Night Ranger – Goodbye
An evening pause: Performed live in 2022 with the Contemporary Youth Orchestra. Make sure you stay till the end.
Hat tip Terry.
An evening pause: Performed live in 2022 with the Contemporary Youth Orchestra. Make sure you stay till the end.
Hat tip Terry.
Lockheed Martin today announced that it intends to purchase the satellite company Terran Orbital, of which it already owns one third of its stock.
Lockheed said Aug. 15 it would buy Terran Orbital for $0.25 per share in cash and retire the company’s existing debt. The deal, expected to close in the fourth quarter, has an enterprise value of $450 million. Shares in Terran Orbital closed Aug. 14 at $0.40.
Lockheed had six months ago offered to buy the company for $1 per share, but then withdrew the offer. It appears this new offer is intended to save the company, as Lockheed needs it. Right now 90% of Terran Orbital’s contracts are with Lockheed, and if the company goes under so do those deals.
This situation appears related to funding problems being experienced by the Rivada 300-satellite constellation. It had signed a $2.4 billion contract with Terran to build those satellites, but Terran removed that contract from its listed deals this week, suggesting that it no longer expected it to happen.
Lockheed Martin has made a strong effort in the past decade to remake itself to meet the challenges of the new space market, including entering the smallsat satellite manufacturing market. Thus it should be able to absorb Terran Orbital’s operations with little major harm to both, and much benefit.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay.
Tim Dodd of Everyday Astronaut on May 30, 2024 was given a detailed tour by founder/owner Jeff Bezos of Blue Origin’s New Glenn factory at Cape Canaveral.
It is incredible to watch, because for the very first time, Bezos shows us what the company is finally doing to prepare for the first New Glenn launch, targeting no earlier than the end of September. Unlike every other visual shown of this facility in the past, this tour actually shows a factory floor where work is going on.
Much of the backgrounds inside the stages have apparently been put out of focus to protect Blue Origin’s proprietary rights. No matter.
As for the state of the manufacture of the BE-4 engines, Bezos stated that he expects next year to be building one engine every three days. Cross your fingers that he is right.
I have embedded the video of the tour below. Enjoy, and get excited by the competition and capability this rocket will create when it finally starts flying.
» Read more
In the past few months the situation in the war between Russia and the Ukraine has had some significant battlefield events that suggested the situation is becoming unstable. First, Russia began an offensive campaign along the northern border of the Ukraine near the Ukrainian city of Kharkiv, pushing back into the same territory it had abandoned during its major retreat and defeats in the fall of 2022.
This offensive, combined with the gains Russia has made in the past few months in eastern Ukraine, suggested that it had completely recovered from those 2022 defeats, and was now moving forward in its effort to conquer the Ukraine in its entirety. At least, that’s how it seemed from a cursory outsider’s view.
Then, last month, the Ukraine launched its own offensive across the border into Russia’s Kursk region, the first time any Russian territory had been invaded since Russia’s unprovoked invasion of the Ukraine in February 2022. That same cursory view suggested that the situation was becoming unstable, and that Russia now faced a serious problem of its own.
To me, the only way to find out how serious these changes are since my last Ukraine War update six months ago, in February 2024, is to do another, and to compare the territorial changes on a map, as I have done every time previously.
Not surprisingly, a look at the map brings clarity to the situation.
» Read more
Astronomers, both professional and amateur, have discovered a nearby star only 400 light years away that is moving so fast, 1.3 million miles per hour (almost three times faster than the Sun), it might very well escape the Milky Way and fly into intergalactic space in the far future.
The star, named CWISE J124909+362116.0 (or “J1249+36” for short), was first spotted by some of the over 80,000 citizen science volunteers participating in the Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 project, who comb through enormous reams of data collected over the past 14 years by NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission. This project capitalizes on the keen ability of humans, who are evolutionarily programmed to look for patterns and spot anomalies in a way that is unmatched by computer technology. Volunteers tag moving objects in data files and when enough volunteers tag the same object, astronomers investigate.
J1249+36 immediately stood out because it was moving at about .1 percent the speed of light.
The star itself is either a very low mass red dwarf, or possibly a brown dwarf that never quite had enough mass to ignite as a star.
You can read the research paper here [pdf]. The researchers posit two possible explanations for the star’s speed. Either it was once part of a binary and thrown out when its white dwarf companion exploded as a supernova, or was once located in a densely packed globular cluster, where the interaction with other stars or even black holes could have flung it away.
