December 3, 2019 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
» Read more
Scientists today published four papers outlining the first scientific results obtained during the first two close fly-bys of the Sun by the Parker Solar Probe.
The four papers, now available online from the journal Nature, describe Parker’s unprecedented near-Sun observations through two record-breaking close flybys. They reveal new insights into the processes that drive the solar wind – the constant outflow of hot, ionized gas that streams outward from the Sun and fills up the solar system – and how the solar wind couples with solar rotation. Through these flybys, the mission also has examined the dust of the coronal environment, and spotted particle acceleration events so small that they are undetectable from Earth, which is nearly 93 million miles from the Sun.
During its initial flybys, Parker studied the Sun from a distance of about 15 million miles. That is already closer to the Sun than Mercury, but the spacecraft will get even closer in the future, as it travels at more than 213,000 mph, faster than any previous spacecraft.
Details about the four main takeaways are described at the link. None of the discoveries is earth-shaking but all help scientists better understand the Sun’s inner atmosphere.
Capitalism in space: SpaceX plans to perform a six hour orbital coast test of its Falcon 9 upper stage following the release of the Dragon cargo capsule tomorrow (scrubbed today due to high winds).
This is why the first stage will land on a drone ship rather than at Kennedy.
According to SpaceX the test is at the request of “other customers”, unnamed. The article adds this speculation:
Jensen says that the coast test will be performed for unspecified “other” customers, presumably referring to the US Air Force (USAF) and other commercial customers interested in direct-to-geostationary (GEO) launch services. Direct GEO launches require rocket upper stages to perform extremely long coasts in orbit, all while fighting the hostile vacuum environment’s temperature swings and radiation belts and attempting to prevent cryogenic propellant from boiling off or freezing solid. In simple terms, it’s incredibly difficult to build a reliable, high-performance upper stage capable of remaining fully functional after 6-12+ hours in orbit.
Although SpaceX said that the test was for “other” customers, that may well have been a cryptic way to avoid indicating that one such customer might be NASA itself. NASA is in the midst of a political battle for the Europa Clipper spacecraft’s launch contract, which is currently legally obligated to launch on NASA’s SLS rocket. Said rocket will likely cost on the order of >$2 billion per launch, meaning that simply using Falcon Heavy or Delta IV Heavy could save no less than ~$1.5 billion. Incredibly, that means that simply using a commercial launch vehicle could save NASA enough money to fund an entire Curiosity-sized Mars rover or even a majority of the cost of building a dedicated Europa lander. Such a launch would demand every ounce of Falcon Heavy’s performance, including a very long orbital coast.
These speculations could all be true. SpaceX might merely be doing what it always does, testing new engineering upgrades during operational missions. It will then be able to sell its rocket’s enhanced capability to all these customers.
The new colonial movement: According to Chinese officials, China plans to launch 30 times in 2020, maintaining the same pace that they met in 2019.
Zhuang Jingguo, chief engineer of the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the country’s man space contractor, told media at the Fifth China International Commercial Aerospace Forum late last month that the state-owned enterprise will launch around 30 rockets next year.
This number is expected to include missions to Mars, the moon, test flights of new launch vehicles, and the completion of the Beidou navigation system. Commercial launch companies will further add to Chinese launch activities.
The article also provides a good overall summary of China’s present space effort, which is extensive and growing.
During an agency meeting where the new manager of NASA’s manned program officially took charge, administrator Jim Bridenstine expressed disagreement with a Trump administration estimate of $2 billion for each SLS launch.
The OMB letter used “over $2 billion” as the estimated cost of an SLS launch, arguing that is $1.5 billion more than a commercial launch. The $2 billion figure has been widely cited since then as an official cost estimate.
Bridenstine was asked about it today, and disagreed. “I do not agree with the $2 billion number. It is far less than that. I would also say the number comes way down when you buy more than one or two. I think in the end we’re going to be in the $800-900 million range.” NASA has bought only two SLS launches so far and negotiations are just starting on the third and fourth, he added. [emphasis mine]
Well that solves everything! SLS will only cost a little less than a billion per launch, not two billion. Any fool can see this is clearly competitive with the $100 million that SpaceX charges for each Falcon Heavy launch. And you’d have to do two Falcon Heavy launches to match what SLS can do in one launch. Obviously we want to buy SLS! It’s what any Washington lawmaker or bureaucrat would clearly conclude.
