May 22, 2020 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Are you enraged yet? The CDC has confirmed that the death rate for the Wuhan flu is probably less than 0.4%, slightly higher than the flu’s 0.1%, but when all factors are considered, including the data that shows it is almost completely harmless to everyone but the elderly who are chronically sick, the disease is essentially just another new flu epidemic, requiring no extreme measures other than acting to protect the vulnerable.
Plus, ultimately we might find out that the IFR [infection fatality rate] is even lower because numerous studies and hard counts of confined populations have shown a much higher percentage of asymptomatic cases. Simply adjusting for a 50% asymptomatic rate would drop their fatality rate to 0.2% – exactly the rate of fatality Dr. John Ionnidis of Stanford University projected.
More importantly, as I mentioned before, the overall death rate is meaningless because the numbers are so lopsided. Given that at least half of the deaths were in nursing homes, a back-of-the-envelope estimate would show that the infection fatality rate for non-nursing home residents would only be 0.1% or 1 in 1,000. And that includes people of all ages and all health statuses outside of nursing homes.
There’s more. Read it all.
What infuriates me the most is that the early data (not the fake models) all pointed in this direction, quite clearly, as noted in detail in this March 17 post, just when panicked state governors were beginning to impose totalitarian rule by edict. Even then it was clear that lock downs made no sense, and would only worsen the situation.
I repeat: Any disease like this requires a rational aggressive and focused response. We can’t ignore it. People need to voluntarily self-quarantine if they feel sick, or if they have older and sick relatives living with them. We should also wash our hands regularly, and avoid unnecessary physical contact with many other individuals.
At the same time, we mustn’t waste our energies doing things that are unnecessary, foolish, or downright counter-productive, such as releasing entire prison populations into the general population.
We also should be outraged by politicians who are using this situation not to deal with it but to impose their pet totalitarian rule over the population, such as passing entirely irrelevant gun bans and shutting down businesses willy-nilly and imprisoning everyone in their homes.
These actions will do little to ease the epidemic. Instead, they might worsen the situation by causing panic (as they have apparently done). Panic is not what this situation warrants. Instead it needs a calm rational response, something that only civilized rational people can give it.
Are we that? Watching what is happening I must sadly say I have my doubts.
In retrospect, it appears if many of our leaders have any rationality, they apply it exclusively to creating schemes for increasing their power and ability to oppress everyone else. Serving the nation and its citizenry appears the last thing on their mind.
Our new fifth column: An investigation by the Department of Education has found that U.S. universities have taken $6 billion in unreported donations from hostile coutnries, all of which could be in violation of the law.
A probe by the Department of Education into colleges that accept foreign investments and donations has uncovered $6 billion in previously unreported foreign donations from US adversaries including China and Russia, a report said Friday.
House Republicans were monitoring the investigation into the schools to determine if they were violating Section 117 of the Higher Education Act of 1965, which prohibits an “Institution of Higher Learning” from failing to properly report foreign gifts of $250,000 or more, Town Hall reported.
It also appears that some of those universities are now uncooperative, apparently placing their loyalties more with their foreign backers than with their own country.
This evidence is not surprising, and is reinforced by the numerous arrests in recent months of many university professors taking money secretly and illegally from China. The culture in the American university community has been downright hostile to the United States for decades. In the past it was dressed up as their effort to not be jingoistic. That was a long time ago. For at least two decades the academic community has been an anti-American fifth column, working as much as it can with foreign powers to both indoctrinate its students against their own country, while providing aid and comfort to authoritarian countries like Russia and China.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX today successfully completed its standard static fire dress rehearsal prior to launch of the Falcon 9 rocket that will place the first manned Dragon capsule, carrying two astronauts, into space on May 27th.
Today NASA also gave its final okay for the launch. It is now set to happen.
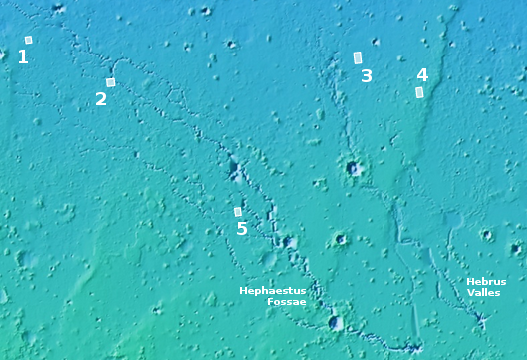
Since 2018 I have made it a point to document every new pit image taken on Mars by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The list of can be found at the bottom of this post.