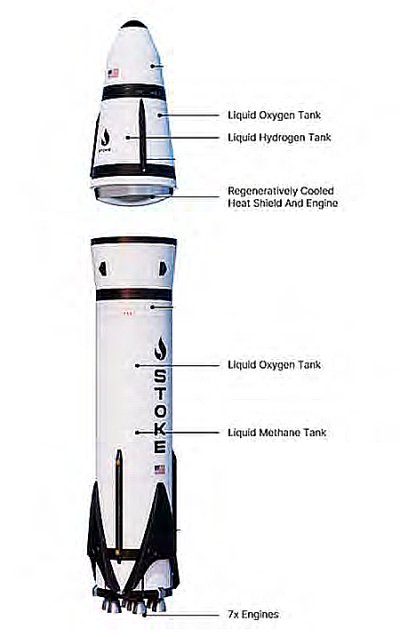

Stoke’s Nova rocket
We’re from the government and we’re here to help you! The rocket startup Stoke Space appears to be struggling with the same kind of environmental red tape that is hindering SpaceX, though in Stoke’s case the red tape appears absurdly unnecessary.
Stoke is the only company besides SpaceX developing a rocket with both its first and second stages returning to Earth to land vertically and then be reused. Unlike SpaceX Starship/Superheavy, which is gigantic and revolutionary in all ways, Stoke’s Nova rocket is comparable in size to the hundreds of rockets that have launched from Florida since the 1960s. Based on that six-decade track record, it would seem that getting rights to launch Nova (but not for its return) would be considered basic and routine, requiring little complex bureaucracy.
Hah! Fooled you!
Before any of this can take place, the Space Force must complete its “environmental assessment” of the company’s plans at LC-14 [the launchpad used for John Glenn’s first orbital mission and many others subsequently], in order to evaluate how repeat launches will affect local flora and fauna. These assessments are mandatory under federal law, and they can often take months — but the upside is that they provide a closer look at a company’s operational plans.
ULA, which hopes to set a company launch record next year, is right now suffering a major loss of its launch crews to SpaceX and Blue Origin.
This year alone, ULA has lost about 45 of its 105 Launch Operations engineers — the people who test, assemble and prepare every rocket and its cargo to fly — at its primary launch site in Florida, according to the person, who asked not to be identified discussing non-public information. The lack of experienced personnel has postponed work for future missions, the person said.
The article says the loss of these launch crew employees is because of higher pay offered by the other companies, but I suspect a contributing factor is ULA’s low rate of launches in recent years (3 in 2023 and 4 so far in 2024). These people have nothing to do, and see the lack of work as detrimental to their future careers. Better to move on, either to SpaceX where a lot of launches occur, one almost every other day, or to Blue Origin, where the rocket is new and the company has plenty of cash.
The flight of crews could also be because people do not see a future at ULA. For almost a year there have been rumors that Boeing and Lockheed Martin, which own it jointly, want to sell it. It was thought that sale would happen after the first Vulcan rocket launch, but it did not. In recent months those rumors have subsided, suggesting that the interest in buying the company has trailed off.
Despite these problems, ULA’s problems could very well be temporary. Its manifest has a lot of launches scheduled, and once Vulcan is certified for the military and operational for all its customers, it is expected to be launching more than twice a month next year. If those launches take place as planned, these issues will be begin to vanish very quickly.
In fact, it does appear that if you are an engineering student with an interest in rocketry, your future is extremely bright. There will be plenty of work opportunities for you in Florida in the future, from any one these companies.
SpaceX this morning successfully launched two commercial high resolution Earth observation satellites for the company Maxar, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
The first stage completed its sixteenth flight, landing back at Cape Canaveral. The two fairings completed their seventh and seventeenth flights.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
81 SpaceX
33 China
10 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
American private enterprise now leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 96 to 50, while SpaceX by itself still leads the entire world combined, including American companies, 81 to 65.
These numbers will continue to go up, as India has a launch scheduled for later today, while SpaceX has another Transporter launch scheduled for tomorrow, carrying dozens of smallsats.
Russia tonight (August 15th in Russia) successfully launched a Progress freight to ISS, its Soyuz-2 rocket lifting off from the Baikonur spaceport in Kazakhstan.