The article notes that NASA has only “bought two SLS launches” but fails to explain why. This is all that Congress has appropriated. NASA is negotiating with Boeing to build as many as ten more, but as far as I know, the authorization from lawmakers has not yet been given to do so.
But then, why not? We are no longer ruled by our elected officials, but by the unelected bureaucrats who live high on the hog in their plush Washington digs.
Chinese engineers have put both Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2 into dormant mode after completed their twelve lunar day on the far side of the Moon.
The article from the Chinese state-run press provides very little information, other than telling us that Yutu-2 traveled 345 meters, written in a way to imply that was the distance the rover traveled in this last lunar day. I think that is wrong, however. Based on the distances traversed during previous lunar days, and that the rover had traveled a total of 290 meters at the end of its tenth lunar day, I think this new number is the total distance traveled.
The article also does not say what the consequences will be for these two spacecraft now that the priority of their communications relay has shifted from communications to being a radio telescope.
It could be that the consequences will be minor, considering that both spacecraft are in sleep mode during the lunar nights and for high noon of the lunar day. During those periods the relay satellite could be devoted full time to radio astronomy and have no impact on the lander and rover.
Unfortunately China has not said.
Boeing has decided to delay its first unmanned demo mission of its Starliner capsule to ISS by two days, to December 19, because of launchpad issues.
An evening pause: Another example of someone who decides he wants to do something, and then goes out and does it. This STOL (short take-off and landing) home-built plane, dubbed Draco, was apparently a big hit in the small plane community. Sadly, in September the plane was totaled (no injuries) during a take-off with strong cross winds (video here).
Hat tip Cotour.

The space telescope TESS, designed to look for exoplanets by imaging one hemisphere of the sky repeatedly over a full year, also successfully captured in those images the full outburst from the comet 46P/Wirtanen that occurred on September 26, 2018.
The animation created from those images is to the right.
According to Farnham, the TESS observations of comet Wirtanen were the first to capture all phases of a natural comet outburst, from beginning to end. He noted that three other previous observations came close to recording the beginning of an outburst event. Observations of a 2007 outburst from comet 17P/Holmes began late, missing several hours of the initial brightening phase of the event. In 2017, observations of an outburst from comet 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 (SW1) concluded early, due to limitations on pre-scheduled observation time. And, while observations from the UMD-led Deep Impact mission captured an outburst from comet Tempel 1 in unprecedented detail in 2005, the outburst was not natural—created instead by the mission’s impactor module. However, the current observations are the first to capture the dissipation phase in its entirety, Farnham said.
Although Wirtanen came closest to Earth on December 16, 2018, the outburst occurred earlier in its approach, beginning on September 26, 2018. The initial brightening of the outburst occurred in two distinct phases, with an hour-long flash followed by a more gradual second stage that continued to grow brighter for another 8 hours. This second stage was likely caused by the gradual spreading of comet dust from the outburst, which causes the dust cloud to reflect more sunlight overall. After reaching peak brightness, the comet faded gradually over a period of more than two weeks. Because TESS takes detailed, composite images every 30 minutes, the team was able to view each phase in exquisite detail.
The data from TESS is likely going to overwhelm the astronomy community for years.
The uncertainty of science: A new peer-reviewed paper in a major astronomy science journal suggests that dark energy might not actually exist, and that the evidence for it might simply be because the original data was biased by the Milky Way’s own movement.
What [the scientists in this new paper] found is that the best fit to the data is that the redshift of supernovae is not the same in all directions, but that it depends on the direction. This direction is aligned with the direction in which we move through the cosmic microwave background. And – most importantly – you do not need further redshift to explain the observations.
If what they say is correct, then it is unnecessary to postulate dark energy which means that the expansion of the universe might not speed up after all.
Why didn’t Perlmutter and Riess [the discoverers of dark energy] come to this conclusion? They could not, because the supernovae that they looked were skewed in direction. The ones with low redshift were in the direction of the CMB dipole; and high redshift ones away from it. With a skewed sample like this, you can’t tell if the effect you see is the same in all directions.
The link is to a blog post by a physicist in the field, commenting on the new paper. Below the fold I have embedded a video from that same physicist that does a nice job of illustrating what she wrote.
This paper does not disprove dark energy. It instead illustrates the large uncertainties involved, as well as show solid evidence that the present consensus favoring the existence of dark energy should be questioned.
