A Martian knife mesa with terraces
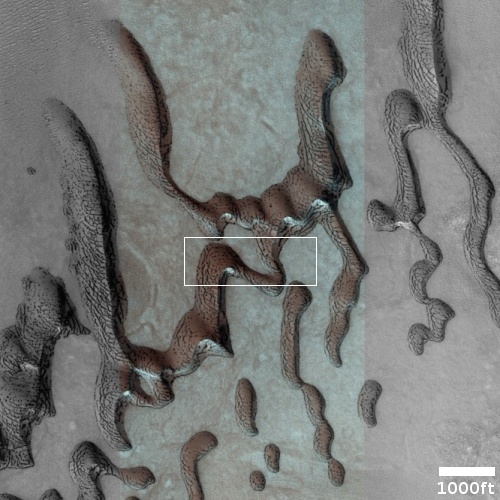
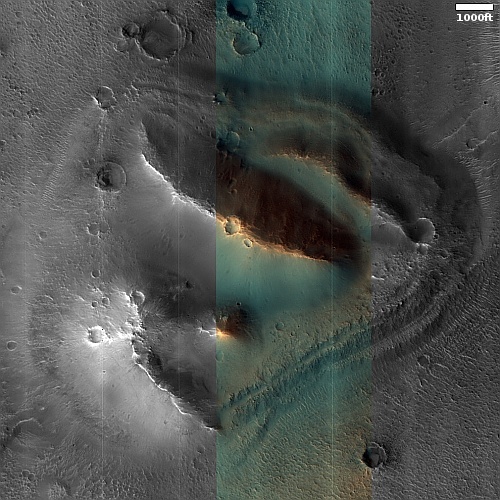
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 21, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists label as a “layered mound.” It also shows a plethora of geological mysteries, all of which relate to the as yet not quite understood geological history of Mars.
First, note the different colors north and south of the ridgeline. According to the science team’s understanding of what these colors mean [pdf], the orange-red to the north suggests dust, while the bluish-green to the south suggests coarser materials, such as rocks and sand. Though frost and ice are generally bluer, such things are generally found on the pole-facing slopes where there is less sunlight. Thus the bluish-green material to the south is unlikely to be ice or frost, though this is not impossible, as the picture was taken in the winter and the latitude is 35 degrees north.
Why however is there such a dichotomy of rocks, sand, and dust between the north and south slopes? And if frost and ice, why is it more prominent to the south, when it should instead be more prominent to the north?
Other mysteries: Is the circular depression on the ridgetop an impact crater or a caldera? If the latter, this suggests the mound is some kind of volcano, likely mud, though lava is not excluded. If so, however, why is there no caldera on top of the ridge to the south?
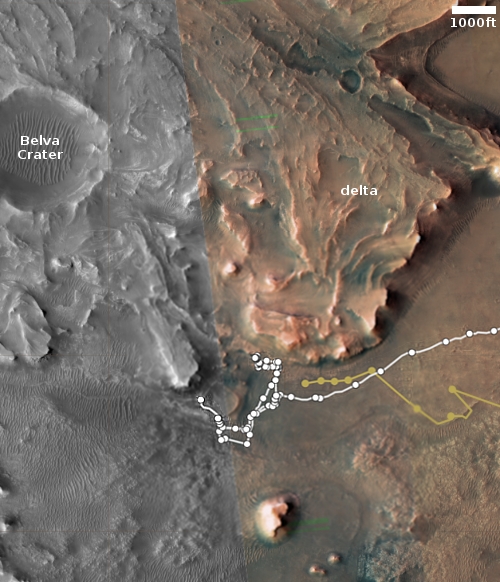
The location, as shown in the overview map below, reveals other puzzles.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 21, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows what the scientists label as a “layered mound.” It also shows a plethora of geological mysteries, all of which relate to the as yet not quite understood geological history of Mars.
First, note the different colors north and south of the ridgeline. According to the science team’s understanding of what these colors mean [pdf], the orange-red to the north suggests dust, while the bluish-green to the south suggests coarser materials, such as rocks and sand. Though frost and ice are generally bluer, such things are generally found on the pole-facing slopes where there is less sunlight. Thus the bluish-green material to the south is unlikely to be ice or frost, though this is not impossible, as the picture was taken in the winter and the latitude is 35 degrees north.
Why however is there such a dichotomy of rocks, sand, and dust between the north and south slopes? And if frost and ice, why is it more prominent to the south, when it should instead be more prominent to the north?
Other mysteries: Is the circular depression on the ridgetop an impact crater or a caldera? If the latter, this suggests the mound is some kind of volcano, likely mud, though lava is not excluded. If so, however, why is there no caldera on top of the ridge to the south?
The location, as shown in the overview map below, reveals other puzzles.
» Read more