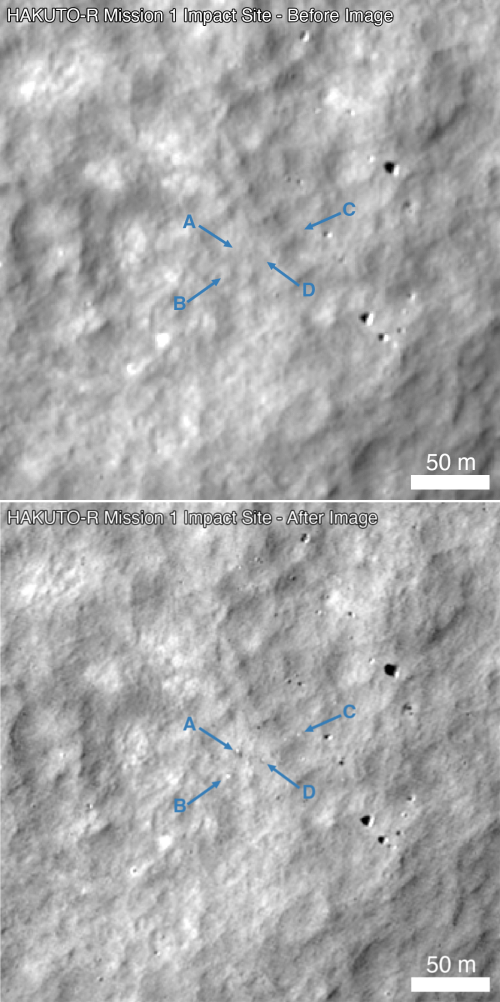
NASA inspector general finds more cost overruns in the agency’s SLS rocket program
Surprise! Surprise! A new NASA inspector general report [pdf] has found that the agency’s SLS rocket program is continuing to experience cost overruns and mismanagement that are “obscene”, as noted in this news report.
An independent report published Thursday contained troubling findings about the money spent by the agency on propulsion for the Space Launch System rocket. Moreover, the report by NASA Inspector General Paul Martin warns that if these costs are not controlled, it could jeopardize plans to return to the Moon.
Bluntly, Martin wrote that if the agency does not rein in spending, “NASA and its contracts will continue to exceed planned cost and schedule, resulting in a reduced availability of funds, delayed launches, and the erosion of the public’s trust in the agency’s ability to responsibly spend taxpayer money and meet mission goals and objectives—including returning humans safely to the Moon.”
Things are really much worse than this, mostly because it appears the Marshall Space Flight Center that runs the SLS program for NASA uses cost-plus contracts, which are essentially a blank check for contractors to run up costs endlessly, all of which the government must cover, and allows the process to go over-schedule against its own regulations. Furthermore, the cost overruns are for rockets and engines that are not newly developed, but in use for decades by Northrop Grumman and Aerojet Rocketdyne.
Note that this really isn’t news. Anyone with any intellectual honesty at all will know that every aspect of SLS and Orion is mismanaged and will go over budget and behind schedule endlessly. These problems are not a bug, however, but a feature of the system. The goals of SLS and Orion are not really to build a rocket to explore the solar system but to create an endless jobs program in congressional districts here on Earth. This misguided approach meanwhile robs America of a viable space effort because the money wasted could have actually been used to jumpstart a viable and competitive space-faring economy that actually achieves something.
Surprise! Surprise! A new NASA inspector general report [pdf] has found that the agency’s SLS rocket program is continuing to experience cost overruns and mismanagement that are “obscene”, as noted in this news report.
An independent report published Thursday contained troubling findings about the money spent by the agency on propulsion for the Space Launch System rocket. Moreover, the report by NASA Inspector General Paul Martin warns that if these costs are not controlled, it could jeopardize plans to return to the Moon.
Bluntly, Martin wrote that if the agency does not rein in spending, “NASA and its contracts will continue to exceed planned cost and schedule, resulting in a reduced availability of funds, delayed launches, and the erosion of the public’s trust in the agency’s ability to responsibly spend taxpayer money and meet mission goals and objectives—including returning humans safely to the Moon.”
Things are really much worse than this, mostly because it appears the Marshall Space Flight Center that runs the SLS program for NASA uses cost-plus contracts, which are essentially a blank check for contractors to run up costs endlessly, all of which the government must cover, and allows the process to go over-schedule against its own regulations. Furthermore, the cost overruns are for rockets and engines that are not newly developed, but in use for decades by Northrop Grumman and Aerojet Rocketdyne.
Note that this really isn’t news. Anyone with any intellectual honesty at all will know that every aspect of SLS and Orion is mismanaged and will go over budget and behind schedule endlessly. These problems are not a bug, however, but a feature of the system. The goals of SLS and Orion are not really to build a rocket to explore the solar system but to create an endless jobs program in congressional districts here on Earth. This misguided approach meanwhile robs America of a viable space effort because the money wasted could have actually been used to jumpstart a viable and competitive space-faring economy that actually achieves something.