NASA experiment on Blue Ghost demonstrates the ability to repel the Moon’s abrasive dust
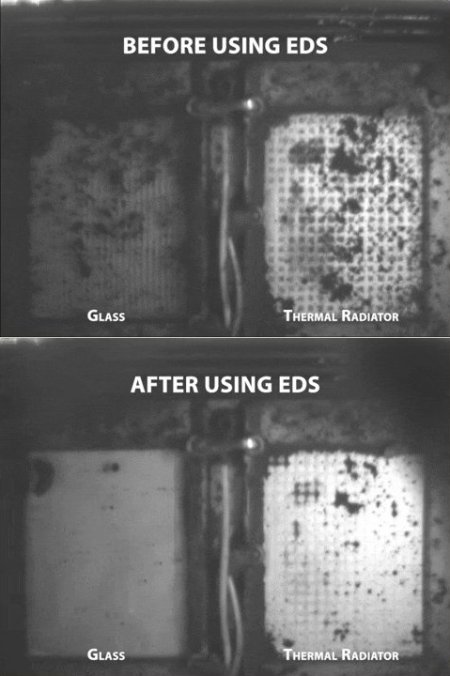

Click for original blink movie.
In a press release yesterday, NASA revealed that one of its technology experiments on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander successfully demonstrated the ability to repel the Moon’s abrasive dust from the surfaces of various materials.
Lunar dust is extremely abrasive and electrostatic, which means it clings to anything that carries a charge. It can damage everything from spacesuits and hardware to human lungs, making lunar dust one of the most challenging features of living and working on the lunar surface. The EDS technology uses electrodynamic forces to lift and remove the lunar dust from its surfaces. The “before” image highlights the glass and thermal radiator surfaces covered in a layer of regolith, while the “after” image reveals the results following EDS activation. Dust was removed from both surfaces, proving the technology’s effectiveness in mitigating dust accumulation.
The images to the right, taken from a blink movie showing the change after the EDS technology was used, suggest that though this technology does work, it is not yet wholly successful in some cases. The thermal radiator was not cleared entirely of dust. More engineering research will be necessary, both on the Moon and here on Earth.
Nonetheless, this success is important and a major step forward for future exploration of the Moon, Mars, and the asteroids. In all these places dust is going to pose a major problem for equipment and spacesuits. New techniques must be developed to clean the dust away, since traditional Earth-based cleaning methods using water will not be available.

Click for original blink movie.
In a press release yesterday, NASA revealed that one of its technology experiments on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander successfully demonstrated the ability to repel the Moon’s abrasive dust from the surfaces of various materials.
Lunar dust is extremely abrasive and electrostatic, which means it clings to anything that carries a charge. It can damage everything from spacesuits and hardware to human lungs, making lunar dust one of the most challenging features of living and working on the lunar surface. The EDS technology uses electrodynamic forces to lift and remove the lunar dust from its surfaces. The “before” image highlights the glass and thermal radiator surfaces covered in a layer of regolith, while the “after” image reveals the results following EDS activation. Dust was removed from both surfaces, proving the technology’s effectiveness in mitigating dust accumulation.
The images to the right, taken from a blink movie showing the change after the EDS technology was used, suggest that though this technology does work, it is not yet wholly successful in some cases. The thermal radiator was not cleared entirely of dust. More engineering research will be necessary, both on the Moon and here on Earth.
Nonetheless, this success is important and a major step forward for future exploration of the Moon, Mars, and the asteroids. In all these places dust is going to pose a major problem for equipment and spacesuits. New techniques must be developed to clean the dust away, since traditional Earth-based cleaning methods using water will not be available.