Mars geology that only makes sense by digging deeper
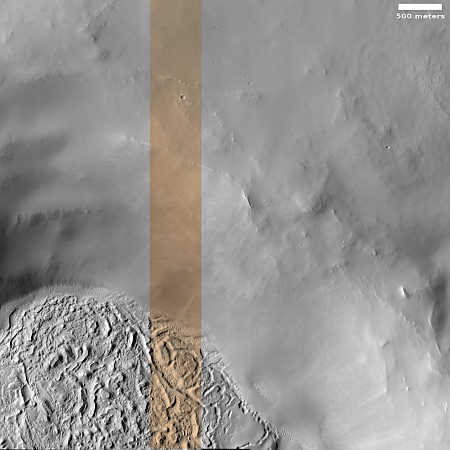
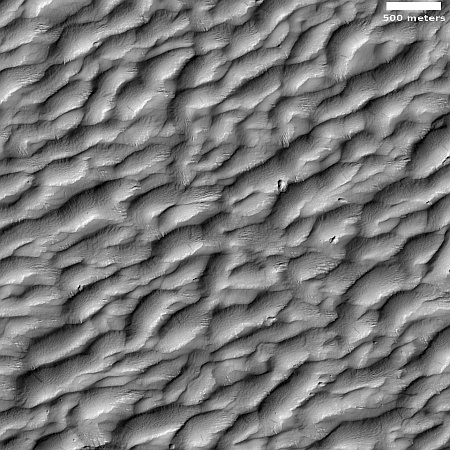
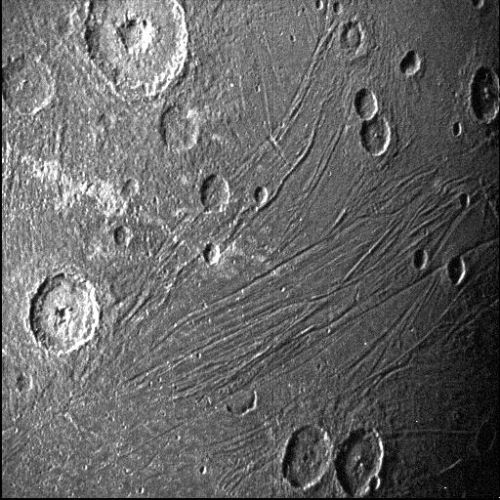
Today’s cool image is a perfect example of why nothing in science research should ever be taken at face value, without digging a bit deeper. The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on October 5, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
First an important technical point. Though the electronics unit for one of the camera’s color filters is still not working — causing a blank strip down the center of all black & white images, the camera team has gotten around this problem by inserting in that strip other color filter data, thus creating a complete image as you see to the right. This work-around means that MRO’s capabilities, though showing signs of age, will continue almost as good as before.
As for the image itself, when I first looked at it, I was baffled by the striking contrast between the mottled and rough ground in the lower left, and the almost featureless and smooth terrain everywhere else. Why this sudden transition? What could cause it? That inexplicable contrast demanded I post it as a cool image.
» Read more
Today’s cool image is a perfect example of why nothing in science research should ever be taken at face value, without digging a bit deeper. The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on October 5, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
First an important technical point. Though the electronics unit for one of the camera’s color filters is still not working — causing a blank strip down the center of all black & white images, the camera team has gotten around this problem by inserting in that strip other color filter data, thus creating a complete image as you see to the right. This work-around means that MRO’s capabilities, though showing signs of age, will continue almost as good as before.
As for the image itself, when I first looked at it, I was baffled by the striking contrast between the mottled and rough ground in the lower left, and the almost featureless and smooth terrain everywhere else. Why this sudden transition? What could cause it? That inexplicable contrast demanded I post it as a cool image.
» Read more