Rendezvous and docking with ISS scheduled for August 17, 2024 in the early morning.
The leaders in the 2024 launch race:
80 SpaceX
33 China
10 Rocket Lab
9 Russia
American private enterprise still leads the rest of the world combined in successful launches 95 to 50, while SpaceX by itself still leads the entire world combined, including American companies, 80 to 65.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
This appears to be a bookeeping maneuver, but suggests that Rivada may be having problems, which is a big deal because its contract with Terran Orbital is for $2.4 billion to build 300 satellites.
This is one of those press releases about nothing. Maritime’s spaceport is years behind schedule. The release includes really no information, and appears to have been issued merely to counter another proposed Canadian spaceport, Nordspace, that recently released its own press release about nothing.
The goal is to do the first test launch in 2025.
“Astronomers on Earth can only see the rings’ edge every 42 years due to the planet’s 84 year orbit.”

Former Marion police Chief Gideon Cody,
apparently proud to emulate Nazi tactics
The wheels of justice ground slow, but grind they do: In August 2023 the entire police department of Marion, Kansas, performed a Gestapo-like raid of a local newspaper’s offices as well as the homes the town’s vice mayor, the newspaper’s 98-year-old owner Joan Meyer (resulting in her death the next day from a heart attack), and one reporter.
All the evidence suggested the police chief, Gideon Cody, had performed the raid as a personal favor to a local businesswoman, Kari Newell, who was worried that newspaper might publish a story about her arrest for driving while intoxicated and without a license. Newell and Cody then worked together to use the police and a local judge, Laura Viar, to harass and hopefully destroy a newspaper. The newspaper survived, but their actions ended up killing its 98-year-old founder.
The public outrage was instantanous. Cody was soon suspended, and if Newell wished to keep her history out of the papers this raid was exactly the wrong way to do it. The story went national, exposing her drunk driving history to the world. Meanwhile five different federal lawsuits were filed against Cody and various other county and city officials. The reporter, Debbie Gruver, also resigned from the newspaper, saying she no longer felt comfortable in the Marion community.
It now appears that Cody, who officially resigned in October 2023, has now been charged with a crime in connection with the raid.
» Read more
Though a decision will not be made until next week, during a press briefing today the nature of the briefing and the wording by NASA officials suggested that they are now leaning strongly to having the two Starliner astronauts, Butch Wilmore and Suni Williams, return on the next Dragon capsule to launch to the station on September 24, 2024 and return in February 2025.
My conclusion is based on several subtle things. First, no Boeing official participated, the second time in row that they were excluded. Second, this briefing included some new individuals who rank higher in the chain of command, and whose opening statements were clearly written carefully in advance and were read aloud.
Third, and most important, the wording of those statements repeatedly indicated they are looking at Dragon return more seriously. For example, NASA’s chief astronaut Joe Acaba suggested strongly that the two astronauts were now well prepared for an eight month mission, rather than coming home in August 2024. Other statements by officials suggested they themselves are less confident about returning on Starliner. Though the data suggests they can return safely, there remains enough uncertainty to make some people uncomfortable.
One factor not stated but is certainly controlling the situation now is the upcoming election in November. The Democrats who control Washington and the White House will allow nothing to happen that could hurt their election chances. We must therefore assume people in the White House are now in control and are the ones who now intend to make the decision about Starliner’s return.
Based on these factors, we should expect NASA to announce next week that the crew will return in a Dragon capsule. In order for the return to happen on Starliner NASA and Boeing engineers must somehow convince those politicos that the return would be entirely safe. Since these politicos are always risk adverse, it would shock me if they can be convinced. It could happen, but understanding the politically framework is important.
The officials stated that they have scheduled the final review next week, and it appears the decision will be announced then.
The science team for the Mars rover Perseverance today outlined the planned route they intend to follow to bring the rover out of Jezero Crater.
The map to the right shows that route in red, with the rover presently at the upper right. Though Perseverance presently sits inside Neretva Vallis, which is the channel that cuts through the rim of the crater through which poured the delta material the rover has been sampling since landing, the route out of the crater will instead head south and west, crossing over the rim.
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover will soon begin a monthslong ascent up the western rim of Jezero Crater that is likely to include some of the steepest and most challenging terrain the rover has encountered to date. Scheduled to start the week of Aug. 19, the climb will mark the kickoff of the mission’s new science campaign — its fifth since the rover landed in the crater on Feb. 18, 2021.
