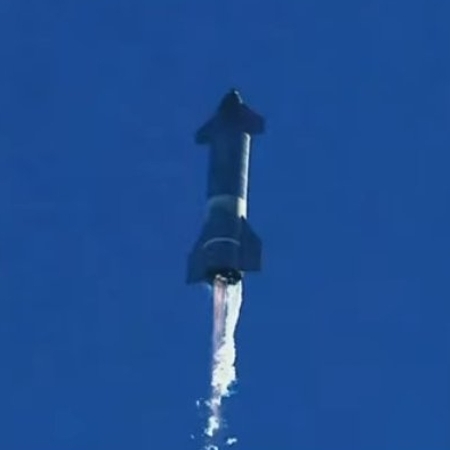
Starship prototype #8 on its first flight test,
December 2020
Capitalism in space: NASA has just announced that it has chosen SpaceX to build the Artemis manned lunar lander, using Starship.
The award, a $2.9 billion fixed price contract, also requires SpaceX to complete an unmanned demo lunar landing with Starship that also returns to Earth, before it lands NASA astronauts on the Moon. The contract also still retains the goal to get this to happen by 2024, though NASA official emphasized that they will only launch when ready.
After these flights the agency says it will open bidding again to the entire industry, which means that others are now being challenged to come up with something that can beat SpaceX in the future.
Nonetheless, the contract award was a surprise, as NASA originally intended to pick two teams to provide redundancy and encourage competition. Instead, the agency completely bypassed lunar landers proposed by Dynetics and a team led by Blue Origin that included Lockheed Martin and Draper.
Even more significantly, though NASA explained in the telecon that they still plan to use SLS and Orion to bring astronauts to Gateway, who will then be picked up by Starship for the landing, this decision is a major rejection of the Space Launch System (SLS), since Starship will not use it to get to the Moon, while the other two landers required it.
In fact, this decision practically makes SLS unnecessary in the Artemis program, as NASA has also awarded SpaceX the contract for supplying cargo to the Lunar Gateway station as well as launching its first two modules, using Dragon capsules and Falcon Heavy. SLS is still slated to launch Orion to Gateway, but Starship can replace Orion as well, since Starship is being designed to carry people from Earth to the Moon. This makes SLS and Orion essentially unneeded, easily abandoned once Starship starts flying.
NASA’s decision also means the Biden administration is willing to use its clout to push for Starship over SLS in Congress, which has favored SLS for years because of the pork it brings to their states and congressional districts. They apparently think that Congress is now ready to risk the end of SLS if it comes with a new program that actually accomplishes something. These developments firmly confirm my sense from February that the political winds are bending away from SLS.
This decision is also a major blow to Blue Origin and the older big space companies that Jeff Bezos’ company partnered with. Their dependence on the very costly and cumbersome SLS rocket meant that their ability to launch on a schedule and cost desired by NASA was severely limited. NASA looked at the numbers, and decided the time was right to go with a more radical system. As was noted by one NASA official during the press teleconference, “NASA is now more open to innovation.”
Based on the details announced during the announcement, NASA was especially drawn to Starship’s payload capability to bring a large payload to the Moon, at the same time it brings humans there as well. It also appears SpaceX’s recent track record of success also added weight to their bid.