Click for full image.
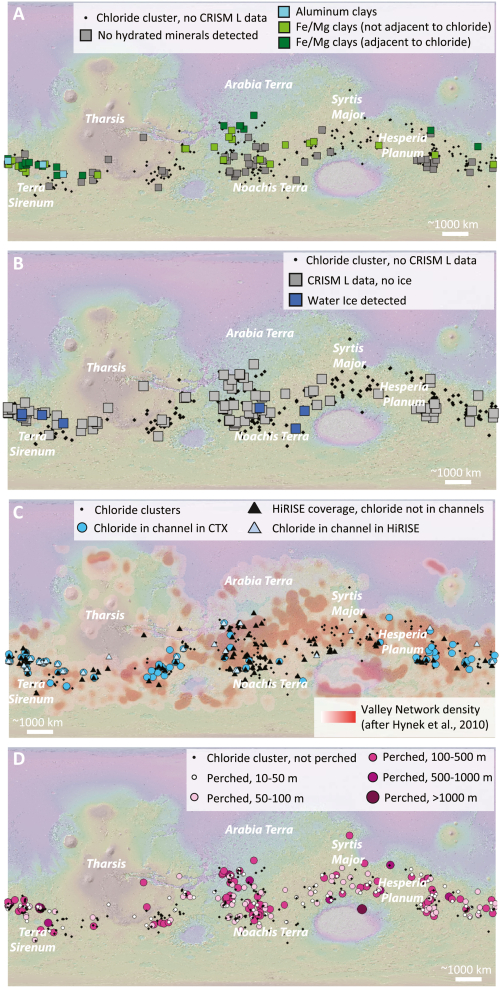
Using orbital data from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), scientists have found salt deposits on Mars where nearby crater counts suggest that the salt water that once held these deposits could have evaporated away as recently as 2.3 billion years ago.
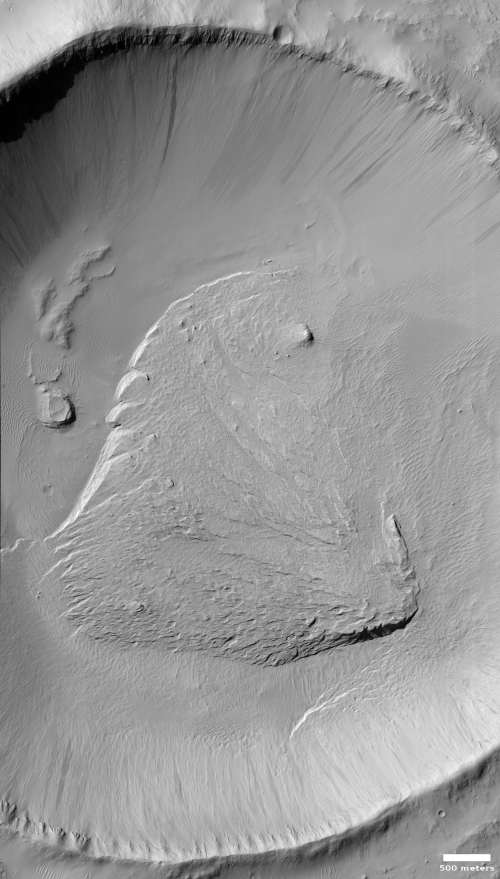
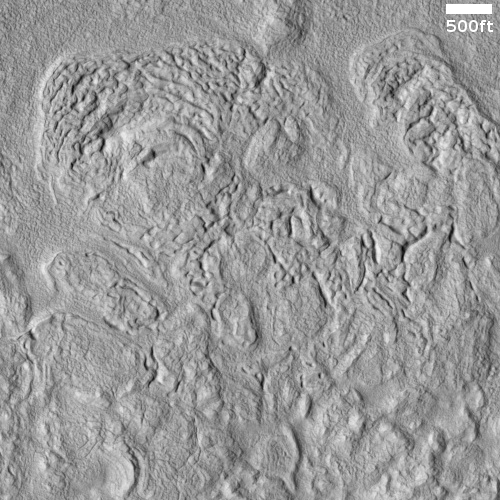
Using [MRO’s] cameras to create digital elevation maps, Leask and Ehlmann found that many of the salts were in depressions – once home to shallow ponds – on gently sloping volcanic plains. The scientists also found winding, dry channels nearby – former streams that once fed surface runoff (from the occasional melting of ice or permafrost) into these ponds. Crater counting and evidence of salts on top of volcanic terrain allowed them to date the deposits.
Past data has suggested that if liquid surface water had existed on Mars, it was gone by three billion years ago.
You can read the scientists’ research paper here.. The maps to the right, figure two from the paper, shows the locations of discovered salt deposits, almost all of which are in the Martian southern cratered highlands of Mars.
Is there uncertainty in these results? My regular readers know that the answer is of course yes. The biggest problem for these Mars researchers is that, despite the surface evidence that liquid water should have once flowed on the surface of Mars, no scientist has yet come up with a satisfactory model of Mars’ past climate that would have made that possible. The planet was either too cold or had too thin an atmosphere, based on other data. And getting it warmer or with a thicker atmosphere involves inventing any number of scenarios that are all questionable, based on what is presently known.
There is also the increasing evidence that glaciers of ice, not water, might have carved those winding, dry channels. If so, many of the assumptions that liquid water existed might simply be wrong, or incomplete. The scientists who wrote this report recognize this importance of ice on Mars, and note in their abstract that
…we think that the water source came from surface runoff, rather than deep groundwater welling up to the surface. The small amounts of water required are most likely from occasional melting of ice.
As always, more data is needed, with the most useful data that will clarify these conclusions being that gathered by future colonists on the surface of Mars itself.