Perseverance moves west, into the barren hinterlands beyond Jezero Crater

Click for full resolution. Original images can be found here and here.
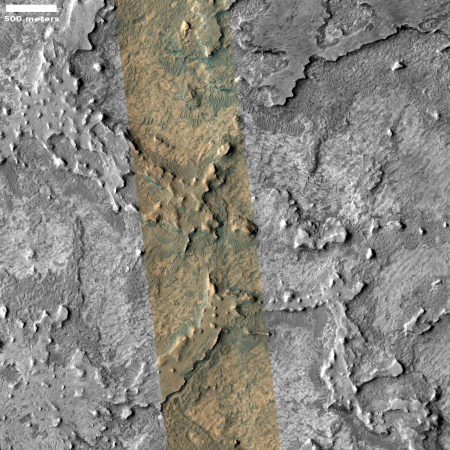
Cool image time! The panorama above was created using two pictures taken on December 4, 2025 (here and here) by the navigation camera on the Mars rover Perseverance. The view I think is looking west, away from the rim of Jezero Crater, which now lies behind the rover to the east.
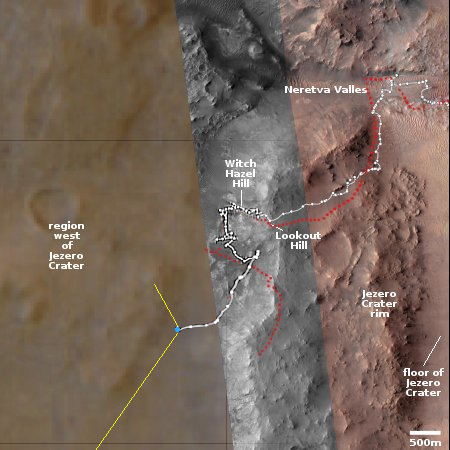
The blue dot on the overview map to the right marks Perseverance’s position when it took this picture. The yellow lines indicate my rough guess as to the area covered by the panorama. The white dotted line marks the actual route the rover has taken, while the red dotted line the original planned route.
As I noted in my previous Perseverance update in mid-November, the science team has apparently decided to revise the route, abandoning initial plan of going back uphill towards the rim and instead travel downhill into the hills beyond. This is a region that orbital data has suggested might be rich in minerals, making it a prime mining location for future colonists. My guess is that the science team decided they needed to get there, that they had enough data from the rim and that it was now more important to get to the western mineralogy.
Though I am sure they are using the highest resolution orbital images from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) to guide them, the Perseverance team has not yet upgraded its interactive location map to show those details in this western region. Thus, the map in this area is fuzzy and not as detailed.
The team has also not published its revised planned route, so there is no way to guess where the rover will go next. It does appear however that it is finally leaving Jezero Crater for good.
And as all recent pictures from Perseverance, these images show this Martian landscape to be utterly barren, its hills and valleys softened by dust and eons of erosion from the very thin Martian wind. This is an alien place, though it has the potential with human ingenuity to bloom if we have the courage to try.

Click for full resolution. Original images can be found here and here.
Cool image time! The panorama above was created using two pictures taken on December 4, 2025 (here and here) by the navigation camera on the Mars rover Perseverance. The view I think is looking west, away from the rim of Jezero Crater, which now lies behind the rover to the east.
The blue dot on the overview map to the right marks Perseverance’s position when it took this picture. The yellow lines indicate my rough guess as to the area covered by the panorama. The white dotted line marks the actual route the rover has taken, while the red dotted line the original planned route.
As I noted in my previous Perseverance update in mid-November, the science team has apparently decided to revise the route, abandoning initial plan of going back uphill towards the rim and instead travel downhill into the hills beyond. This is a region that orbital data has suggested might be rich in minerals, making it a prime mining location for future colonists. My guess is that the science team decided they needed to get there, that they had enough data from the rim and that it was now more important to get to the western mineralogy.
Though I am sure they are using the highest resolution orbital images from Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) to guide them, the Perseverance team has not yet upgraded its interactive location map to show those details in this western region. Thus, the map in this area is fuzzy and not as detailed.
The team has also not published its revised planned route, so there is no way to guess where the rover will go next. It does appear however that it is finally leaving Jezero Crater for good.
And as all recent pictures from Perseverance, these images show this Martian landscape to be utterly barren, its hills and valleys softened by dust and eons of erosion from the very thin Martian wind. This is an alien place, though it has the potential with human ingenuity to bloom if we have the courage to try.