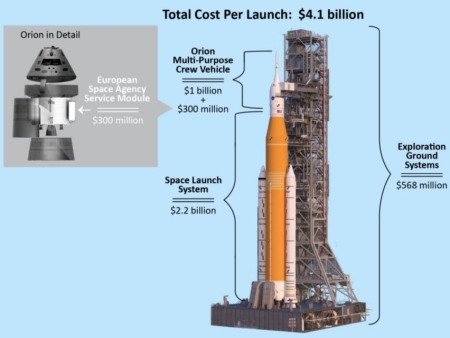
FAA targets finalizing Starship environmental report by end of year
The FAA today announced that it hopes to complete the permit process for SpaceX’s Starship operations at Boca Chica by the end of this year.
If you go to the link you will see a table that shows the agency’s overall plan. The table also suggests that extensions in the permitting process are also possible, though it appears the FAA is working now to avoid this.
I say excellent. I also say I will believe it when I see it. I want the FAA to show me my skepticism of this bureaucratic process is not justified. I want it to prove to me that there is no politics working in the background to slow the process.
Remember, after six months of work the FAA’s draft reassessment approved SpaceX’s Starship operations. To now delay or reject that approval will require a some heavy outside pressure, since the majority of the comments received by the the FAA during the comment period were favorable to the project.
The FAA today announced that it hopes to complete the permit process for SpaceX’s Starship operations at Boca Chica by the end of this year.
If you go to the link you will see a table that shows the agency’s overall plan. The table also suggests that extensions in the permitting process are also possible, though it appears the FAA is working now to avoid this.
I say excellent. I also say I will believe it when I see it. I want the FAA to show me my skepticism of this bureaucratic process is not justified. I want it to prove to me that there is no politics working in the background to slow the process.
Remember, after six months of work the FAA’s draft reassessment approved SpaceX’s Starship operations. To now delay or reject that approval will require a some heavy outside pressure, since the majority of the comments received by the the FAA during the comment period were favorable to the project.