But then, that’s how real science works. When the data is sketchy or thin, with many assumptions, it is essential that everyone, especially the scientists in the field, question the results. We shall see now if the physics community will do this.
Hat tip to reader Mike Nelson.

The photograph to the right, reduced and cropped to post here, was imaged on October 20, 2019 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a spectacular thousand-foot-deep canyon in the region of Cerberus Fossae, an area of Mars crossed by numerous deep east-west fissures and depressions.
Hidden in the small white box on the eastern end of that canyon are Martian geological features, small and at first glance not that interesting, that are of great significance and the focus of intense research.
The map to the right shows an overview of the region. The yellow cross shows the location of this particular crack.
In my previous post about Cerberus Fossae, I had incorrectly assumed that these cracks and similar lines of pits or depressions were caused by the sinking of surface material into underground lava tubes. While this is possible in some cases, it is not the main cause of these cracks. Instead, they were formed due to the pressure from below caused by the rise of the surrounding giant volcanoes, Elysium Mons to the north and Olympus Mons to the east. That pressure stretched the crust until it cracked in numerous places. In Cerberus Fossae this produced a series of parallel east-west fissures, some more than seven hundred miles long.
The young age of Cerberus Fossae is dramatically illustrated by the wider mosaic below, showing the entire crack.
» Read more
Today Kamala Harris announced she is dropping out of the race to be the Democratic Party’s presidential candidate.
Not surprisingly, activists in the Democratic Party immediately blamed racism for her failure. From the leftist New York Times:
Still, Ms. Harris had already qualified for the next presidential debate, scheduled for Dec. 19, the only non-white candidate to do so thus far. Without her, Democrats may have an all-white debate stage after beginning the primaries with the most racially diverse field in history, though candidates like Representative Tulsi Gabbard of Hawaii and businessman Andrew Yang may still qualify in the coming days.
“No matter your candidate, you have to recognize that going from the most diverse field ever in January to a potentially all-white debate stage in December is catastrophic,” wrote Leah Greenberg, a co-executive director of Indivisible, a national progressive group, on Twitter.
…“She really showed the importance of having different perspectives on the debate stage,” said Amanda Hunter, research and communications director at the Barbara Lee Family Foundation, which supports women in politics and studies double standards. “Her personal story about being bused to school was something that a historically typical older white man would not bring to the conversation.”
But “there is still a very entrenched stereotype of what a presidential candidate looks like in this country,” Ms. Hunter said. “Simply by running, Senator Harris challenged that and broke down stereotypes. But a lot of the questions around electability and the challenges she faced were probably motivated by that entrenched stereotype that so many people held.” [emphasis mine]
Note how everything to these Democrat officials is based on race. Everything. To them, Harris lost because she wasn’t white, and because Americans can only conceive a white man as president.
Of course, this thinking is quite idiotic, considering that these same Americans voted twice for a black president, in 2008 and 2012. That’s hardly ancient history.
The only diversity that should matter is diversity of thought, of ideas, of policy suggestions. Among Democrats that’s the last thing we’ve seen in the past three years. All they have shown us is hate and opposition to all things Trump, followed by a desire to destroy the free capitalist United States and replace it with their warped view of the Soviet Union.
If you are normal decent person who happens to belong to the Democratic Party and routinely vote for them, be aware that this party is not the party you think it is. These comments above illustrate again the corrupt, racist, and bigoted make-up of the party’s power structure. They hate Trump, they hate ordinary whites, they hate freedom, and they hate you, if you oppose them in any way at all, even if you have been a loyal Democrat for decades.
For my part Harris’s exit is a great relief. She has repeatedly demonstrated her fascist tendencies in recent years.
I suspect this history had a lot more to do with her failure than her skin color.
Democratic Party coup update: The president of the Ukraine yesterday once again stated that President Trump applied no pressure on him to begin an investigation into Joe Biden.
Once again, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has denied again that President Trump withheld military aid in order to pressure him to investigate the Bidens or Ukrainian election interference. In an interview with TIME magazine, Zelensky made this absolutely clear. “Look, I never talked to the President from the position of a quid pro quo. That’s not my thing,” he said. “I don’t want us to look like beggars. But you have to understand. We’re at war. If you’re our strategic partner, then you can’t go blocking anything for us. I think that’s just about fairness. It’s not about a quid pro quo. It just goes without saying.”
This is not the first time he has stated this publicly. Furthermore, his foreign minister has said the same thing, as has the U.S. ambassador during testimony to Congress.