…Two of the priority regions the science team wants to study at the top of the crater are nicknamed “Pico Turquino” and “Witch Hazel Hill.” Imagery from NASA’s Mars orbiters indicates that Pico Turquino contains ancient fractures that may have been caused by hydrothermal activity in the distant past.
Rover looking back at the “Bright Angel” areaOrbital views of Witch Hazel show layered materials that likely date from a time when Mars had a very different climate than today. Those views have revealed light-toned bedrock similar to what was found at “Bright Angel,” the area where Perseverance recently discovered and sampled the “Cheyava Falls” rock, which exhibits chemical signatures and structures that could possibly have been formed by life billions of years ago when the area contained running water.
For Perseverance’s recent travels, go here.
Using the Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have detected evidence of hydrated minerals and even possibly a very tiny amount of water ice on the surface of the metal asteroid Psyche.
The Webb data point to hydroxyl and perhaps water on Psyche’s surface. The hydrated minerals could result from external sources, including impactors. If the hydration is native or endogenous, then Psyche may have a different evolutionary history than current models suggest. “Asteroids are leftovers from the planetary formation process, so their compositions vary depending on where they formed in the solar nebula,” said SwRI’s Dr. Anicia Arredondo, another co-author. “Hydration that is endogenous could suggest that Psyche is not the remnant core of a protoplanet. Instead, it could suggest that Psyche originated beyond the ‘snow line,’ the minimum distance from the Sun where protoplanetary disc temperatures are low enough for volatile compounds to condense into solids, before migrating to the outer main belt.”
However, the paper found the variability in the strength of the hydration features across the observations implies a heterogeneous distribution of hydrated minerals. This variability suggests a complex surface history that could be explained by impacts from carbonaceous chondrite asteroids thought to be very hydrated.
You can read the research paper here [pdf]. The actual amount of water possible is at most 39 parts per million and is also an order of magnitude lower than that found on the Moon, which strongly suggests that it comes from outside sources, such as impacts from other asteroids, not from the inherent geological history of Psyche itself.
The uncertainties of this research, which are large, which should be resolved when the probe Psyche, launched last year, reaches the asteroid Psyche in August 2029.
Link here. The report provides a lot of detail about the ramped up operations of Blue Origin in Florida in preparation for the first launch of New Glenn, previously announced as September 29, 2024. It appears the company is finally getting something done, and is getting closer to that launch.
Nonetheless, this detailed report makes no mention of that launch date. Furthermore, based on the work presently being done, it appears that launching by that date is impossible. With less than two months to go, the rocket has not yet been stacked and brought to the launchpad for even one dress rehearsal countdown. In March the company did tanking tests using an engineering test prototype, but so far such tests have not been done on the actual flightworthy rocket. It seems there will not be enough time to do them and meet that September 29th date.
The report also claims that Blue Origin “continues to ramp up testing its BE-4 and BE-3U engines” and “should have no problem supporting engine demand for both New Glenn and Vulcan,” but provides no hint as to the actual number of engines produced. Recent numbers suggest that ULA will have sufficient engines to launch its rockets, but will New Glenn, which needs seven BE-4 engines compared to the two needed for ULA’s Vulcan? We presently have no idea.
All in all, however, things at Blue Origin in 2024 appear to finally be happening, after a five year lull of nothing under the previous CEO, Bob Smith. Even if that launch doesn’t happen in September, it appears that it will happen sometime within the six months that follow.
VIPER’s now canceled planned route at the Moon’s south pole
The lunar lander startup Intuitive Machines has now revealed it is putting together an industry partnership to bid on flying NASA’s VIPER lunar rover on its own largest lander, still under development.
In an Aug. 13 earnings call about its second quarter financial results, Intuitive Machines executives said they were planning to respond to a request for information (RFI) that NASA issued Aug. 9 seeking input from companies and organizations interested in taking over the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission that the agency said in July it would cancel.
Steve Altemus, chief executive of Intuitive Machines, said on the call that his company, which also responded to an earlier call for “expressions of interest” from NASA regarding VIPER, is working with other companies, universities and international partners on responding to NASA’s RFI. He did not identify any of those prospective partners.