In the most recent release from MRO, a number of new pits were photographed. All continue to suggest that Mars has a lot of underground voids, some caused by lava flow, some by tectonic activity, some by water ice erosion, and some almost certainly caused by processes we don’t yet know. The images also suggest that we have only identified a small fraction of those underground voids.
The first image to the right, cropped to post here, shows the one new pit in the northern lowlands of Utopia Planitia, near a series of meandering channels and canyons dubbed Hephaestus Fossae and Hebrus Valles.
This appears to be the fifth such pit found in this region. Previously I had documented the first four. The overview map to the right adds this fifth pit. Note how the pit is much closer to the head of Hephaestus. In the full image you can see fissures both to the north and south, as well as many nearby aligned depressions, suggesting the existence of more underground passages, some possibly linked to voids under this very pit.
The pit itself seems filled, with no apparent side passages, though to the southwest there might be something leading off in the shadows.
The overall terrain in this region, including these pits, the fissures, and the many aligned depressions, strongly suggests a lot of underground voids. As I noted in 2019:
» Read more
For those who want to hear me on the radio, I will be doing one hour at 6:00 pm (Central) later today with Robert Pratt on Pratt on Texas, aired on 790-AM KFYO in Lubbock, 1470-AM KYYW in Abilene, and 1290-AM KWFS in Wichita Falls.
We will be talking about space, and also about masks and the tyrants presently found in many statehouses nationwide.
On Sunday I will also be talking space and science with Steve Thompson in Minnesota on WCCO-AM, also for an hour, beginning at 6:00 pm (Central).
Using the precise location and motion data obtained by the space telescope Gaia, astronomers have identified a star that 1.4 million years will come within a trillion miles of the Sun.
That distance puts it well within the outer parts of the theorized Oort cloud at the edge of the solar system. Since the star, Gliese 710, has a mass half that of the Sun, it will thus disturb many objects in that Oort Cloud, causing many to eventually fall sunward and produce a hail of comets several million years later. It will be, for a long time, the brightest object in the night sky, by far.
The data also identified a number of other stars that have in past or will in the future get close to the Sun. The most important result is not that these close approaches occur, but that they have found that they are relatively rare, and even the closest, Gliese 710, never really gets that close.
The universe is big, far bigger than we can really imagine.
Using the ALMA ground-based telescope array in Chile, astronomers have detected two energetic “spots” that appear to be orbiting Sagittarius A* (pronounced A-star), the super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
The spots appear to be regions in the accretion disk surrounding the black hole that are emitting energy.
Their scenario is as follows. Hot spots are sporadically formed in the disk and circle around the black hole, emitting strong millimeter waves. According to Einstein’s special relativity theory, the emission is largely amplified when the source is moving toward the observer with a speed comparable to that of light. The rotation speed of the inner edge of the accretion disk is quite large, so this extraordinary effect arises. The astronomers believe that this is the origin of the short-term variation of the millimeter emission from Sgr A*.
The team supposes that the variation might affect the effort to make an image of the supermassive black hole with the Event Horizon Telescope. “In general, the faster the movement is, the more difficult it is to take a photo of the object,” says Oka. “Instead, the variation of the emission itself provides compelling insight for the gas motion. We may witness the very moment of gas absorption by the black hole with a long-term monitoring campaign with ALMA.” The researchers aim to draw out independent information to understand the mystifying environment around the supermassive black hole.
Everyone please repeat after me: Though this scenario makes sense, based on the facts and our knowledge, there is a lot of uncertainty about these conclusions.
The Russians today used their Soyuz-2 rocket to successfully launch a military satellite designed to detect missile launches from other countries.
The leaders in the 2020 launch race:
8 China
7 Russia
6 SpaceX
3 ULA
The U.S. still leads China 11 to 8 in the national rankings.
In the past week or so there have been numerous stories in the press suggesting that Americans have finally lost patience with the unreasonable Wuhan flu lock downs that have been arbitrarily imposed in the past two months by elected officials, sometimes indefinitely, for no justifiably rational reasons.
In Michigan there were armed protests, and then barbers began publicly defying the lock down orders of their fascist governor.
In New Jersey a health club defied the order of that state’s fascist governor and reopened to cheers from its customers.
In Baltimore a pastor stood at the pulpit and ripped apart the shut down order by that city’s health department.