On the other side, the accusations of misbehavior from Democratic Party witnesses have either been hearsay from people not even present during Trump’s phonecalls with Zelinsky, or from low-level bureaucrats who merely have a difference of opinion with Trump about U.S. foreign policy. I don’t remember however ever voting for them for President. Do you?
This ridiculous effort by the Democrats to overturn a legal election would be hilarious if it wasn’t so offensive. However, increasingly it appears it is serving a good end, as it is revealing their power-hungry, totalitarian, and anti-democratic culture to the entire country. They don’t support democracy and elections, only their guaranteed unopposed right to rule. Such people should never be given positions of power, and if they manage to do so, they should be removed by the voters as soon as possible.
The new colonial movement: The second stage engine for China’s new Long March-8 rocket has successfully passed its engine tests.
Developed by the CASC [China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, China’s equivalent to NASA], the Long March-8 rocket is a new type of rocket that uses module design and can be prepared in a short time, making it competitive for commercial launch.
The first stage of the Long March-8 rocket is similar to that of the Long March-7 rocket and the second stage rocket is similar to the third stage of the Long March-3A rocket. It has a payload capacity of 5 tonnes to sun-synchronous orbit and 2.8 tonnes to geostationary transfer orbit.
This payload capacity is about a fourth that of the Falcon 9, but because the weight and size of satellites is shrinking, that smaller capacity might actually be an advantage. There is less need for the larger rockets in the commercial unmanned satellite industry, so for China to build a new smaller rocket that can be launched for less, even though it is not reusable, gives them a route for competing with SpaceX’s reuseability.
They hope to launch 10 to 20 times per year, beginning next year.
After spending two weeks testing its main ion engines just beyond the gravitational sphere of influence of the asteroid Ryugu, Japanese engineers today initiated full engine operation, beginning the spacecraft’s journey back to Earth.
Hayabusa-2 is expected to return to Earth space in December 2020, where it will release a small capsule containing the two samples it obtained of Ryugu will be released to land on Earth and be recovered. At that point, if Hayabusa-2 is still in good condition it will be available to send to other locations in the solar system.
Astronomers have discovered the most massive black hole yet discovered, having a mass 40 billion times the mass of our Sun.
The new data obtained at the USM Wendelstein observatory of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University and with the MUSE instrument at the VLT [Very Large Telescope in Chile] allowed the team to perform a mass estimate based directly on the stellar motions around the core of the galaxy. With a mass of 40 billion solar masses, this is the most massive black hole known today in the local universe. “This is several times larger than expected from indirect measurements, such as the stellar mass or the velocity dispersion of the galaxy,” remarks Roberto Saglia, senior scientist MPE and lecturer at the LMU.
The light profile of the galaxy shows a centre with an extremely low and very diffuse surface brightness, much fainter than in other elliptical galaxies. “The light profile in the inner core is also very flat,” explains USM doctoral student Kianusch Mehrgan, who performed the data analysis. “This means that most of the stars in the centre must have been expelled due to interactions in previous mergers.”
To give some perspective, the mass of the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A* (pronounced A-Star), is thought to be about 4.6 million solar masses. This newly discovered supermassive black hole is almost nine thousand times heavier.
A evening pause: Performed live December 3, 2014 at the Udvar-Hazy Center of the Air & Space Museum in Virginia. They call this a flash mob but it isn’t, since the crowds clearly know what is about to happen. The music however is wonderful, and makes for a nice start to the holiday season.
Hat tip Edward Thelen.
Using a mosaic of Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) images, citizen scientist Shanmuga Subramanian located on the Moon the debris and impact point for India’s Vikram lander that crashed there in September, an identification that has since been confirmed by LRO scientists.
The image on the right, reduced to post here, has been modified by the scientists to bring out the features that changed before and after the impact.
After receiving this tip the LROC team confirmed the identification by comparing before and after images. When the images for the first mosaic were acquired the impact point was poorly illuminated and thus not easily identifiable. Two subsequent image sequences were acquired on 14, 15 October and 11 November. The LROC team scoured the surrounding area in these new mosaics and found the impact site (70.8810°S, 22.7840°E, 834 m elevation) and associated debris field. The November mosaic had the best pixel scale (0.7 meter) and lighting conditions (72° incidence angle).
