Fractured crater close to the Phoenix lander on Mars
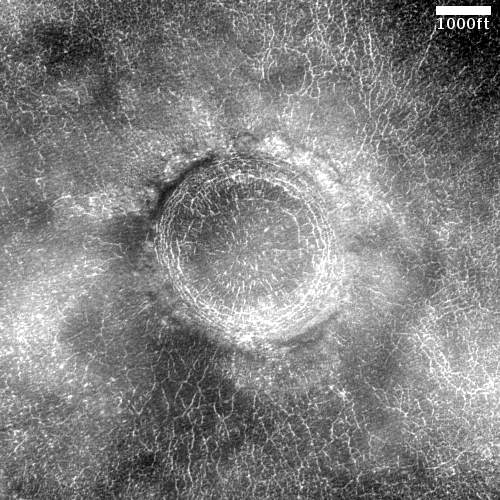
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on May 3, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a remarkably fractured crater that lies only a few miles to the southeast of where the now-inactive Phoenix lander put down back in 2008, at the very high latitude of 69 degrees north.
Phoenix was purposely sent to this high latitude to find out what the ground and atmosphere was like there. It found the following:
Phoenix’s preliminary science accomplishments advance the goal of studying whether the Martian arctic environment has ever been favorable for microbes. Additional findings include documenting a mildly alkaline soil environment unlike any found by earlier Mars missions; finding small concentrations of salts that could be nutrients for life; discovering perchlorate salt, which has implications for ice and soil properties; and finding calcium carbonate, a marker of effects of liquid water.
Phoenix findings also support the goal of learning the history of water on Mars. These findings include excavating soil above the ice table, revealing at least two distinct types of ice deposits; observing snow descending from clouds; providing a mission-long weather record, with data on temperature, pressure, humidity and wind; observations of haze, clouds, frost and whirlwinds; and coordinating with NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to perform simultaneous ground and orbital observations of Martian weather.
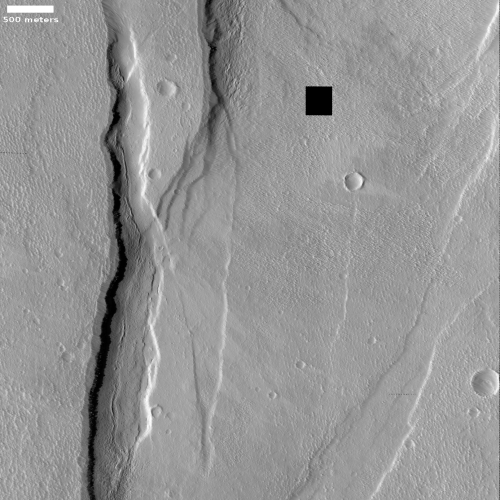
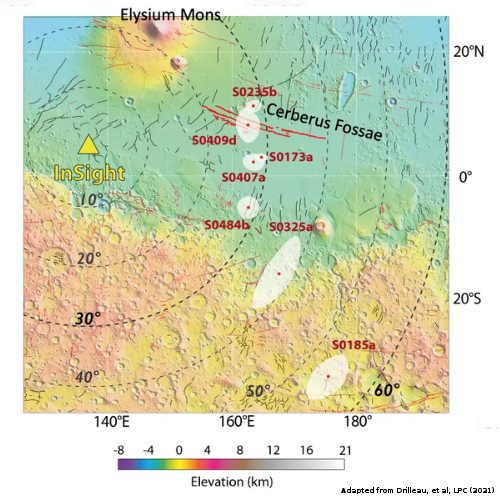
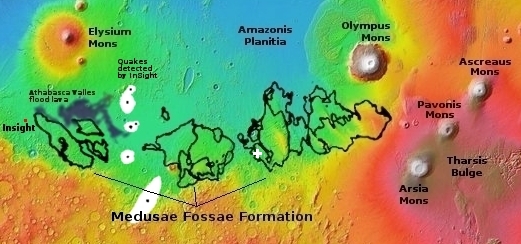
Below is an overview map showing the location of both this crater and the Phoenix lander.
» Read more
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on May 3, 2021 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a remarkably fractured crater that lies only a few miles to the southeast of where the now-inactive Phoenix lander put down back in 2008, at the very high latitude of 69 degrees north.
Phoenix was purposely sent to this high latitude to find out what the ground and atmosphere was like there. It found the following:
Phoenix’s preliminary science accomplishments advance the goal of studying whether the Martian arctic environment has ever been favorable for microbes. Additional findings include documenting a mildly alkaline soil environment unlike any found by earlier Mars missions; finding small concentrations of salts that could be nutrients for life; discovering perchlorate salt, which has implications for ice and soil properties; and finding calcium carbonate, a marker of effects of liquid water.
Phoenix findings also support the goal of learning the history of water on Mars. These findings include excavating soil above the ice table, revealing at least two distinct types of ice deposits; observing snow descending from clouds; providing a mission-long weather record, with data on temperature, pressure, humidity and wind; observations of haze, clouds, frost and whirlwinds; and coordinating with NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to perform simultaneous ground and orbital observations of Martian weather.
Below is an overview map showing the location of both this crater and the Phoenix lander.
» Read more