In Minnesota the Catholic church announced it was reopening for church services, in direct defiance of the orders of that state’s governor.
I could cite many other examples, across the country, in both conservative and liberal states.
Are these push backs necessary? Certainly. These fascist governors and mayors, most of whom have been Democrats, have imposed unreasonable and blatantly illegal arbitrary restrictions on the freedoms of Americans, which must be resisted at all costs.
Are these push backs real? Forgive me if I must sadly remain skeptical. For fifty years I have watched as politicians, mostly from the Democratic Party but with more than ample support from large numbers of Republican Party hacks, have slowly but steadily worked to erode the freedoms of Americans.
» Read more
According to anonymous sources, Trump has decided to pull the U.S. out of the Open Skies Treaty, negotiated in 2002 to allow countries to overfly other nations freely.
President Trump will be pulling the United States out of the Open Skies Treaty, an agreement between more than 30 countries that allow for those involved to fly in each other’s air spaces, a senior administration official confirmed to Fox News. The New York Times first reported that Trump was planning to withdraw from the agreement, worrying NATO member nations who are concerned that once the U.S. is out, Russia will block their flights, which provide valuable surveillance of their own borders.
U.S. officials have warned that Russia had been violating the treaty already by not allowing flights over areas where military exercises were taking place or sites where Russia had nuclear weapons deployed. Each nation in the treaty agrees to make all its territory available for surveillance flights.
Note also that China is not a signatory.
Not surprisingly, their Democratic Party allies, always ready to aid other countries over U.S. interests, are already blasting this decision by the Trump administration.
Reason 10,328,467 to stop using Google: Google routinely steals the intellectual property of others for its own benefit, and then distorts all search results to hide any news stories that report on this theft.
The author at the article documents in great detail Google’s history of theft. He then compares search results from Google, Bing, and Yahoo to show how Google then manipulates search results to hide any stories that report these thefts.
The bottom line: Stop using Google! There are plenty of other search engines, some of which, like DuckDuckGo, that protect the privacy of your searches. Google is a corrupt, unethical company that needs to lose business, fast.
The ATLAS telescope has discovered the first Jupiter Trojan asteroid to spout a tail like a comet.
Early in June 2019, ATLAS reported what seemed to be a faint asteroid near the orbit of Jupiter. The Minor Planet Center designated the new discovery as 2019 LD2. Inspection of ATLAS images taken on June 10 by collaborators Alan Fitzsimmons and David Young at Queen’s University Belfast revealed its probable cometary nature. Follow-up observations by the University of Hawaiʻi’s J.D. Armstrong and his student Sidney Moss on June 11 and 13 using the Las Cumbres Observatory (LCO) global telescope network confirmed the cometary nature of this body.
Later, in July 2019, new ATLAS images caught 2019 LD2 again – now truly looking like a comet, with a faint tail made of dust or gas. The asteroid passed behind the Sun and was not observable from the Earth in late 2019 and early 2020, but upon its reappearance in the night sky in April of 2020, routine ATLAS observations confirmed that it still looks like a comet. These observations showed that 2019 LD2 has probably been continuously active for almost a year.
While ATLAS has discovered more than 40 comets, what makes this object extraordinary is its orbit. The early indication that it was an asteroid near Jupiter’s orbit have now been confirmed through precise measurements from many different observatories. In fact, 2019 LD2 is a special kind of asteroid called a Jupiter Trojan – and no object of this type has ever before been seen to spew out dust and gas like a comet.
There are a number of mysteries here. First, why should it have suddenly become active, since its orbit is relatively circular (similar to Jupiter’s)? Second, it had been assumed that the Jupiter Trojans had been in their orbits for a long time and had long ago vented any ice on their surfaces. This discovery proves that assumption false. It suggests that either this asteroid is a comet that was recently captured, or that things can happen on these asteroids to bring some buried volatiles up to the surface, where they can then vent.
Above all, this asteroid shows that it is dangerous to assume all Jupiter Trojan asteroids are the same. I guarantee when we finally get a close look at a bunch, when the Lucy mission arrives beginning in 2027, the variety will be quite spectacular.
The new colonial movement: An op-ed in India today called for that nation to exit the anti-capitalist 1979 Moon Treaty, different than the 1967 Outer Space Treaty in that it specifically outlaws all private ownership in space and was thus only signed by a very small handful of nations.
India has signed but never ratified the Moon Treaty. The U.S., Russia, and China never did.