The debris first located by Shanmuga is about 750 meters northwest of the main crash site and was a single bright pixel identification in that first mosaic (1.3 meter pixels, 84° incidence angle). The November mosaic shows best the impact crater, ray and extensive debris field. The three largest pieces of debris are each about 2×2 pixels and cast a one pixel shadow.
No word yet on what this new information reveals about Vikram’s failure.
Cool image time! In digging through the new images that come down from the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), my reaction sometimes is “What the heck caused that?”
That was my reaction when I looked at the image to the right, cropped to post here.
The full image, taken on October 6, 2019, shows the floor of one of the many north-south fissures found in the volcanic Tharsis Bulge west of Valles Marineris and east of Olympus Mons. The fissures are caused when the crust is pushed upward by volcanic pressure, causing the surface to crack.
In this case the mystery is that patch of east-west ridges at the bottom of this somewhat wide fissure. While they might be dunes, they do not resemble dunes, as they have a rigid and somewhat sharp appearance. More puzzling is their somewhat abrupt appearance and disappearance. Except for its northern end, the edges of the patch are so sharply defined. If these were dunes you’d think they’d fade away more gradually.
Could the ridges be a more resistant subsurface feature slowly being revealed as surface material erodes away? Sure, but their orientation is completely opposite to the north-south fissures that dominate this region. One would expect deeper features to reflect that same general orientation. These ridges do not.
This image was dubbed a “Terrain Sample,” which means it was taken not because of any specific research goal, but because the scientists who run MRO’s high resolution camera had a gap in their schedule and needed to take a picture to maintain the camera’s proper temperature. In such cases they often take somewhat random images, not knowing what they will find. In this case they struck geological gold, a mystery that some postdoc student could spend a lot of time analyzing.
The New Horizons science team today released data that confirms that, as theorized, the speed of the solar wind decreases as it travels farther from the Sun.
As the solar wind moves farther from the Sun, it encounters an increasing amount of material from interstellar space. When interstellar material is ionized, the solar wind picks up the material and, researchers theorized, slows and heats in response. SWAP [an instrument on New Horizons] has now detected and confirmed this predicted effect.
The SWAP team compared the New Horizons solar wind speed measurements from 21 to 42 astronomical units to the speeds at 1 AU from both the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) and Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory (STEREO) spacecraft. (One AU is equal to the distance between the Sun and Earth.) By 21 AU, it appeared that SWAP could be detecting the slowing of the solar wind in response to picking up interstellar material. However, when New Horizons traveled beyond Pluto, between 33 and 42 AU, the solar wind measured 6-7% slower than at the 1 AU distance, confirming the effect.
The data also suggests that New Horizons could exit the heliosphere and enter interstellar space as early as sometime in the 2020s.
An evening pause: This pause starts with a heartfelt thank you for the support to this guy’s project. You will never guess what the project involves.
It does prove that, give true freedom, people will derive pleasure from the wildest things..
Giving Thanks from Awen & Logos on Vimeo.
The European Space Agency (ESA) received its largest budget increase ever, 20%, from its 22 member nations at a high level meeting yesterday.
The meeting also included commitments to remain a partner in ISS to 2030 and increase participation in Lunar Gateway. From the press release:
With worldwide partners, Europe will take its place at the heart of space exploration going farther than we have ever gone before – we continue our commitment to the International Space Station until 2030 as well as contributing vital transportation and habitation modules for the Gateway, the first space station to orbit the Moon. ESA’s astronauts recruited in 2009 will continue to receive flight assignments until all of them have been to space for a second time, and we will also begin the process of recruiting a new class to continue European exploration in low Earth orbit and beyond. European astronauts will fly to the Moon for the first time. Member States have confirmed European support for a ground-breaking Mars Sample Return mission, in cooperation with NASA.
ESA will help develop the commercial benefits of space for innovators and governments across the Member States, boosting competitiveness in the NewSpace environment. We will develop the first fully flexible satellite systems to be integrated with 5G networks, as well as next-generation optical technology for a fibre-like ‘network in the sky’, marking a transformation in the satellite communication industry. Satellite communications will join forces with navigation to begin satnav for the Moon, while closer to home commercial companies can access funding for new applications of navigation technologies through the NAVISP programme. ESA Ministers have secured a smooth transition to the next generation of launchers: Ariane 6 and Vega-C, and have given the green light to Space Rider, ESA’s new reusable spaceship.
