Gilmour to attempt first launch again next year
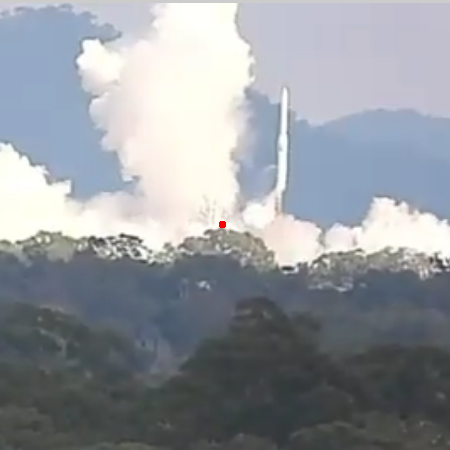

Eris rocket falling sideways from launchpad
(indicated by red dot). Click for video, cued
to just before launch.
According to a presentation by the CEO and founder of Australian rocket startup Gilmour Space, the company now sufficiently understands what caused the failure on its first launch attempt on July 30 to plan a second attempt in 2026.
The company is still investigating the root cause of the failure. “It looks like what went wrong on the launch is something we’ve never tested close enough to the launch conditions before,” he said, but didn’t elaborate.
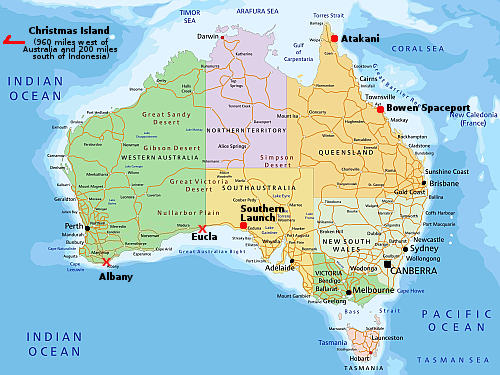
One factor in the launch was the long delay between shipping the rocket to the launch site, known as the Bowen Orbital Spaceport, and the launch itself. “Rockets aren’t designed to be at the launch site for 18 months,” he said. The launch site, he noted, is just a kilometer from the ocean, creating salty conditions that can be corrosive.
That extended time at the launch site stemmed from delays securing regulatory approvals for the launch. That included not just a launch license from the Australian Space Agency but also airspace, maritime and environmental permits. “We had to get 24 different permits from the Queensland government,” Gilmour said. “All of these things take a long time to do.” He acknowledged that the company had not put enough resources into those regulatory processes. “The approval processes just took way too long.”
What is ironic is that as bad as Australia appears to be in terms of red tape, it is far better that it mother country, Great Britain. At least in Australia spaceports have been approved and at least one launch has taken place. And it only took eighteen months! In Great Britain the permitting process for its two proposed rocket spaceports has taken almost a decade, and still no vertical launches have occurred at either.

Eris rocket falling sideways from launchpad
(indicated by red dot). Click for video, cued
to just before launch.
According to a presentation by the CEO and founder of Australian rocket startup Gilmour Space, the company now sufficiently understands what caused the failure on its first launch attempt on July 30 to plan a second attempt in 2026.
The company is still investigating the root cause of the failure. “It looks like what went wrong on the launch is something we’ve never tested close enough to the launch conditions before,” he said, but didn’t elaborate.
One factor in the launch was the long delay between shipping the rocket to the launch site, known as the Bowen Orbital Spaceport, and the launch itself. “Rockets aren’t designed to be at the launch site for 18 months,” he said. The launch site, he noted, is just a kilometer from the ocean, creating salty conditions that can be corrosive.
That extended time at the launch site stemmed from delays securing regulatory approvals for the launch. That included not just a launch license from the Australian Space Agency but also airspace, maritime and environmental permits. “We had to get 24 different permits from the Queensland government,” Gilmour said. “All of these things take a long time to do.” He acknowledged that the company had not put enough resources into those regulatory processes. “The approval processes just took way too long.”
What is ironic is that as bad as Australia appears to be in terms of red tape, it is far better that it mother country, Great Britain. At least in Australia spaceports have been approved and at least one launch has taken place. And it only took eighteen months! In Great Britain the permitting process for its two proposed rocket spaceports has taken almost a decade, and still no vertical launches have occurred at either.