India must formally exit this agreement, says Dr Chaitanya Giri, a Gateway House Fellow of Space and Ocean Studies Programme, who was earlier affiliated to the Earth-Life Science Institute at Tokyo Institute of Technology and the Geophysical Laboratory at Carnegie Institution for Science.
The problem with the Moon Agreement, Dr Giri told BusinessLine, lies in the Article 4.1, which says that “the exploration and use of the Moon shall be the province of all mankind and shall be carried out for the benefit and in the interests of all countries, irrespective of their degree of economic and scientific development.”
This can be interpreted to mean that if you are a signatory to the agreement, you shall share the fruits of your efforts on the Moon with everybody, whereas if you are not a signatory you won’t have to do so.
The article also notes that, under Trump’s Artemis Accords and executive order allowing for private ownership of any resources extracted in space, India will not be able to partner with the U.S. as long as it remains a signatory to the 1979 Moon Treaty.
That there are now demands in India to leave the Moon Treaty so it can work with the U.S. under Trump’s Artemis Accords also means that those accords are working to convince nations to abandon the Outer Space Treaty’s restrictions on owning land and claiming sovereignty. And they are doing so very quickly.
Capitalism in space: A British private company has successfully completed the first static fire test of a rocket in Great Britain in a half century.
Skyrora effectively made the UK ready for launching rockets into space after a team successfully built a mobile launch complex and completed a full static fire test with the Skylark L rocket on it – in only five days. Skyrora’s combined achievement also signifies the first vertical static fire test of this magnitude in the UK since the Black Arrow Programme, 50 years ago. The Skylark L rocket could be ready to launch from a British spaceport as early as spring 2021 and the inaugural launch of the low Earth orbital (LEO) Skyrora XL rocket by 2023.
The Skylark L is intended as a suborbital rocket. The XL will the the first orbital rocket. The company’s goal here is to create a rocket with a very inexpensive mobile ground infrastructure, that needs only a concrete pad to launch. Several smallsat American companies have been working towards this goal. The Chinese, using military equipment, have apparently achieved it. They all now have competition from Great Britain.
Because of delays caused by the Wuhan flu panic, the European Space Agency (ESA) and ArianeGroup now expect that the first launch of their new rocket, the Ariane 6, will likely be delayed from late in 2020 to 2021.
The loss of the flight’s payload is also a problem.
Finally, megaconstellation startup OneWeb had booked 30 small broadband satellites on the Ariane 6 maiden flight, but filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in March, putting the mission in question. Luinaud said if Arianespace can’t find another customer for the Ariane 6 maiden flight this year, it may wait until 2021 to find a payload and avoid flying the rocket empty.
Overall Ariane 6 has been having trouble getting customers. Though it is less expensive that the Ariane 5, it it is entirely expendable and thus remains much more expensive than SpaceX’s Falcon 9. And with the Russians slashing the price of their Russia Proton rocket satellite companies have ample other options. It is for this reason I do not expect Ariane 6 to stick around long. ESA will be quickly forced to replace it with something less expensive and probably reusable.
The American flag that flew on the first and last shuttle mission and was left on ISS for the next crew flown on an American spacecraft to claim apparently went missing during the decade since the last American shuttle flight, and took several weeks of searching in 2018 for astronauts to find it.
“We looked and looked and looked,” said Tingle. “I talked to my fellow astronauts that were on board the ISS and everybody had a little bit of a different memory on where it could be or where it might be. So we spent probably three or four weeks just kind of scouring in our spare time, trying to find it.”
They did find it, and now it awaits the arrival of the two-person crew of SpaceX’s Dragon capsule, Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley, set to launch on May 27th, the first Americans to launch from American soil on an American rocket in an American spacecraft in almost a decade.
More important: This will be the first flight of any Americans on a private rocket and spacecraft, built and owned by a private commercial company instead of the government. For the capitalistic and free United States, it marks the end of a half century of a government-run Soviet-style space program and a return to capitalism and freedom.
Capitalism in space: Virgin Orbit has announced that it will attempt the first orbital launch of its LauncherOne rocket this coming Sunday, May 24.
The company is targeting Sunday (May 24) for its Launch Demo mission, with a backup opportunity on Monday (May 25). The four-hour window will open each day at 1 p.m. EDT (1700 GMT), Virgin Orbit representatives announced today (May 20).
