Wales Day 6
 c
c

 c
c
After yesterday’s long hike on Mount Snowdon, today was planned as an easier day. First we changed locations, driving south to the village of Dolgellau.
In the morning we heard two short presentations, first about the first discovery of Wales by tourists in the 1700s, and second a more scholarly look at the place names of Wales that appear connected to Arthur. In this case the speaker, Scott Lloyd of the Royal Commission on Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales, was focused more on what is really known, and was thus less sure about Arthur’s links to Wales than our previous expert, Gareth Roberts. Lloyd has documented the many place names (see his book, The Arthurian Place Names of Wales), but he has also documented the important detail that most started appearing after the first writings about Arthur started to appear, with most appearing several centuries after Arthur supposedly lived. This suggests that the names were chosen because of the legend, not because the man had been there.
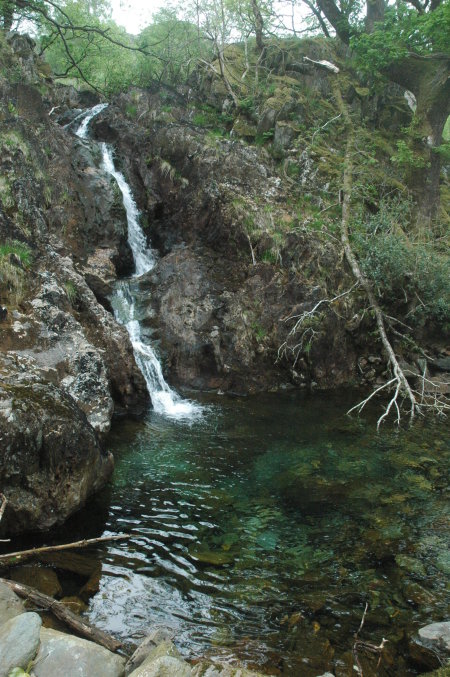
In the afternoon some of us did a short hike halfway up the nearby mountain Cader Idris. The first picture shows the mountain at the top right, with sheep in the center, and a hawthorn tree in bloom to the left. The second picture shows the trail going uphill parallel to one of the many typical stone walls found everywhere in Wales. The land is very rocky, and to make it better for grazing farmers would clear the stones from the fields, putting them in piles to the side. Then, when the enclosure laws were passed in the early 1800s they used those stones to build the walls to define their property lines.
The third picture shows Taff and Barbara ahead of me, with Cader Idris in the distance. Shortly thereafter we stopped to lie on the soft heather to chat and admire the countryside and the grey rocky slope going up to the peak ahead of us. We then headed back down for dinner and an evening in town.
 c
c

 c
c
After yesterday’s long hike on Mount Snowdon, today was planned as an easier day. First we changed locations, driving south to the village of Dolgellau.
In the morning we heard two short presentations, first about the first discovery of Wales by tourists in the 1700s, and second a more scholarly look at the place names of Wales that appear connected to Arthur. In this case the speaker, Scott Lloyd of the Royal Commission on Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales, was focused more on what is really known, and was thus less sure about Arthur’s links to Wales than our previous expert, Gareth Roberts. Lloyd has documented the many place names (see his book, The Arthurian Place Names of Wales), but he has also documented the important detail that most started appearing after the first writings about Arthur started to appear, with most appearing several centuries after Arthur supposedly lived. This suggests that the names were chosen because of the legend, not because the man had been there.
In the afternoon some of us did a short hike halfway up the nearby mountain Cader Idris. The first picture shows the mountain at the top right, with sheep in the center, and a hawthorn tree in bloom to the left. The second picture shows the trail going uphill parallel to one of the many typical stone walls found everywhere in Wales. The land is very rocky, and to make it better for grazing farmers would clear the stones from the fields, putting them in piles to the side. Then, when the enclosure laws were passed in the early 1800s they used those stones to build the walls to define their property lines.
The third picture shows Taff and Barbara ahead of me, with Cader Idris in the distance. Shortly thereafter we stopped to lie on the soft heather to chat and admire the countryside and the grey rocky slope going up to the peak ahead of us. We then headed back down for dinner and an evening in town.