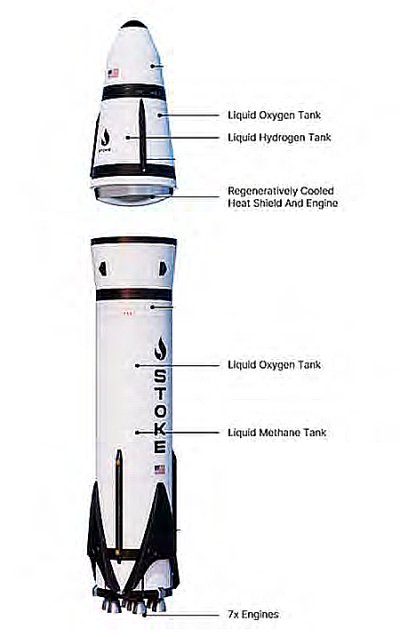
ULA’s new management predicts it will achieve 18-22 launches in 2026
Before Tory Bruno resigned as CEO of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) to go work for Blue Origin, he had predicted in August last year that ULA was primed to complete two launches per month for the rest of ’25 and throughout ’26.
That prediction did not happen, as the company was only able to do four launches in the last five months of 2025, and no launches so far in 2026.
Yesterday the new management of ULA insisted that Bruno’s prediction was still reasonable, and that the company will complete between 18 to 22 launches before the end of this year.
Speaking during a virtual media roundtable on Feb. 10, Gary Wentz, ULA’s vice president of Atlas and Vulcan Programs, said the company aims to launch two to four Atlas 5 missions and 16 to 18 Vulcan missions. He said the Vulcan rockets will be split between pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and pad 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base. “It’s a balance. We’re working with our customers to determine specific priorities and order of missions and in the case of Space Force and NRO (National Reconnaissance Office), to determine which missions they wan to get off with higher priority,” Wentz said. “And as we finalize that over the next about six to eight months out of the mission, then we’ll assign whether or not its going to be an Atlas mission or a Vulcan mission.”
John Elbon, the interim CEO following the departure of Tory Bruno in December, said that the company has a “strong commitment” from their commercial and government customers, citing a backlog of more than 80 missions.
That backlog is mostly split between ULA’s big contract to launch Amazon’s Leo satellites and a variety of different agencies in the Pentagon. Both are desperate to get their satellites into space, and it appears ULA is struggling to figure out how to do it. In its early years (from 2007 to 2016) the company was generally able to average about one launch a month, but since then that launch rate as been less than half that. To not only return to those launch rates from a decade ago but to almost double them will be challenging, to say the least.
Before Tory Bruno resigned as CEO of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) to go work for Blue Origin, he had predicted in August last year that ULA was primed to complete two launches per month for the rest of ’25 and throughout ’26.
That prediction did not happen, as the company was only able to do four launches in the last five months of 2025, and no launches so far in 2026.
Yesterday the new management of ULA insisted that Bruno’s prediction was still reasonable, and that the company will complete between 18 to 22 launches before the end of this year.
Speaking during a virtual media roundtable on Feb. 10, Gary Wentz, ULA’s vice president of Atlas and Vulcan Programs, said the company aims to launch two to four Atlas 5 missions and 16 to 18 Vulcan missions. He said the Vulcan rockets will be split between pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and pad 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base. “It’s a balance. We’re working with our customers to determine specific priorities and order of missions and in the case of Space Force and NRO (National Reconnaissance Office), to determine which missions they wan to get off with higher priority,” Wentz said. “And as we finalize that over the next about six to eight months out of the mission, then we’ll assign whether or not its going to be an Atlas mission or a Vulcan mission.”
John Elbon, the interim CEO following the departure of Tory Bruno in December, said that the company has a “strong commitment” from their commercial and government customers, citing a backlog of more than 80 missions.
That backlog is mostly split between ULA’s big contract to launch Amazon’s Leo satellites and a variety of different agencies in the Pentagon. Both are desperate to get their satellites into space, and it appears ULA is struggling to figure out how to do it. In its early years (from 2007 to 2016) the company was generally able to average about one launch a month, but since then that launch rate as been less than half that. To not only return to those launch rates from a decade ago but to almost double them will be challenging, to say the least.