Launch Demo will be a huge milestone for Virgin Orbit, which has been developing its air-launch system for five years. That system involves a modified Boeing 747 jet called Cosmic Girl and a 70-foot-long (21 meters) rocket known as LauncherOne, which is capable of delivering about 1,100 lbs. (500 kilograms) to a variety of destinations in low Earth orbit.
If the launch succeeds, than Virgin Orbit will stand ready to begin commercial launches later this year.
The head of the Palestinian Authority (PA), Mahmoud Abbas, threatened yesterday to scrap all cooperative agreements with Israel that are used by both to run the differently controlled sections of West Bank if Israel goes ahead with declaring sovereignty over its settlements in that West Bank, as outlined in the Trump-offered peace deal.
Palestinian Authority President Mahmud Abbas has said he is ending “all agreements” with Israel and the United States in response to Israeli plans to annex parts of the occupied West Bank. Israel would now have to “bear all responsibilities… as an occupying power”, Mr Abbas said.
Similar warnings in the past have ultimately not been followed through.
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu wants to apply Israeli sovereignty to Jewish settlements and the Jordan Valley. The move would be in line with US President Donald Trump’s “vision for peace” between Israel and the Palestinians, which was unveiled in January. Mr Trump’s plan also envisages a Palestinian state in about 70% of the West Bank, all of Gaza, and with its capital on the fringes of East Jerusalem.
The Palestinians – who claim all of the West Bank, Gaza and East Jerusalem – have dismissed the plan as biased towards Israel and a denial of their rights.
If Abbas goes through with this threat, it will mean that the Palestinians will no longer cooperate with the Israelis on security matters. In that case do not expect the Israelis to stand by meekly when there is an almost guaranteed subsequent rise in Palestinian terrorist attacks. Like all actions by the Palestinian leadership since 1948, such a course by Abbas would end up shooting the Palestinians in the foot. Israel would be forced to move in and take power again, throwing Abbas and his corrupt PA out. There might be some initial objections by the Palestinian population, but since their lot has suffered since rule in their areas was shifted from Israel to the PA after the Oslo Accords, I suspect the protests will be superficial and short-lived.
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
A sign of things to come, at last? The voters in Staunton, Virginia, yesterday tossed from office three Democrat incumbent city council members, making that city council now all Republican.
All three had been on the council for years, since 08, 10, and 12, so these were not new faces. They had been well established, and are now gone,
This in a city that voted twice for Barack Obama, once for Hillary Clinton, and also for black-face-loving, gun-control loving Democratic Governor Ralph Northram. Moreover, the defeated Democrats actually got twice as many votes as during the last election, but were still soundly defeated by a much larger opposition.
In addition, another nearby city, Waynesboro, Republicans gained two seats on the city council, giving the Republicans a council majority.
I wonder what events recently might have raised the ire of the voters? Can anyone make a guess?
An evening pause: Hat tip Rex Ridenoure of Ecliptic Enterprises, who adds, “Since most of us have been bouncing off walls…”
The OSIRIS-REx science team today announced that, in order to give them more preparation time needed because of the coronavirus protocols, they have rescheduled their second rehearsal of the spacecraft’s touch-and-go sample grab from the asteroid Bennu from June to August, and delayed the actual touch-and-go sample grab from August to October.
The mission had originally planned to perform the first Touch-and-Go (TAG) sample collection event on Aug. 25 after completing a second rehearsal in June. This rehearsal, now scheduled for Aug. 11, will bring the spacecraft through the first three maneuvers of the sample collection sequence to an approximate altitude of 131 ft (40 m) over the surface of Bennu. The first sample collection attempt is now scheduled for Oct. 20, during which the spacecraft will descend to Bennu’s surface and collect material from sample site Nightingale.
Previously they had said that the rehearsal would get as close as 82 feet. Nothing has changed. That distance was the closest they expected the spacecraft to get. The new number, 131 feet, is in the middle of possible ranges. As explained to me by Erin Morton, head of communications for OSIRIS-REx in the Principal Investigator’s Office, “I originally chose the lowest altitude in that range to include in our public outreach materials, but later realized that it made more sense to use the mid-point altitude number, since that’s the average of the high and low possibilities.”
Though they have the ability to do two more sample grabs if the first in October is unsuccessful, they won’t bother if it succeeds. They must leave Bennu regardless in mid-2021 to return the sample to Earth on September 24, 2023.
Japan today successfully launched to ISS the last of its first generation HTV cargo ships.