…NASA, in its RFI, said that prospective partners would be responsible for the costs of any final testing and other work on the rover itself, as well as delivering it to the lunar surface and operating it once there. NASA, in its July 17 announcement that it would cancel VIPER, said the agency would save at least $84 million by halting work now on the rover, now complete and undergoing environmental testing.
Whether this company can raise the capital to finish this mission, now that NASA has said it cannot, remains unclear. That it is trying, and NASA is not, illustrates however why NASA should get out of the business of building anything and just buy it from the private sector. NASA’s attempt to build VIPER went 3Xs over budget and is considerably behind schedule. Now the private sector see profits in finishing the job, which will in turn save the agency considerable money. Imagine if NASA had done this from the beginning. The savings would have been even greater, and VIPER might right now be even closer to launch.
An evening pause: Performed live on television in 1969 by the group’s original members, Billy Davis Jr., Florence LaRue, Marilyn McCoo, Lamonte McLemore, and Ronald Townson. This music, from the Broadway musical Hair, reflects the naive and somewhat arrogant attitude of that baby boom generation. It is also a very beautiful song, sung beautiful.
Hat tip Diane Zimmerman.
Apparently too many college students and teachers
support Hamas despite these very obvious facts.
Courtesy of Doug Ross.
Fight! Fight! Fight! At the website Campus Reform one of its reporters, Michael Duke, has been doing magnificent work in identifying in detail college by college the students and professors who rioted this spring on numerous university campuses in support of the terrorist organization Hamas and its October 7, 2023 massacre of more than 1200 people, including the rape, torture, and murder of men, women, children, and babies.
I thought it was time to do the public a service and provide a link to all of Duke’s reports, so that future employees will have a handy place to go to find out whether the future college prospect before them thinks it is acceptable to kill babies in support of an ideology. Duke’s work has only begun, but it appears he is trying to identify every single pro-Hamas rioter this year who was arrested. His list so far:
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on April 13, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the MRO science team labels as “streamlined features”, though that doesn’t seem to me to be the best description.
Granted, the prevailing winds, from the northeast to the southwest, appear to pushing the sand dune fields to the southwest. The dark line — created recently by a dust devil — indicates the wind direction. The mesas, from 100 to 200 feet high, do not however appear very streamlined. Instead, they simply look like they are poking up through this sea of sand and dunes, with the wind able over time to successfully push that sand uphill a hundred-plus feet into the saddle between the mesas.
The overview map below provides some context and possibly an explanation, though not a very conclusive one.
» Read more
The short clip below from the Stephen Colbert late night show has been making the rounds today. Colbert is interviewing a CNN news anchor and says the following, ““I know you guys are objective over there, that you just report the news as it is.”
To his shock the audience laughs, clearly recognizing how inaccurate, stupid, and clueless Colbert’s description of CNN is. Kaitlan Collins, the news anchor, responds, “That supposed to be a laugh line?” and Colbert, clearly uncomfortable, answers, “It wasn’t supposed to be.”
Watch an enjoy:
» Read more

How today’s journalists analyze potential stories
Today’s example of modern bad journalism from our dismal mainstream press concerns a paper published yesterday in the journal of the National Academy of Sciences describing the possibility of liquid water in the Martian “mid-crust,” based on InSight seismological data and computer modeling.
I read the paper yesterday and decided that there really wasn’t much there. While the data suggests a lot of liquid water might be saturated within the fractured rocks of this deep underground crustal layer six to twelve miles down, the paper was based on many assumptions and had many uncertainties. It is also not confirmed by other researchers, and remains nothing more than educated speculation at this point.
Not surprisingly, our ignorant mainstream press today has immediately declared the discovery of a vast underground ocean on Mars, ready for the taking and possibly harboring life!
» Read more
The Japanese-based orbital tug startup Astroscale has signed an agreement with the European company Airbus to expand their partnership beyond an earlier agreement to use Airbus’s robot arm on Astroscale’s tug.
Under the MoU, Astroscale and Airbus will explore ways to boost the development of navigation and docking technologies for satellite servicing and debris removal missions they did not specify. According to the news release, the expanded partnership seeks to combine Airbus’s satellite manufacturing and space systems heritage with technologies Astroscale is developing for in-orbit servicing.
Astroscale has been aggressively working to get business both in Europe and the U.S. by opening divisions in both regions. This deal is clearly part of that effort. It also provides Astroscale resources as a new startup it previously did not have.
