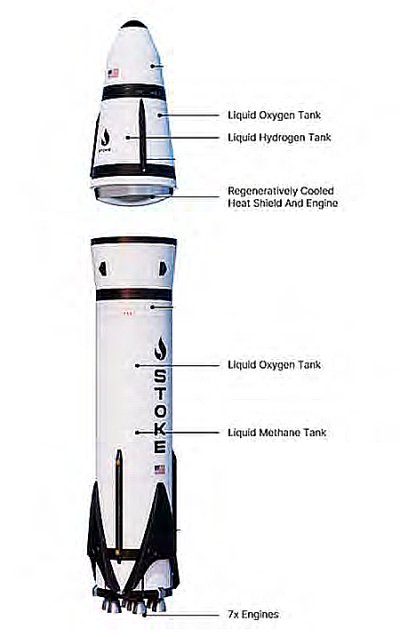
Axiom raises another $350 million in private investment capital

Axiom’s module assembly sequence
The space station Axiom today announced that it has raised another $350 million in private investment capital, in addition to the $100 million commitment obtained in December from the Hungarian communications company 4iG.
Type One Ventures and Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) co-led the round, with participation from 1789 Capital, 4iG, LuminArx Capital Management, and others. Axiom Space Founder and Executive Chairman Kam Ghaffarian also participated in the round, reinforcing his commitment to the company’s mission. J.P. Morgan served as sole placement agent to Axiom Space in connection with the financing.
It appears that even if the 2024 rumors that the company was having cash flow issues were true (they were never confirmed), those issues are now long gone.
Below is my revised rankings of the five American consortiums/companies developing space stations. The rankings haven’t changed, but I have updated the text.
» Read more

Axiom’s module assembly sequence
The space station Axiom today announced that it has raised another $350 million in private investment capital, in addition to the $100 million commitment obtained in December from the Hungarian communications company 4iG.
Type One Ventures and Qatar Investment Authority (QIA) co-led the round, with participation from 1789 Capital, 4iG, LuminArx Capital Management, and others. Axiom Space Founder and Executive Chairman Kam Ghaffarian also participated in the round, reinforcing his commitment to the company’s mission. J.P. Morgan served as sole placement agent to Axiom Space in connection with the financing.
It appears that even if the 2024 rumors that the company was having cash flow issues were true (they were never confirmed), those issues are now long gone.
Below is my revised rankings of the five American consortiums/companies developing space stations. The rankings haven’t changed, but I have updated the text.
» Read more