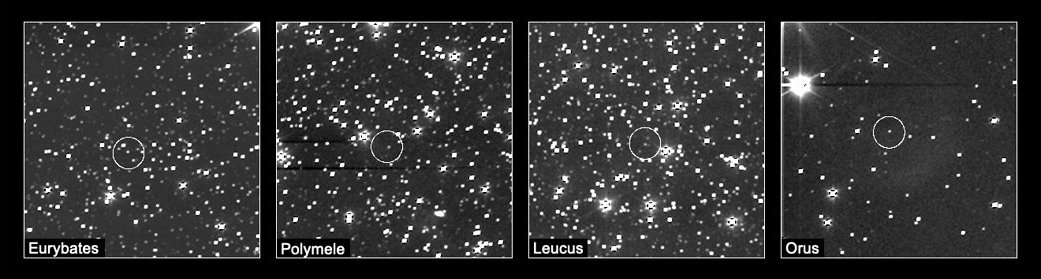
Lucy snaps its first pictures of four of the Trojan asteroids it will visit
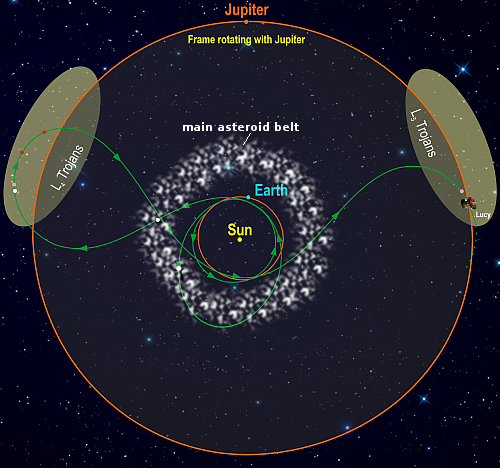
Lucy’s route through the solar system
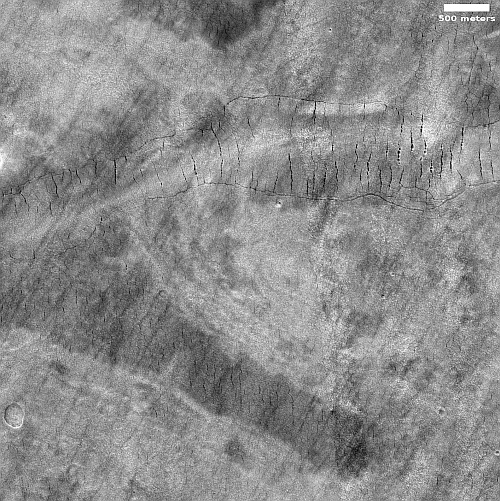
Though still many millions of miles away and really nothing more than tiny dots moving across the field of stars, the science team for the asteroid probe Lucy have used the probe to take its first pictures of four of the eight Trojan asteroids it will visit during its travels through the solar system, as shown on the map to the right. The dots along its path show where Lucy will fly past asteroids, some of which are binaries.
The image at the top is a screen capture from a very short movie created from all of the images Lucy took of each asteroid. If you click on the picture you will see that movie. As I say, at this distance, more than 330 million miles away, the asteroids are nothing more than dots. The short films of each were obtained by pictures taken over periods from two to 10 hours long, depending on the asteroid.
These asteriods are all in the L4 Trojans, the first that Lucy will visit from ’27 to ’28.

Lucy’s route through the solar system
Though still many millions of miles away and really nothing more than tiny dots moving across the field of stars, the science team for the asteroid probe Lucy have used the probe to take its first pictures of four of the eight Trojan asteroids it will visit during its travels through the solar system, as shown on the map to the right. The dots along its path show where Lucy will fly past asteroids, some of which are binaries.
The image at the top is a screen capture from a very short movie created from all of the images Lucy took of each asteroid. If you click on the picture you will see that movie. As I say, at this distance, more than 330 million miles away, the asteroids are nothing more than dots. The short films of each were obtained by pictures taken over periods from two to 10 hours long, depending on the asteroid.
These asteriods are all in the L4 Trojans, the first that Lucy will visit from ’27 to ’28.