Click for high resolution panorama. For original images, go here and here.
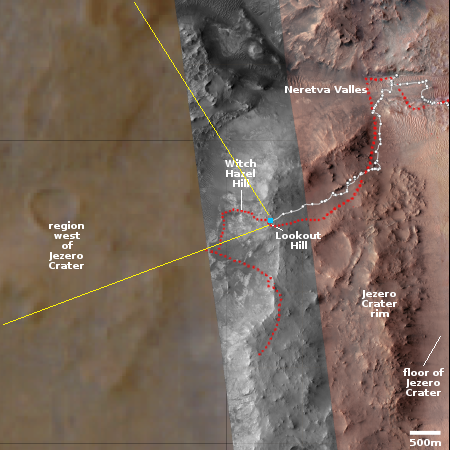
Click for interactive map.
After spending more than three and a half years exploring the floor of Jezero Crater, the rover Perseverance has finally reached the top of the crater’s western rim, and is about to begin exploring the mountainous and potentially rich mining region to the west.
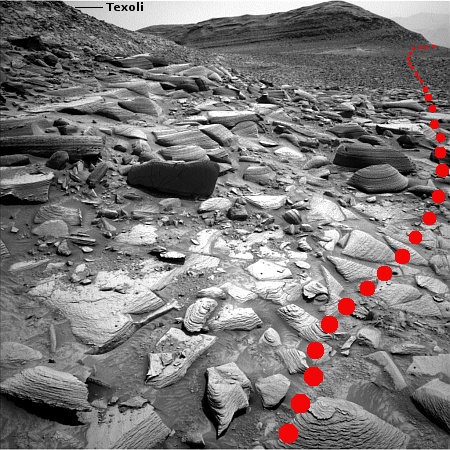
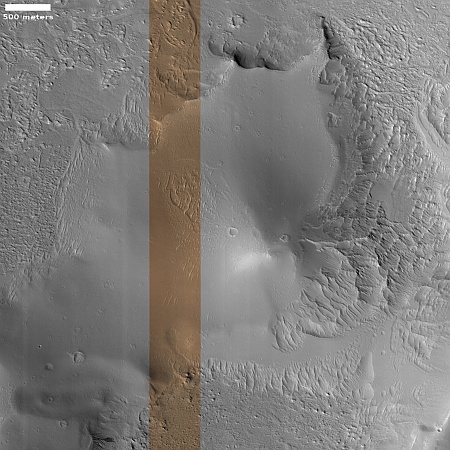
The panorama above, created from two pictures taken by Perseverance’s right navigation camera on December 11, 2024 (here and here), has been cropped, reduced, enhanced, and annotated to post here. It looks west into that mountainous region, with the yellow lines on the overview map to the right indicating the approximate view. The blue dot on that map marks Perseverance’s present position, on top of Lookout Hill, the name the rover team has given to that spot on the rim.
The low resolution of the region beyond the grey strip is unexplained. For some reason the rover team has not yet updated the interactive map showing Perseverance’s travels with the many high resolution pictures that Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has taken of this region, in anticipation of Perseverance’s travels there. I expect however this will change shortly.
Witch Hazel Hill is the first target beyond the rim, where there is an outcrop 330-feet-high with many layers. The rover will then head downhill and south to check out a spot that the scientists believe might show features existing from before Jezero Crater was formed. The rover will then head back up to the rim further south to look at an outcrop of blocks that might actually be ejecta from another much larger Martian impact.
These blocks may represent ancient bedrock broken up during the Isidis impact, a planet-altering event that likely excavated deep into the Martian crust as it created an impact basin some 745 miles (1,200 kilometers) wide, 3.9 billion years in the past.
Jezero sits on the northwestern rim of Isidis.