Isn’t competition wonderful? ESA’s budget has been stagnant for years. Then SpaceX comes along and threatens its commercial market share while generating a new political will in the U.S. to renew its own space effort, and suddenly the European nations that make up ESA decide they need to do the same.
Much of the proposed program for ESA is very likely to happen, especially the commitments to a variety of astronomical and planetary missions. The agency’s commercial effort is also likely to happen, but whether it can happen fast enough to be competitive is questionable. As a government agency ESA’s track record in its effort to compete in the launch market has not been impressive. It took them far too long to accept the idea of reuseable rockets or the need to cut their costs drastically.
An afternoon pause: We are all too busy right this moment with turkey, friends, family, and socializing. Here Louis Armstrong tells you what it all means, really.
Recorded in 1967.
Washington, D.C.
October 3, 1863
By the President of the United States of America.
A Proclamation.
The year that is drawing towards its close, has been filled with the blessings of fruitful fields and healthful skies. To these bounties, which are so constantly enjoyed that we are prone to forget the source from which they come, others have been added, which are of so extraordinary a nature, that they cannot fail to penetrate and soften even the heart which is habitually insensible to the ever watchful providence of Almighty God.
In the midst of a civil war of unequalled magnitude and severity, which has sometimes seemed to foreign States to invite and to provoke their aggression, peace has been preserved with all nations, order has been maintained, the laws have been respected and obeyed, and harmony has prevailed everywhere except in the theatre of military conflict; while that theatre has been greatly contracted by the advancing armies and navies of the Union. Needful diversions of wealth and of strength from the fields of peaceful industry to the national defence, have not arrested the plough, the shuttle or the ship; the axe has enlarged the borders of our settlements, and the mines, as well of iron and coal as of the precious metals, have yielded even more abundantly than heretofore. Population has steadily increased, notwithstanding the waste that has been made in the camp, the siege and the battle-field; and the country, rejoicing in the consciousness of augmented strength and vigor, is permitted to expect continuance of years with large increase of freedom.
No human counsel hath devised nor hath any mortal hand worked out these great things. They are the gracious gifts of the Most High God, who, while dealing with us in anger for our sins, hath nevertheless remembered mercy.
It has seemed to me fit and proper that they should be solemnly, reverently and gratefully acknowledged as with one heart and one voice by the whole American People. I do therefore invite my fellow citizens in every part of the United States, and also those who are at sea and those who are sojourning in foreign lands, to set apart and observe the last Thursday of November next, as a day of Thanksgiving and Praise to our beneficent Father who dwelleth in the Heavens. And I recommend to them that while offering up the ascriptions justly due to Him for such singular deliverances and blessings, they do also, with humble penitence for our national perverseness and disobedience, commend to His tender care all those who have become widows, orphans, mourners or sufferers in the lamentable civil strife in which we are unavoidably engaged, and fervently implore the interposition of the Almighty Hand to heal the wounds of the nation and to restore it as soon as may be consistent with the Divine purposes to the full enjoyment of peace, harmony, tranquillity and Union.
In testimony whereof, I have hereunto set my hand and caused the Seal of the United States to be affixed.
Done at the City of Washington, this Third day of October, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, and of the Independence of the United States the Eighty-eighth.
By the President: Abraham Lincoln
Some background here.
Using its Long March 4C rocket China yesterday successfully launched Gaofen-12, a remote sensing satellite designd to study Earth resources.
The leaders in the 2019 launch race:
27 China
18 Russia
11 SpaceX
7 Europe (Arianespace)
China now leads the U.S. 27 to 23 in the national rankings.
The launch schedule remains very busy, with a Rocket Lab launch set for early tomorrow and two launches to ISS (a Dragon and Progress) scheduled next week. In fact, seventeen launches are tentatively listed for launch in December, which would be once every other day. Several are unlikely, but regardless December will be a very busy month in the launch industry.
An evening pause: For Thanksgiving week. If life gets you down, think of this man and buck up.
Hat tip Cotour.
