Midnight repost: Genocide is coming to America
Today I came across this tweet:
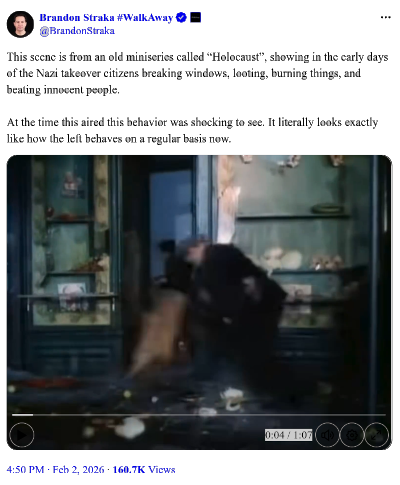
The comparison between the tactics of the Nazi storm troopers and our modern Antifa thugs is apt. It illustrates the time we now live in. It also immediately made me want to repost my 2020 essay, Genocide is coming to America. That essay sadly remains pertinent, because the same unwillingness of decent Germans to believe the Nazis were a threat is the same unwillingness of too many modern Americans to believe the same thing about Antifa and the Democratic Party (which now enthusiastically uses Antifa as its storm troopers).
Worse, we now have a large minority of Americans who support this violent behavior. To them, violence is wholly justified against those who disagree with them. The proof of this horrible fact was demonstrated in the 2025 elections, where in Virginia a Democrat won his election despite openly wishing death not only on a Republican but on that Republican’s children, while in New York an anti-Semitic communist won election as mayor.
————————-
Genocide is coming to America
In my last visit to Israel in 2018, my brother and sister-in-law took me sight-seeing to the northern parts of Israel near the Sea of Galilee. On our first night, we stayed at the home of one of their older friends, a man in his seventies.
That night we sat around their kitchen table so that they could catch up on family matters. At one point in the conversation our host reminisced about an older woman, now gone, who he had known in his childhood in the 1950s who had lived in Germany before and during World War II and had survived a concentration camp.
» Read more