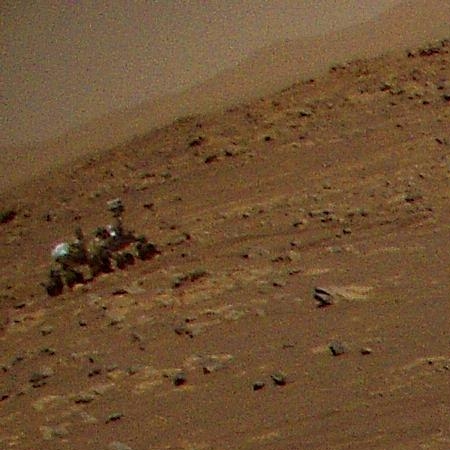
Ingenuity’s fourth flight today a success

For original images, go here, here, here, and here.
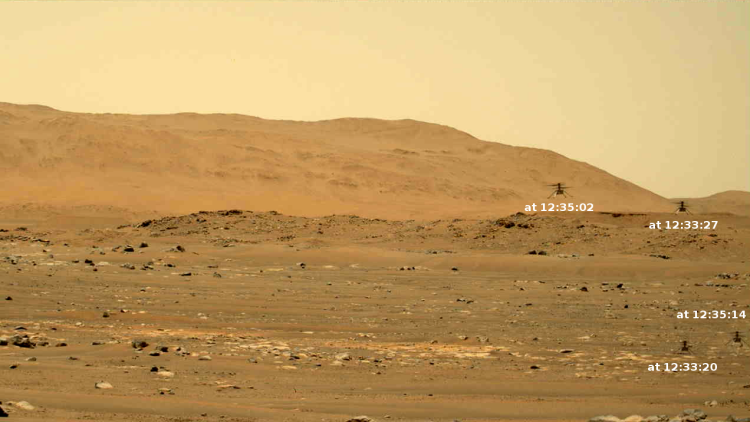
As planned, Ingenuity took off early today on Mars at 12:33:20 pm (local Mars time). Data from the full flight has now arrived on Earth, with images that show the helicopter rising, moving about, and then landing. The montage above captures the part of the flight visible from one of Perservance’s cameras.
Apparently Ingenuity was in the air for about two minutes, and landed a bit to the right of its take-off point. We will have to wait for an update from the engineering team to find out exactly what happened.
UPDATE: Mimi Aung, the Ingenuity project manager, posted a report later today:
The helicopter took off at 10:49 a.m. EDT (7:49 a.m. PDT, or 12:33 local Mars time), climbing to an altitude of 16 feet (5 meters) before flying south approximately 436 feet (133 meters) and then back, for an 872-foot (266-meter) round trip. In total, we were in the air for 117 seconds.
The helicopter also took a lot of images, which they are presently in the process of downloading and reviewing.

For original images, go here, here, here, and here.
As planned, Ingenuity took off early today on Mars at 12:33:20 pm (local Mars time). Data from the full flight has now arrived on Earth, with images that show the helicopter rising, moving about, and then landing. The montage above captures the part of the flight visible from one of Perservance’s cameras.
Apparently Ingenuity was in the air for about two minutes, and landed a bit to the right of its take-off point. We will have to wait for an update from the engineering team to find out exactly what happened.
UPDATE: Mimi Aung, the Ingenuity project manager, posted a report later today:
The helicopter took off at 10:49 a.m. EDT (7:49 a.m. PDT, or 12:33 local Mars time), climbing to an altitude of 16 feet (5 meters) before flying south approximately 436 feet (133 meters) and then back, for an 872-foot (266-meter) round trip. In total, we were in the air for 117 seconds.
The helicopter also took a lot of images, which they are presently in the process of downloading and reviewing.