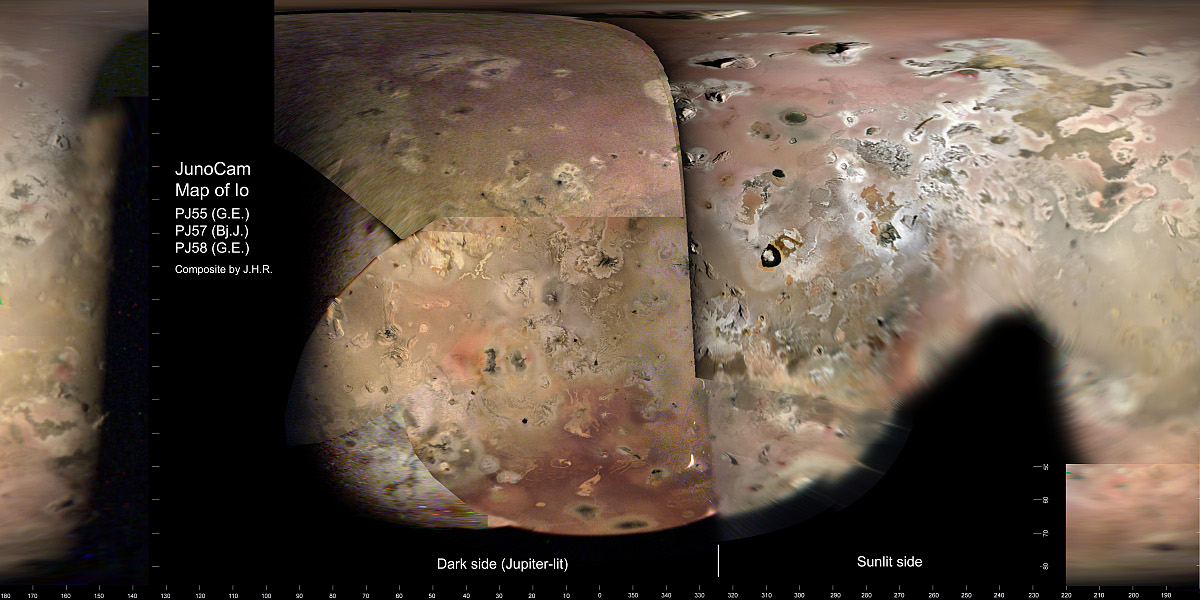
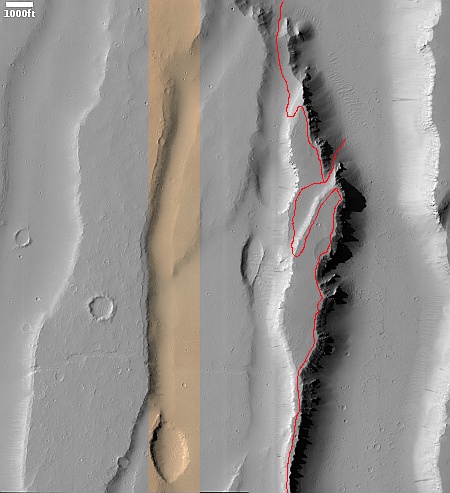
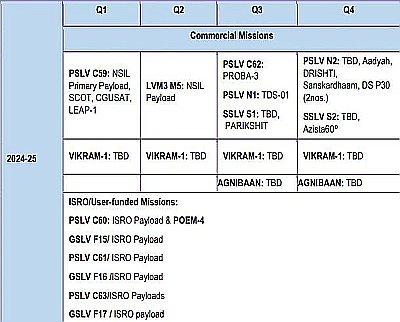
Musk: 3rd Starship/Superheavy test launch expected in early March
According to a tweet on X by Elon Musk, the third test flight of SpaceX’s heavy-lift Starship/Superheavy rocket is now expected in about three weeks, in early March.
The rocket is presently on the launchpad, undergoing final tests.
This confirms my December prediction that the launch would not happen earlier than March. SpaceX was ready to launch in January, but as I predicted red tape in the federal government have left the rocket sitting on the ground.
However, that prediction may have been too optimistic. First, SpaceX has still not gotten its launch license from the FAA, with no word from that agency when it will rubber-stamp SpaceX’s investigation into the second test launch in November. Second, the lawsuit by activists challenging the right of local authorities to close beaches at Boca Chica for launches remains active. It is very possible those activists will be successful in getting the court to issue an injunction preventing any beach closures (and thus launches) while the case is being litigated. If so, the next test launch could be months away.
According to a tweet on X by Elon Musk, the third test flight of SpaceX’s heavy-lift Starship/Superheavy rocket is now expected in about three weeks, in early March.
The rocket is presently on the launchpad, undergoing final tests.
This confirms my December prediction that the launch would not happen earlier than March. SpaceX was ready to launch in January, but as I predicted red tape in the federal government have left the rocket sitting on the ground.
However, that prediction may have been too optimistic. First, SpaceX has still not gotten its launch license from the FAA, with no word from that agency when it will rubber-stamp SpaceX’s investigation into the second test launch in November. Second, the lawsuit by activists challenging the right of local authorities to close beaches at Boca Chica for launches remains active. It is very possible those activists will be successful in getting the court to issue an injunction preventing any beach closures (and thus launches) while the case is being litigated. If so, the next test launch could be months away.