December 31, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
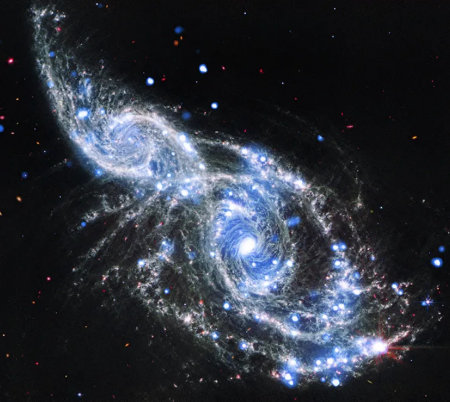
- Astronomers detect a three-galaxy merger, the third ever discovered
The headline at the link is utter garbage, designed as clickbait. The headline I have given you describes the story’s text accurately. One other detail: All three galaxies also appear to have active nuclei, suggesting the presence of supermassive black holes.
- SpaceX accounts for more than 70% of the world’s total payload mass launched in 2025
This graph is a nice additional data point I will use in my annual global launch report.
- On this day in 1924 astronomer Edwin Hubble announced that the spiral nebula Andromeda is a distant galaxy like the Milky Way
Thus proving that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies in the universe.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Astronomers detect a three-galaxy merger, the third ever discovered
The headline at the link is utter garbage, designed as clickbait. The headline I have given you describes the story’s text accurately. One other detail: All three galaxies also appear to have active nuclei, suggesting the presence of supermassive black holes.
- SpaceX accounts for more than 70% of the world’s total payload mass launched in 2025
This graph is a nice additional data point I will use in my annual global launch report.
- On this day in 1924 astronomer Edwin Hubble announced that the spiral nebula Andromeda is a distant galaxy like the Milky Way
Thus proving that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies in the universe.