. This means that the Earth’s eccentricity, which affects the large climatic variations on its surface, cannot be traced back more than 60 million years ago. This is indeed bad news for Paleoclimate studies. [emphasis mine]
The scientists found that it became impossible to calculate the orbits of the two largest asteroids after only several ten thousand years. They also found that “numerous asteroids in the main belt will behave in the same way with . . . much more chaotic behavior than previously thought.” Worse, the possibility of collisions was far higher than ever thought. Ceres and Vesta have a 1 in 500 chance of colliding with each other every billion years, while other asteroids have chances as low as 1 in 1000.
The importance of this discovery, which still needs to be confirmed by other researchers, cannot be understated.
» Read more
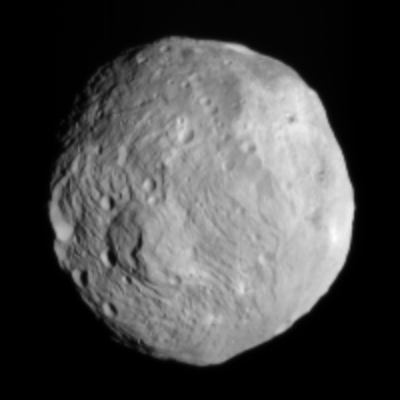

Another image of Vesta from Dawn has been released. This image was taken on July 9 from a distance of 26,000 miles away. It is definitely an improvement over the previous image, with more small details becoming visible. However, I once again wonder about the softness of the image. Look at the limb of the planet. It is soft against the black sky. This is not what one would expect from perfectly focused camera.
Dawn goes into orbit around Vesta next week. We sure learn then for sure if there is a problem with its camera, or whether I am merely being a bit too nervous.