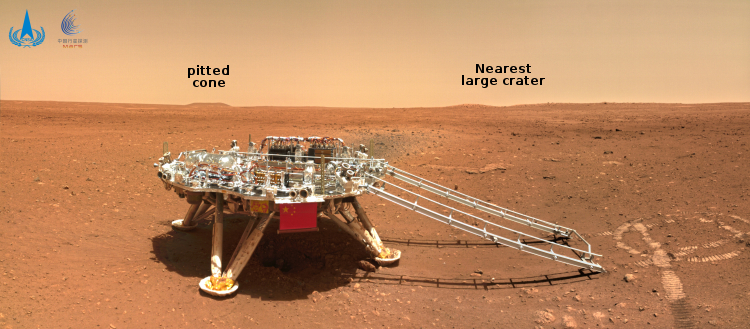
Northrop Grumman launches three military satellites using Minotaur rocket
Early this morning Northrop Grumman successfully used a former Minuteman rocket repurposed as a commercial rocket dubbed Minotaur to launch three military reconnaissance satellites for the National Reconnaissance Office.
The rocket’s solid-fueled stages were in themselves amazingly old.
The 69-foot-tall (21-meter) rocket is based on leftover solid-fueled motors from the U.S. Air Force’s Minuteman missile program. Designers added two Orion solid rocket motors on top of the lower two stages of a Minuteman missile to turn the bomb carriers into satellite launchers.
The Minotaur 1 rocket’s M55A1 first stage motor was cast with solid propellant in 1966 by Thiokol, now part of Northrop Grumman. The SR19 second stage motor, produced by Aerojet, was filled with its solid propellant in 1983, according to a Northrop Grumman spokesperson.
The age of the first stage means it is likely the oldest rocket motor ever used on a space launch.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
18 SpaceX
16 China
8 Russia
3 Northrop Grumman
The U.S. now leads China 26 to 16 in the national rankings.
Early this morning Northrop Grumman successfully used a former Minuteman rocket repurposed as a commercial rocket dubbed Minotaur to launch three military reconnaissance satellites for the National Reconnaissance Office.
The rocket’s solid-fueled stages were in themselves amazingly old.
The 69-foot-tall (21-meter) rocket is based on leftover solid-fueled motors from the U.S. Air Force’s Minuteman missile program. Designers added two Orion solid rocket motors on top of the lower two stages of a Minuteman missile to turn the bomb carriers into satellite launchers.
The Minotaur 1 rocket’s M55A1 first stage motor was cast with solid propellant in 1966 by Thiokol, now part of Northrop Grumman. The SR19 second stage motor, produced by Aerojet, was filled with its solid propellant in 1983, according to a Northrop Grumman spokesperson.
The age of the first stage means it is likely the oldest rocket motor ever used on a space launch.
The leaders in the 2021 launch race:
18 SpaceX
16 China
8 Russia
3 Northrop Grumman
The U.S. now leads China 26 to 16 in the national rankings.