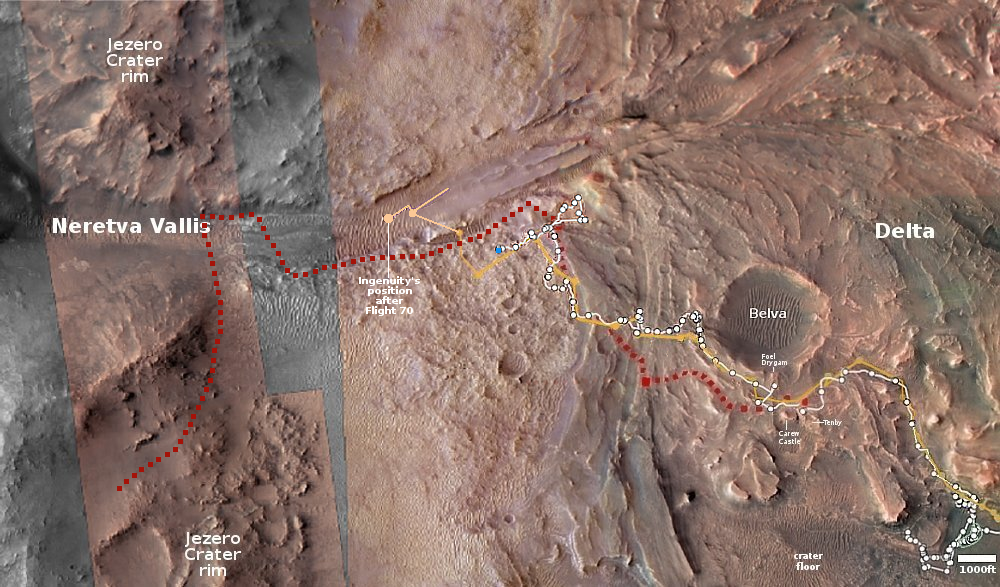
Scientists finally look at prime samples captured by OSIRIS-REx of the asteroid Bennu
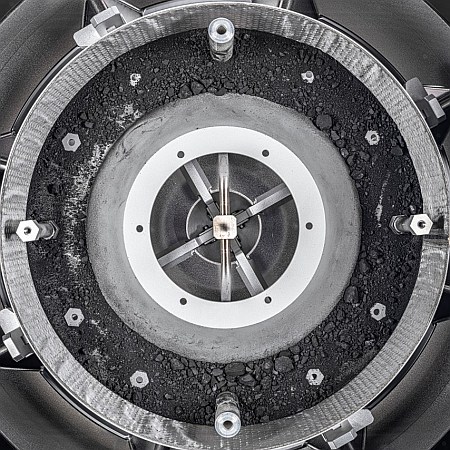
Scientists have finally opened the sample capsule from OSIRIS-REx to see the prime asteroid material obtained from the asteroid Bennu during the spacecraft’s touch-and-go sample grab.
The captured material inside the capsule can be seen in the picture to the right. It is the debris inside the ring.
Erika Blumenfeld, creative lead for the Advanced Imaging and Visualization of Astromaterials (AIVA) and Joe Aebersold, AIVA project lead, captured this photograph of the open TAGSAM head including the asteroid material inside using manual high-resolution precision photography and a semi-automated focus stacking procedure. The result is an image that shows extreme detail of the sample.
Next, the curation team will remove the round metal collar and prepare the glovebox to transfer the remaining sample from the TAGSAM head into pie-wedge sample trays.
The final mass of material will be determined once it is removed and weighed, though the team has already recovered more than 70 grams that had clung to the outside the capsule, which in itself exceeded the mission’s targeted goal.
Scientists have finally opened the sample capsule from OSIRIS-REx to see the prime asteroid material obtained from the asteroid Bennu during the spacecraft’s touch-and-go sample grab.
The captured material inside the capsule can be seen in the picture to the right. It is the debris inside the ring.
Erika Blumenfeld, creative lead for the Advanced Imaging and Visualization of Astromaterials (AIVA) and Joe Aebersold, AIVA project lead, captured this photograph of the open TAGSAM head including the asteroid material inside using manual high-resolution precision photography and a semi-automated focus stacking procedure. The result is an image that shows extreme detail of the sample.
Next, the curation team will remove the round metal collar and prepare the glovebox to transfer the remaining sample from the TAGSAM head into pie-wedge sample trays.
The final mass of material will be determined once it is removed and weighed, though the team has already recovered more than 70 grams that had clung to the outside the capsule, which in itself exceeded the mission’s targeted goal.