China’s Long March 2D rocket launches classified remote sensing satellite
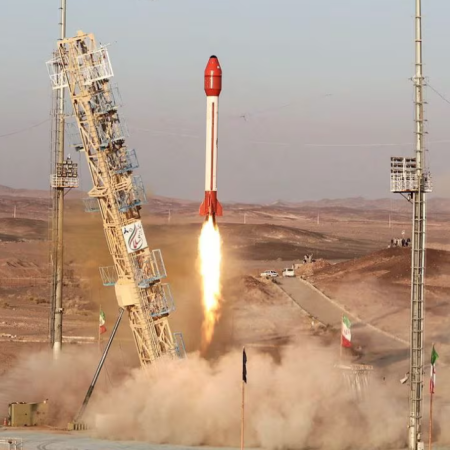
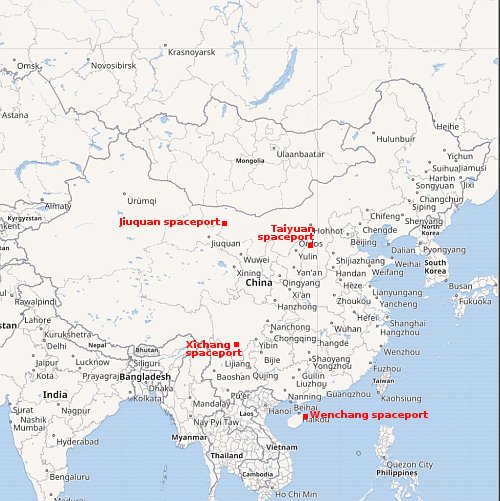
Early on December 10, 2023 (Chinese time) China successfully launched a classified remote sensing satellite, its Long March 2D rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in the south of China.
The state-run Chinese press released almost no information. Nor did it say where within China the lower stages of the rocket, using toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed.
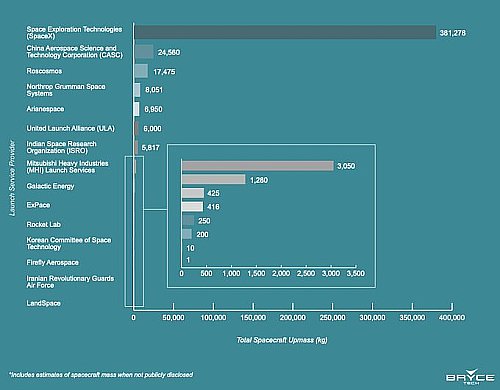
As expected, China’s launch pace in December has picked up, as it has routinely in recent years. The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
91 SpaceX
58 China
16 Russia
7 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise still leads China in successful launches, 103 to 58, and the entire world combined 103 to 92. SpaceX by itself now trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies), 91 to 92, though it plans two launches on December 10th.
Early on December 10, 2023 (Chinese time) China successfully launched a classified remote sensing satellite, its Long March 2D rocket lifting off from its Xichang spaceport in the south of China.
The state-run Chinese press released almost no information. Nor did it say where within China the lower stages of the rocket, using toxic hypergolic fuels, crashed.
As expected, China’s launch pace in December has picked up, as it has routinely in recent years. The leaders in the 2023 launch race:
91 SpaceX
58 China
16 Russia
7 Rocket Lab
7 India
American private enterprise still leads China in successful launches, 103 to 58, and the entire world combined 103 to 92. SpaceX by itself now trails the rest of the world (excluding other American companies), 91 to 92, though it plans two launches on December 10th.