This was the ninth such cargo ship launched by Japan. The mission was also the last launch of Mitsubishi’s H-2B rocket, Japan’s most powerful. It is being replaced with the H-3 rocket, which they hope to fly for the first time before the end of this year. They also hope that the H3 will be cheaper to operate, and will allow Mitsubishi to garner some commercial business with it, something they failed entirely to do with the H-2B.
This was also Japan’s second launch in 2020, which means they remain outside the leaders in the 2020 launch race:
8 China
6 SpaceX
6 Russia
3 ULA
The U.S. continues to lead China 11 to 8 in the national rankings.
When dawn comes to the airless rough terrain of the Moon’s poles, it comes in fits and spurts. The floors of some craters never see it, while the high crater rims might have only a short time in darkness, their elevation high enough to keep the Sun above the horizon almost continuously. While there appear to be no places at the poles that have eternal daylight, there are places where night is short and infrequent.
The cool image to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, shows one such place close to the Moon’s north pole, the rim of Aepinus Crater. Taken by Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) on March 10, 2020, the illuminated area on this oblique image is about one by four miles in size. With dawn approaching this rim sees the Sun before the rest of the polar region, and remains illuminated long after the surrounding region has returned to darkness.
To get an idea of how small this one illuminated area is, below is a panorama showing the wide region around the rim.
» Read more
Capitalism in space: A fire during most recent Starship prototype test that did not do any apparent serious damage has however left that prototype in limbo.
The fate of SpaceX’s fourth full-scale Starship prototype appears to be in limbo after a third (seemingly successful) engine ignition test unintentionally caught the rocket on fire.
Now more than 12 hours after Starship SN4 fired up its new Raptor engine, the ~30m (~100 ft) tall, 9m (~30 ft) wide prototype is apparently trapped with one or both of its propellant tanks still partially filled with liquid (or gaseous) methane and/or oxygen. An initial road closure scheduled from noon to 6pm local quickly came and went and SpaceX and Cameron County Texas have since modified the paperwork, extending the closure a full 24 hours. In other words, SpaceX has reason to believe that Starship SN4 may continue to be unsafe (i.e. pressurized) as many as ~30 hours after it technically completed its third static fire test – extremely unusual, to say the least.
The article at the link offers a lot of speculation. The bottom line is that the first actual hop of this prototype is probably delayed. SpaceX had said it wanted to do it before the end of the month (probably to maximize publicity by having it occur about the same time as the manned Dragon launch). They will need to get this prototype safed, review the data and damage from the fire, and then make repairs before doing that hop. I would also expect SpaceX to do another tank and engine test first as well, to make sure those repairs worked.
This is not to say that the delay will be long. SpaceX does not waste time in these matters. It just probably means the hop won’t occur until mid- to late June.
NASA today announced that it has renamed the proposed Wide Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST) the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope in honor of the agency’s first head of astronomy.
Considered the “mother” of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, which launched 30 years ago, Roman tirelessly advocated for new tools that would allow scientists to study the broader universe from space. She left behind a tremendous legacy in the scientific community when she died in 2018.
…When she arrived at NASA, astronomers could obtain data from balloons, sounding rockets and airplanes, but they could not measure all the wavelengths of light. Earth’s atmosphere blocks out much of the radiation that comes from the distant universe. What’s more, only a telescope in space has the luxury of perpetual nighttime and doesn’t have to shut down during the day. Roman knew that to see the universe through more powerful, unblinking eyes, NASA would have to send telescopes to space.
Through Roman’s leadership, NASA launched four Orbiting Astronomical Observatories between 1966 and 1972. While only two of the four were successful, they demonstrated the value of space-based astrophysics and represented the precursors to Hubble. She also championed the International Ultraviolet Explorer, which was built in the 1970s as a joint project between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency) and the United Kingdom, as well as the Cosmic Background Explorer, which measured the leftover radiation from the big bang and led to two of its leading scientists receiving the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Above all, Roman is credited with making the Hubble Space Telescope a reality. In the mid-1960s, she set up a committee of astronomers and engineers to envision a telescope that could accomplish important scientific goals. She convinced NASA and Congress that it was a priority to launch the most powerful space telescope the world had ever seen.
This is a nice and very fitting gesture to honor one of the many unsung heroes who were important in the history of space astronomy. I just hope that Roman’s telescope doesn’t end up like James Webb’s, so over budget and behind schedule that it destroys all other NASA space telescope projects. Sadly, its track record so far suggests this is what will happen, which is why the Trump administration has been trying to get it canceled.