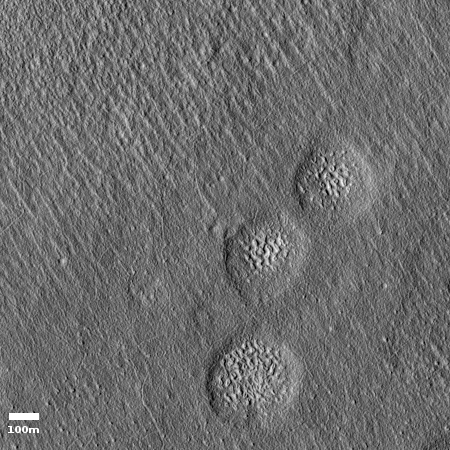

Cool image time! Even though it appears that SpaceX has completed its first round of images of its candidate landing sites surrounding the Erebus Montes mountains in the Arcadia Planitia plains in the Martian northern lowlands, this does not mean that other planetary scientists are not asking for more images of this region, for their own scientific research.
The photograph on the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was released in the early November image download from the high resolution camera of Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Uncaptioned but dubbed “Beginning of Possible Glacial Unit,” it shows what appears at first glance to be a relatively featureless area south of Erebus Montes, out in the flat plains.
A closer look suggests otherwise. For one, the full image shows darker and lighter areas. The close-up to the right, its location indicated by the white box in the wider image above, also shows several intriguing depressions that appear to be revealing a knobby lower layer. In fact, in the full image it appears that the darker areas are areas where material has covered that knobby lower layer. Where it is bright the ground resembles the floors of these depressions, knobby and complex.
I do not know why they label this the “beginning” of a glacial unit. What I do know is that the research of this region has consistently found evidence of a lot of buried ice. To quote Donna Viola of the University of Arizona noted, “I think you could dig anywhere to get your water ice.” The knobby features to me suggest a surface that is showing signs of sublimation, where the exposed ice is slowly eroding. Think of what happens to a block of ice when you spray warm water on it. As it melts it leaves behind just these kinds of strange formations.
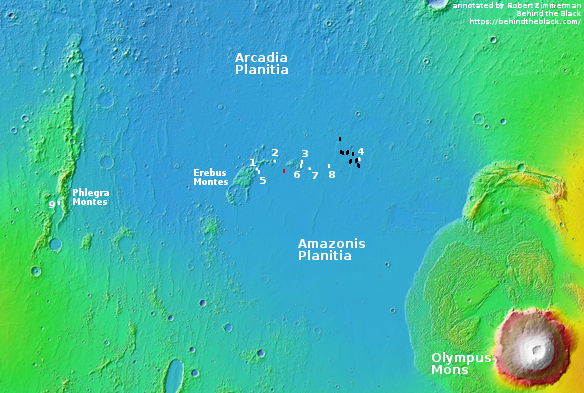
The red box in the map on the right shows the location of this photograph relative to the other images taken for SpaceX. The white boxes are the company’s images taken for Starship. The black boxes are the images it obtained in 2017 when it was thinking of sending a Dragon capsule to Mars.
This map does not show all images taken by MRO’s high resolution camera in this area, but the coverage is very scattered, with many gaps. Over time I suspect these gaps will be filled more quickly than other northern plain regions, because the scientists know that SpaceX has an interest in this area. That interest means there is an increased chance that a mission will fly here in the relatively near future, which in turn is going to generate more scientific interest as well.
Chinese engineers have unfolded and activated the Dutch radio antennas on Queqiao, their lunar relay satellite orbiting the Moon, an action that had been delayed because the lander Chang’e-4 and rover Yutu-2 had both exceeded their nominal mission on the surface.
The Chinese satellite was previously mainly seen as a communications satellite. However, the Chinese moon mission has by now achieved its primary goals. Consequently, the Chinese have redefined the satellite to be a radio observatory. As such, the Netherlands-China Low Frequency Explorer is the first Dutch-Chinese space observatory for radio astronomy.
Marc Klein Wolt, Managing Director of the Radboud Radio Lab and leader of the Dutch team, is happy: “Our contribution to the Chinese Chang’e 4 mission has now increased tremendously. We have the opportunity to perform our observations during the fourteen-day-long night behind the moon, which is much longer than was originally the idea. The moon night is ours, now.”
If Queqiao is now dedicated to being a radio antenna full time during the lunar night, I wonder if this means the Chinese are shutting down Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2. Up to now both spacecraft have only operated during the lunar night, which suggests that was the only time they could relay data. It is possible that data relay could take place at other times, and that the lander and rover can function autonomously, but I have my doubts.
Both Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2 functioned for twelve lunar nights, four times longer than planned, so shifting gears on Queqiao to do radio astronomy is not unreasonable. Unfortunately, the lack of transparency from China leaves us in the dark about the fate of Chang’e-4 and Yutu-2.