Axiom’s next commercial manned mission to ISS, dubbed Ax-4, which had been targeting an October 2024 launch date, has now been delayed until 2025 because of “required interagency approval processes.”
NASA’s only announcement describing the delay was a tweet on X, which stated the following:
The Ax-4 crew members are pending approval to fly to the orbiting lab by the Multilateral Crew Operations Panel.
Neither Axiom nor NASA provided further comment or explanation. The mission will fly three passengers from India, Poland, and Hungary and be commanded by Peggy Whitson, a former NASA astronaut who now fulfills that role for Axiom. Since the three passengers are all government astronauts, it is possible that the bureaucracies from all three nations, plus NASA and its ISS partners, are entangled in negotiations far more complex than necessary.
This situation highlights quite clearly why both billionairs Jared Isaacman and Chun Wang have signed on with SpaceX to flight orbital missions — avoiding a docking with ISS — that require no permissions from NASA. Wang for example announced his deal yesterday, for a flight that is targeting a launch before the end of the year. Though that schedule is tight and might not be met, it appears the mission will likely fly before the Axiom one, which has been planned now for quite awhile.
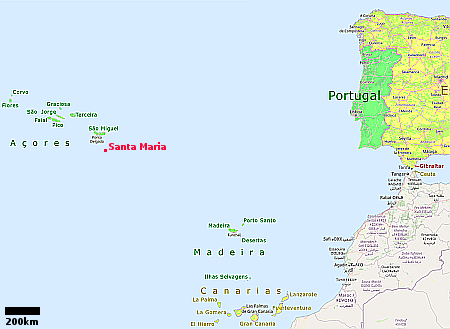
Portugal’s air traffic agency, Portugal NAV, today signed an agreement with the spaceport company Atlantic Spaceport Consortium, to work out the details of placing a commercial spaceport on the island of Santa Maria in the Azores.
Under the cooperation agreement, the pair aim to define the guidelines that a future spaceport will need to adhere to when launching from Santa Maria. This includes defining exclusion zones, examining how to monitor and authorize launch activities, and studying under what conditions to impose partial or total launch restrictions for safety reasons.
The map to the right shows the location of the island, relative to Europe and Africa. No timeliine for construction has been given, though the consortium hopes to launch “a small atmospheric rocket” in September. It has also signed a deal in 2022 (just before Russia’s invasion) with a Ukrainian rocket startup.
SpaceX today announced it will fly a four-passenger commerical flight, using the Dragon capsule dubbed Endurance and flying the first manned human flight to circle the poles.
The private Crew Dragon mission will be led by a Chinese-born cryptocurrency entrepreneur named Chun Wang, and he will be joined by a polar explorer, a roboticist, and a filmmaker whom he has befriended in recent years.
The “Fram2” mission, named after the Norwegian research ship Fram, will launch into a polar corridor from SpaceX’s launch facilities in Florida and fly directly over the north and south poles. The three-to-five day mission is being timed to fly over Antarctica near the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere, to afford maximum lighting.
As with the Jared Isaacman’s previous and future Dragon manned missions, the flight avoids any of the NASA bureucracy and costs by not docking with ISS. The flight is targeting a launch date before the end of this year, but that date is not firm.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
It will be released on August 15, 2025. More and more it appears Bezos is trying to get his so-far failed company off the ground.
A similar camera flew on the Intuitive Machines mission, and is scheduled to fly on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lander.
The launch is scheduled for August 15, 2024.
Doesn’t matter much even if it was mandatory if the upper stages break up into hundreds of pieces, right after launch, as China’s Long March 6A has now done on two of seven launches.
That was the flight in which Haise commented afterward, “It flies like a brick.” He meant that as a complement, because even so the shuttle made a perfect glided landing.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on July 1, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The image is labeled simply as a “terrain sample,” which usually means it was taken not as part of any specific research project but to fill a gap in the picture-taking schedule in order to maintain the camera’s proper temperate. When the camera team needs to do this, they try to picture interesting features availabe at that time slot. Sometimes the image is boring. Sometimes it is surprisingly interesting.
In this case the picture is the latter, and certainly quite alien. The curly parallel dark lines appear to be grooves, and seem to have ripple dunes within them, as if the only dust here got trapped in those low spots. It is also possible that the dunes are frozen and ancient, and are only being revealed as the top layer in each groove goes away.
What could possibly explain what we are looking at? The overview map below gives only a clue.
» Read more