Update on the private Fram2 manned orbital spaceflight

In the past day the crew of the private Fram2 manned orbital spaceflight have released several updates, describing their initial experience in weightlessness as well as releasing some images of themselves inside the Resilience capsule.
First, on April 1, 2025 the mission commander, Chun Wang, the billionaire who paid for the flight, posted a tweet describing how all four crew members experienced space sickness the first day in orbit.
The first few hours in microgravity weren’t exactly comfortable. Space motion sickness hit all of us—we felt nauseous and ended up vomiting a couple of times. It felt different from motion sickness in a car or at sea. You could still read on your iPad without making it worse. But even a small sip of water could upset your stomach and trigger vomiting.
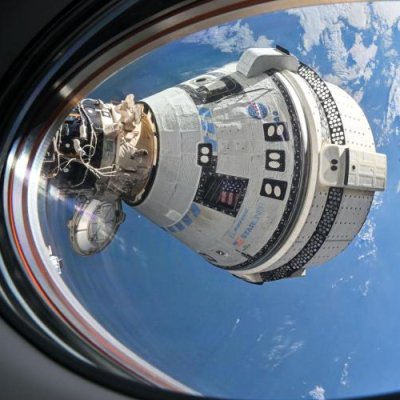
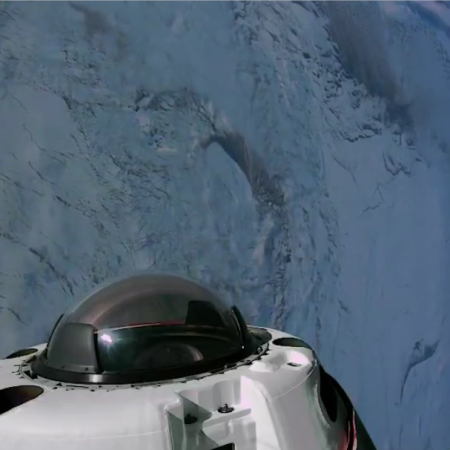
Things however quickly settled down, allowing them to open the nose cone so that they could see out the large cupola window. They released the first images of the Antarctic, and followed soon after with the first images of themselves inside Resilience. The picture to the right, taken by Wang, shows is three crewmates, Jannicke Mikkelsen, Rabea Rogge, and Eric Philips clearly now enjoying the experience of weightlessness.
Still no word on a return date. The mission was initially supposed to last 3 to 5 days. We are now on day three, with no indications of a planned return date.

In the past day the crew of the private Fram2 manned orbital spaceflight have released several updates, describing their initial experience in weightlessness as well as releasing some images of themselves inside the Resilience capsule.
First, on April 1, 2025 the mission commander, Chun Wang, the billionaire who paid for the flight, posted a tweet describing how all four crew members experienced space sickness the first day in orbit.
The first few hours in microgravity weren’t exactly comfortable. Space motion sickness hit all of us—we felt nauseous and ended up vomiting a couple of times. It felt different from motion sickness in a car or at sea. You could still read on your iPad without making it worse. But even a small sip of water could upset your stomach and trigger vomiting.
Things however quickly settled down, allowing them to open the nose cone so that they could see out the large cupola window. They released the first images of the Antarctic, and followed soon after with the first images of themselves inside Resilience. The picture to the right, taken by Wang, shows is three crewmates, Jannicke Mikkelsen, Rabea Rogge, and Eric Philips clearly now enjoying the experience of weightlessness.
Still no word on a return date. The mission was initially supposed to last 3 to 5 days. We are now on day three, with no indications of a planned return date.